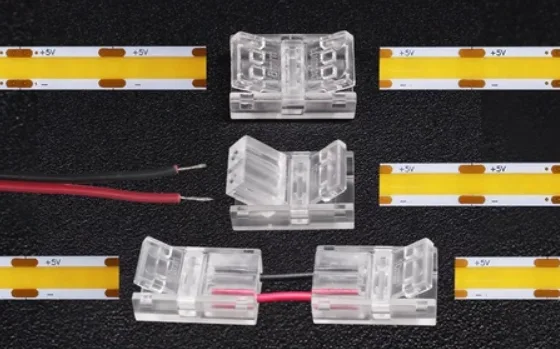
Bei Fernlicht-LED-Leuchten ist der Spannungsabfall das Kernproblem, das eine ungleichmäßige Helligkeit und eine verkürzte Lebensdauer verursacht. Da der Strom in Niederspannungs-LED-Streifen (12V/24V) mit zunehmender Entfernung abnimmt, wirkt sich der Spannungsverlust aufgrund des Drahtwiderstands erheblich auf die Lichtleistung am anderen Ende aus.
Ohne Eingriff kann ein Spannungsabfall im vorderen Bereich zu übermäßiger Helligkeit und hinten zu einer Dämmerung führen, was möglicherweise die Alterung des Chips durch Überstrom beschleunigt. Zusätzlich können Spannungsschwankungen Kettenreaktionen wie örtliche Überhitzung oder Ausfall des Treiberkreises auslösen.
Daher erfordert die systematische Adressierung des Spannungsabfalls einen mehrdimensionalen Ansatz, der das Design der Stromversorgung, die Schaltung zur Schaltung und die Ausrüstungsauswahl umfasst, um einen stabilen Betrieb des LED-Streifen-Beleuchtungssystems zu gewährleisten.
Was ist Spannungsabfall?
Der Spannungsabfall in LED-Streifen bezieht sich auf die allmähliche Abnahme der Spannung, die während des Betriebs auftritt, da der Strom durch Komponenten wie LEDs und Platinen fließt. Dieses Phänomen verursacht eine verringerte Helligkeit und ungleichmäßige Beleuchtung über den Streifen.
In Laienbegriffen manifestiert es sich in einer inkonsistenten Helligkeit zwischen dem Anfang und dem Ende des Streifens - wobei der Abschnitt in der Nähe der Stromquelle heller erscheint, während das hintere Ende merklich abnimmt.
Spannungsabfall beeinträchtigt nicht nur die Helligkeit und die ästhetische Attraktivität von LED-Streifen, sondern kann auch die Lebensdauer verkürzen. Daher ist das korrekte Verständnis und Behebung von Spannungsabfallproblemen entscheidend für die Verbesserung der Leistung von LED-Streifen.
Wie unten gezeigt: Wenn die Eingangsspannung zum LED-Streifen 12 V beträgt, fällt die Spannung nach einer Entfernung von 5 Metern auf 9,01 V. Diese 3-V-Differenz stellt den Spannungsabfall dar.
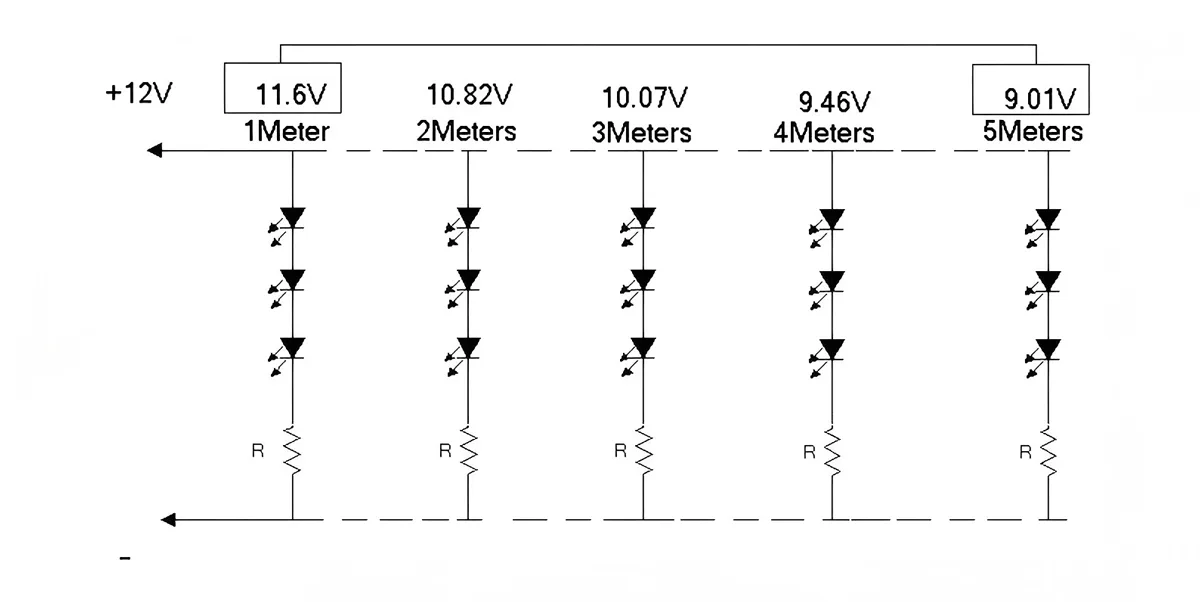
Je länger der LED-Streifen ist, desto größer ist der Spannungsabfall. Ein Spannungsabfall von 51 tp3t kann den Betriebsstrom der LED-Chips verringern und folglich ihre Helligkeit verringern.
Spannungsabfall ist eine physikalische Größe, die die Fähigkeit eines elektrischen Feldes beschreibt, Ladung zu bewegen, auch als Potentialdifferenz oder Spannung bezeichnet. Wenn Strom durch einen Leiter fließt (wie Drähte oder Widerstände), wird die elektrische Energie aufgrund des Widerstands des Leiters in Wärme umgewandelt, was zu einer Verringerung der Potentialdifferenz über die Anschlüsse führt.
Verwandte Lektüre: Spannungsabfall bei LED-Streifen: Ursachen und Lösungen.
Ursachen für Spannungsabfall in LED-Streifen
Der Spannungsabfall in LED-Streifen ist ein häufiges Problem bei der Gleichmäßigkeit der Beleuchtung, die sich aus drei Kernfaktoren ergibt: Verlust des Eingangsdrahtwiderstands, unzureichende Leitfähigkeit der Leiterplattenkupferfolie und zu niedrige Eingangsspannung. Nachfolgend analysieren wir diese drei Aspekte.
Drahtwiderstand
Der Drahtwiderstand ist eine physikalische Größe, die den Grad der Opposition misst, der durch einen Leiter fließende Strom misst. Es zeigt die Fähigkeit des Leiters, den Stromfluss zu behindern, und wird in Ohm (Ω) gemessen. Seine Größe hängt vom Material, der Länge, dem Querschnitt und der Temperatur ab.

Metalle wie Kupfer und Aluminium haben einen geringeren spezifischen Widerstand, während Legierungen und Halbleitermaterialien einen höheren spezifischen Widerstand aufweisen. Längere Drähte weisen einen größeren Widerstand auf, während eine größere Querschnittsfläche den Widerstand verringert. Zusätzlich kann eine Temperaturerhöhung die Widerstandsfähigkeit in bestimmten Materialien (z. B. Metallen) erhöhen.
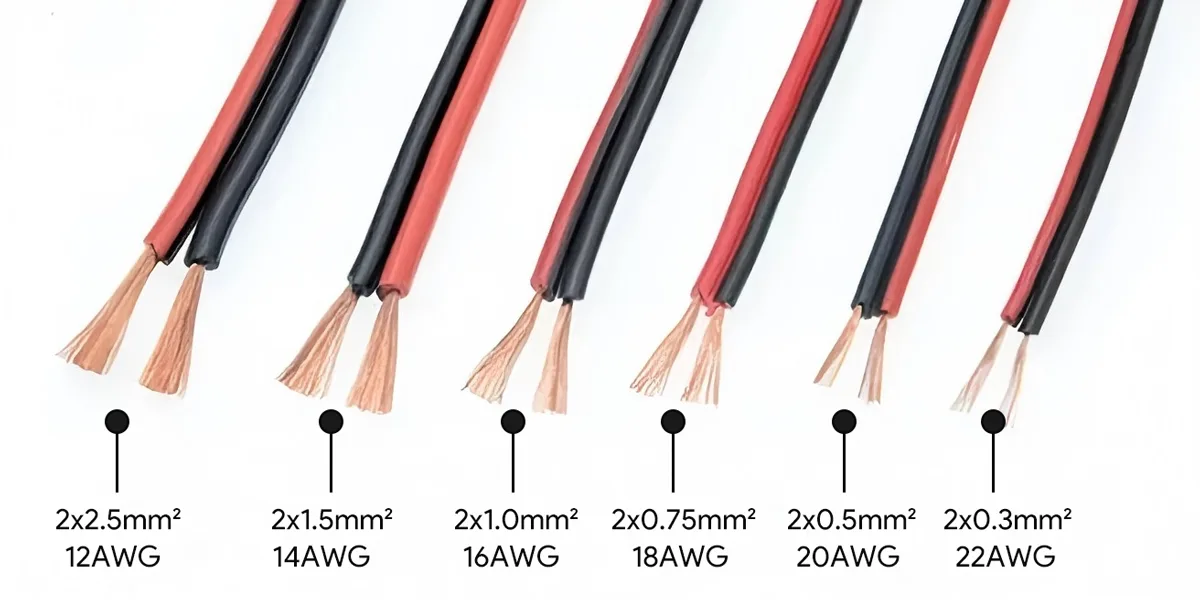
Achten Sie während des Betriebs auf eine angemessene Verdrahtung zwischen der Stromquelle und dem Lichtstreifen. Dickere Drähte haben einen geringeren Widerstand, was bedeutet, dass sie Elektrizität effizienter übertragen. Basierend auf Ihrer Leistungsbelastung (in Watt) und der Kabellänge (in Fuß) können Sie anhand der folgenden Tabelle die geeignete Drahtgröße für ein bequemes Spannungsabfallmanagement auswählen.
| 12-Volt-Spannungsabfall-Diagramm (5%-Abfall) | ||||||||||
| Drahtspur | 12 w | 24 W | 36 W | 48 W | 60 W | 72 W | 84 W | 96 W | 108 w | 120 W |
| 22 AWG | 16 ft. | 8 ft. | 5 ft. | 4f. | 3 ft. | 3 ft. | 2 ft. | 2 ft. | 2 ft. | 2 ft. |
| 20 AWG | 25 ft. | 13 ft. | 8 ft. | 6 Ft. | 5 ft. | 4 ft. | 4 ft. | 3 ft. | 3 ft. | 3 ft. |
| 18 AWG | 42 ft. | 21 ft. | 14 ft. | 10 ft. | 8 ft. | 7 Ft. | 6 Ft. | 5 ft. | 5 ft. | 4 ft. |
| 16 AWG | 75 ft. | 38 ft. | 25 ft. | 19 ft. | 15 ft. | 13 ft. | 11 ft. | 9 Ft. | 8 ft. | 8 ft. |
| 14 AWG | 117 4. | 58 ft. | 39 ft. | 29 ft. | 23 ft. | 19 ft. | 17 ft. | 15 ft. | 13 ft. | 12 ft. |
| 12 AWG | 183 Ft. | 92 ft. | 61 ft. | 46 ft. | 37 ft. | 31 ft. | 26 ft. | 23 ft. | 20 ft. | 18 ft. |
| 10 AWG | 275 Ft. | 138 ft. | 92 ft. | 69 Ft. | 55 ft. | 46 ft. | 39 ft. | 34 ft. | 31 ft. | 28 ft. |
| 24-Volt-Spannungsabfall-Diagramm (5%-Abfall) | ||||||||||
| Drahtspur | 12 w | 24 W | 36 W | 48 W | 60 W | 72 W | 84 W | 96 W | 108 w | 120 W |
| 22 AWG | 73 Ft. | 37 ft. | 24 ft. | 18 ft. | 15 ft. | 12 ft. | 10 ft. | 9 Ft. | 8 ft. | 7 TT. |
| 20 AWG | 117 ft. | 58 ft. | 39 ft. | 29 ft. | 23 ft. | 19 ft. | 17 ft. | 15 ft. | 13 ft. | 12 ft. |
| 18 AWG | 183 Ft. | 92 ft. | 61 F +. | 46 ft. | 37 ft. | 31 ft. | 26 ft. | 23 ft. | 20 ft. | 18 ft. |
| 16 AWG | 300 ft. | 150 ft. | 100 ft. | 75 ft. | 60 ft. | 50 ft. | 43 ft. | 38 ft. | 33 ft. | 30 ft. |
| 14 AWG | 475 ft. | 238 ft. | 158 ft. | 119 Ft. | 95 ft. | 79 Ft. | 68 ft. | 59 ft. | 53 ft. | 48 ft. |
| 12 AWG | 750 Ft. | 375 ft. | 250 ft. | 188 Ft. | 150 ft. | 125 Ft. | 107 Ft. | 94 ft. | 83 ft. | 75 ft. |
| 10 AWG | 1092 Ft. | 546 Ft. | 364 Ft. | 273 Ft. | 218 ft. | 182 ft. | 156 ft. | 136 ft. | 121 ft. | 109 Ft. |
Anmerkung:
- Berechnen Sie die Gesamtlast in Watt.
- Abstand von Stromquelle zu LED-Streifen messen.
- Wählen Sie eine geeignete Drahtstärke.
Minimieren Sie die Betriebslänge des LED-Streifens. Der beste Ansatz ist es, es aus dem Mittelteil anzutreiben.
Angenommen, Sie benötigen einen 50-Fuß-Streifen, um einen Raum zu beleuchten. Wir empfehlen, die Stromquelle in der Mitte zu platzieren und den Streifen in zwei links und rechts verlaufende 25-Fuß-Abschnitte zu teilen, anstatt eine durchgehende Länge von 50 Fuß. Es muss nicht genau in zwei Hälften geteilt werden - wenn es bequemer ist, ist es akzeptabel, dass es in 20-Fuß- und 30-Fuß-Abschnitte aufgeteilt wird.
Wenn die Platzierung der Stromquelle in der Mitte nicht möglich ist, besteht die zweite Option darin, einen geeigneten Draht (siehe Spannungsabfalldiagramm) von der Stromquelle bis zur Mitte des Streifens zu führen. Auf diese Weise halten Sie zu Beginn des Laufs die Leistung, während der ordnungsgemäß dimensionierte Draht (der weniger Widerstand bietet als der LED-Streifen selbst) das schwere Heben übernimmt.
Einschränkungen auf Kupferfolie für LED-Streifen
Während Kupferfolie im Vergleich zu Standardmaterialien eine überlegene Wärmeleitfähigkeit bietet, oxidiert sie in Hochtemperaturumgebungen leicht und verringert die Wärmeableitungseffizienz. Ein längerer Betrieb bei erhöhten Temperaturen kann die Verschlechterung der Kupferfolie beschleunigen und die Lebensdauer des Streifens verkürzen.
Kupferfolie ist dünn und spröde. Externer Druck oder Biegung während der Installation oder Verwendung kann zu Brüchen führen, die zu Kurzschlüssen oder nicht funktionierenden Lichtern führen.
Außerdem korrodiert Kupferfolie in feuchten oder hohen Temperaturen leicht und erfordert zusätzliche Antioxidationsbehandlungen (wie Nickelplattieren oder Silan-Kupplungsmittelbeschichtung), um ihre Lebensdauer zu verlängern.
Spannungsversorgungsspannungspegel (12V vs. 24V vs. 48V)
12V, 24V und 48V LED-Streifen weisen signifikante Unterschiede bei der Auswirkungen auf den Spannungsabfall und dem Leistungsvergleich auf:
- 12V-Streifen weisen spürbare Leitungsverluste durch niedrigere Spannung und höheren Strom auf. Die Helligkeit bleibt innerhalb von 5 Metern stabil, aber ein signifikanter Spannungsabfall tritt über 5 Meter hinaus, was zu einer Helligkeitsabnahme am Heckende führt.
- 24V-Streifen halbieren den Strom, reduzieren die Leitungsverluste und ermöglichen eine spannungsfreie Übertragung über 10 Meter mit überlegener Helligkeitsgleichmäßigkeit.
- 48-V-Streifen arbeiten bei niedrigeren Strömen - nur 1/4 von 12-V-Streifen bei gleichwertiger Leistung - und minimiert den Spannungsabfall. Sie passen zu Ultra-Langstreckenbeleuchtung (z. B. über 30 Meter), erfordern aber eine stabile Stromversorgung.
Bei gleicher Länge liefern 24-V-Streifen normalerweise eine höhere Leistung und Helligkeit als 12-V-Streifen. 48V-Streifen, die bei höherer Spannung arbeiten, können mehr LED-Chips zur weiteren Helligkeitsverbesserung antreiben. Hochspannungsstreifen (24V/48V) verbrauchen weniger Strom und erleiden geringere Leitungsverluste, was sie für den langfristigen Einsatz energieeffizienter macht.
12V-Streifen erfordern einen höheren Strom, erfordern eine höhere Wärmeabgabe und neigen zu Überhitzung in engen Räumen. 24V/48V: Niedrigerer Strom reduziert die Wärmebelastung, aber der Isolationsschutz in Hochspannungsumgebungen muss gewährleistet sein. 12-V-Streifen haben niedrigere Anfangskosten, aber längere Längen erfordern zusätzliche Transformatoren oder Verkabelung, was möglicherweise die Gesamtkosten erhöht.
12V gegen 24V gegenüber 48V LED-Streifen-Leistungsvergleich
| LED-Streifen Typ | DC12V | DC24V | DC48V |
| Aktuell | Höher | Unter | unterste |
| Installationsabstand | ≤5M | ≤10m | ≤30 m |
| Kosten | Erhöhte Stromkosten für lange Strecken | Niedrige Kosten | Relativ wirtschaftlich |
| Schnittlänge | Kurzstrecke | mittlere Entfernung | relativ große Entfernung |
| Sicherheit | Niederspannung, relativ sicher | sicher | Geringere Sicherheit, erfordert Isolationsvorkehrungen |
| Wärmeableitung | Schlecht | Gut | ziemlich gut |
Zusammenfassung: Die Spannungsauswahl erfordert Auswuchtdistanz, Helligkeit, Kosten und Sicherheit. Entscheiden Sie sich für 12 V für den kurzen Aufenthalt im Wohnbereich, 24 V für gewerbliche Anwendungen mit mittlerer bis langer Entfernung und priorisieren Sie 48 V für Ultra-Langstrecken oder Hochleistungsprojekte.
Lesen Sie den Blog “Wann wählen Sie 12V, 24V oder 48V LED-Streifensysteme? (aktualisiert für den kommerziellen Gebrauch)”, um mehr zu lernen.
Wie berechnet man den Spannungsabfall?
Die Berechnung des Spannungsabfalls von LED-Streifen erfordert die Berücksichtigung von Faktoren wie Strom, Drahtwiderstand und Länge.
Grundformel: Spannungsabfall = Strom × Drahtwiderstand
wo:
- Strom (A) = Gesamtbandleistung (W) ÷ Betriebsspannung (V)
- Leiterwiderstand (Ω) = Widerstand (Kupferdraht: 0,0175 Ω·mm²/m) × Leiterlänge (m) ÷ Leiterquerschnitt (mm²)
Beispiel: 24V LED-Streifen, 240W Leistung, 40m Leiterlänge, 4mm² Drahtstärke:
Strom = 240 ÷ 24 = 10A
Widerstand = 0,0175 × 40 ÷ 4 = 0,175Ω
Spannungsabfall = 10A × 0,175Ω = 1,75V
In Niederspannungssystemen (z. B. 12 V / 24 V) überschreitet der Spannungsabfall typischerweise 51 tp3t der Nennspannung (z. B. 24 V-Systeme erlauben ≤ 1,2 V Abfall). Wenn der Spannungsabfall die Spezifikationen überschreitet, erhöhen Sie die Kabelstärke oder verkürzen Sie die Stromversorgungsabstände.
Sie möchten sich nicht mit komplizierten Berechnungen befassen? Dann verwenden Sie eine Online-Spannungsabfall-Rechner!
Empfehlungen zur Drahtauswahl: Bei langen Läufen (>10 Meter) sollten 24-V/48-V-Systeme zur Stromreduzierung priorisiert werden. Die Stromversorgung für 12-V-LED-Streifen wird für ≤5 Meter; 24V ≤10 Meter empfohlen; eine Doppel-End-Stromversorgung kann bis zu 20 Metern reichen.
Praktische Prüfung: Ein Multimeter kann den Spannungsaufteilungseffekt von Serienwiderständen in LED-Schaltungen überprüfen.
Praktische Lösungen zur Vermeidung von Spannungsabfall
Der durch Schaltungswiderstand und Stromverlust verursachte Spannungsabfall in LED-Streifen wirkt sich direkt auf die Gleichmäßigkeit und Lebensdauer der Beleuchtung aus. Nachfolgend finden Sie einige wirksame Methoden, um Spannungsabfall zu verhindern.
Power Injection von beiden Enden
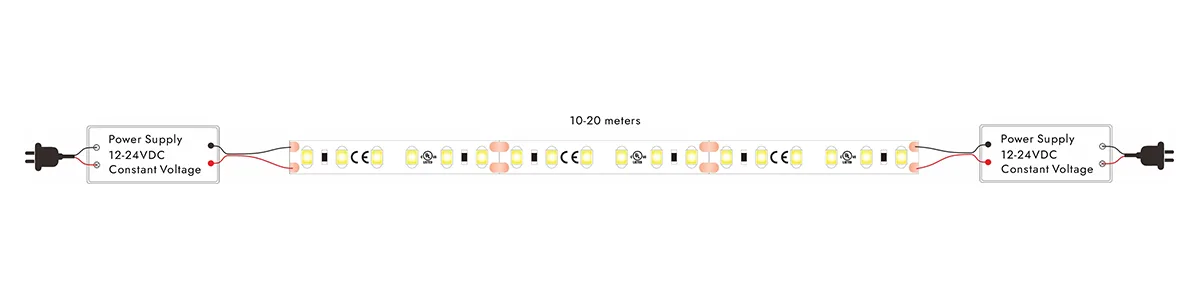
Dual-End-Netzteil: Implementieren Sie für längere Streifen eine Dual-End-Stromversorgungslösung, indem Sie Stromquellen sowohl an den Anfang als auch an den Ende des Streifens anschließen. Dies gewährleistet eine stabile Spannungsversorgung über den gesamten Streifen und verhindert so eine ungleichmäßige Helligkeit. Wenn möglich, fügen Sie Zwischenleistungspunkte entlang des Streifens hinzu, um den Spannungsabfall weiter zu reduzieren.
Mehrere Power Injection-Punkte
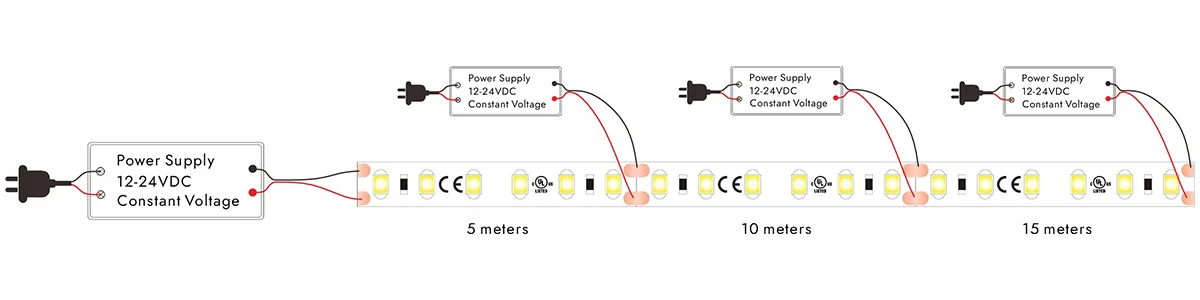
Segmentierte Steuerung: Teilen Sie lange LED-Streifen in mehrere Abschnitte, die jeweils von einem unabhängigen Treiber betrieben werden. Dieser Ansatz minimiert effektiv den Spannungsabfall pro Abschnitt und verbessert gleichzeitig die Stabilität des Gesamtsystems und die Helligkeitsgleichmäßigkeit.
Optimieren Sie das Layout und die Verbindungen der Streifen: Stellen Sie sicher, dass die Verkabelung sowohl funktional als auch ästhetisch ansprechend ist, und vermeiden Sie verhedderte oder übermäßig gebogene Kabel. Beim Anschließen von Streifen sicheren, zuverlässigen Kontakt garantieren, um zusätzliche Widerstands- und Spannungsabfälle durch lose oder fehlerhafte Anschlüsse zu vermeiden.
Verwenden Sie 24V oder 48V LED-Streifen
Der Einsatz von 24V- oder 48V LED-Streifen mildert effektiv Spannungsabfallprobleme und zeigt deutlich weniger Auswirkungen als 12-V-Streifen. Während 12-V-Streifen über 5 Meter einen merklichen Helligkeitsabfall aufweisen, unterstützen 24-V-Streifen Längen von bis zu 10 Metern, ohne dass zusätzliche Stromquellen erforderlich sind. Ihre flexiblen Schnittpunkte (alle 6 LEDs) machen sie ideal für Ferninstallationen.
Bei gleicher Leistungsstufe ziehen 48-V-Streifen nur die Hälfte des Stroms von 24-V-Streifen. Gemäß der Leistungsverlustformel Q=I²R weisen 48V-Systeme deutlich reduzierte thermische Verluste und niedrigere Spannungsabfallverhältnisse auf. 48V-Systeme ermöglichen den in Reihe geschalteten Anschluss, was die Verdrahtung und die Arbeitskosten senkt, 24-V-Streifen vereinfachen die Installation durch die Eliminierung häufiger Leistungsverstärker. 24V-Streifen erzeugen weniger Wärme und sind somit für einen längeren Betrieb geeignet, 48V-Systeme optimieren die Energieeffizienz weiter.

Hohe Helligkeit DC24V 2835 LED-Streifenleuchten – 180lm/Watt
Modell: FQX10T128C
LED-Anzahl pro Meter: 128
Leiterplattenbreite: 10mm
Farbtemperatur: 2700K/3000K/4000K/5000K/6500K
Eingangsspannung: DC24V
Leistung pro Meter: 12W
IP-Grad: IP20/IP54/IP65/IP67/IP68
Garantie: 5 Jahre
Die Funktion oben unterstützt die Anpassung.
Dickere Drähte
Verwenden Sie dickere Drähte oder reduzieren Sie die Kabellänge: Der Drahtwiderstand ist ein Hauptfaktor, der zu Spannungsabfall führt. Daher kann die Verwendung dickerer Drähte den Widerstand verringern und Probleme mit dem Spannungsabfall verringern. Außerdem reduziert die Minimierung der Drahtlänge zwischen Streifen und Stromquelle effektiv Widerstand und Spannungsabfall.
Verwenden Sie Konstantstromlösungen
Konstantstrom-LED-Streifen lösen durch präzise Stromregelung inhärente Spannungsschwankungen induzierte Spannungsabfälle in Eigenregie.
Ihre Kernvorteile manifestieren sich in drei Aspekten: Erstens stellen Konstantstromkreise den Stromfluss automatisch ein. Wenn die Netzimpedanz zunimmt oder die Versorgungsspannung schwankt, halten sie die LED-Stromstabilität auf einem eingestellten Wert (z. B. 20 mA ± 31 TP3T) und sorgen so für eine gleichbleibende Helligkeit von Anfang bis Ende. Zweitens verhindert konstanter Strom einen beschleunigten Lichtabfall, der durch eine örtliche Überhitzung in LEDs verursacht wird. Tests zeigen, dass die LED-Lebensdauer bei Konstantstromantrieb um über 301 tp3t verlängert wird.
Zusätzlich zeigt diese Lösung eine geringe Empfindlichkeit gegenüber dem Leitungswiderstand. Selbst bei dünnen Drähten (z. B. 28 AWG) oder bei der Fernverdrahtung passt sich der dynamische Spannungsabfallausgleich dynamisch an Offset-Linienverluste an. Dieses Design eignet sich besonders für Szenarien, die eine flexible Verdrahtung erfordern, wie z. B. dekorative Lichtstreifen für die Ferne, die eine gleichbleibende LED-Streifenhelligkeit gewährleisten.

DC24V/DC48V Konstantstrom-Long-Run-LED-Streifen
Hauptmodell: FQW10T120D
LED-Typ: SMD2835
LED-Anzahl pro Meter: 120
Leiterplattenbreite: 10mm/12mm
Länge: 10m/15m/20m/30m/40m/50m
Eingangsspannung: DC24V/DC48V
Leistung pro Meter: 10W / 7,2W
Farbtemperatur: 2700K/3000K/4000K/5000K/6500K
IP-Grad: IP20/IP54/IP65/IP67/IP68
Garantie: 3 Jahre
Die Funktion oben unterstützt die Anpassung.
Verwenden Sie Verstärker / Repeater im RGB/RGBW-Streifen
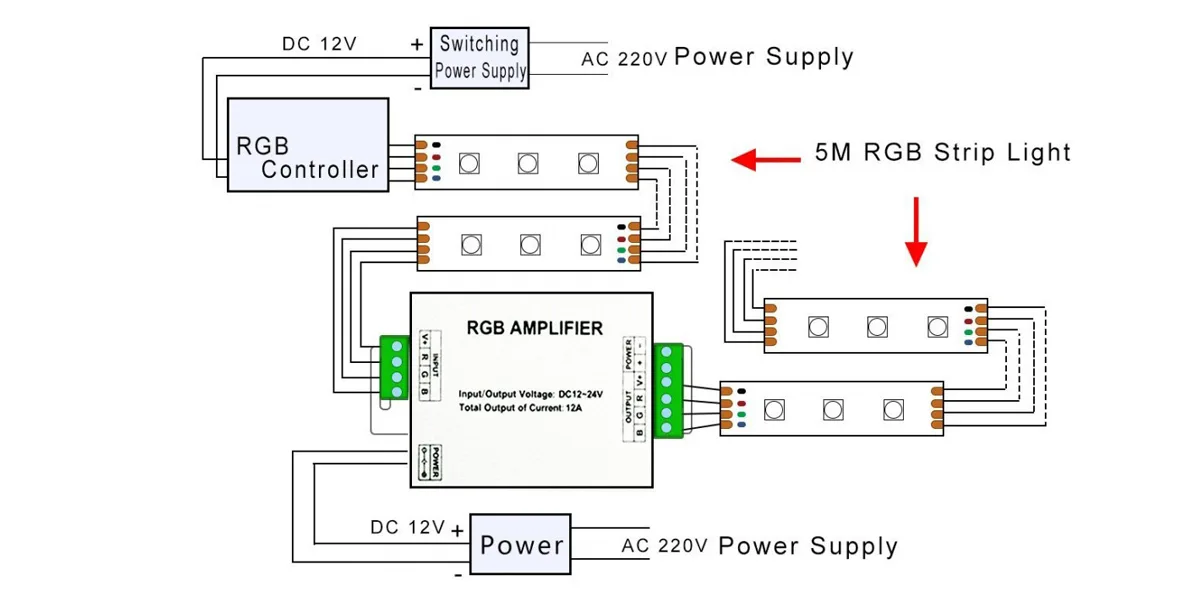
Während der Fernübertragung von RGB/RGBW-Streifen verschlechtern sich die Signale durch Widerstand und Interferenz und verursachen am Ende des Streifens eine ungleichmäßige Helligkeit oder Farbverzerrung. Bei 12V-Streifen (typischerweise ≤5 Meter) ermöglichen Verstärker/Repeater eine stabile Kontrolle über längere Strecken (z. B. 30+ Meter). Hochspannungsstreifen (z. B. 24V/48V) haben eine geringere Stromaufnahme und einen geringeren Spannungsabfall, wodurch die Abhängigkeit von Verstärkern/Repeatern minimiert wird. Bei Verwendung von 12-V-Streifen Installieren Sie alle 10 Meter einen Repeater, um den Spannungsabfall auszugleichen.
Zusammenfassend erfordert die Adressierung des Spannungsabfalls der LED-Streifen einen facettenreichen Ansatz, einschließlich Verbesserung der Stromversorgungsmethoden, Optimierung der Verdrahtung und des Layouts und der Verwendung von Hilfsausrüstung. Benutzer können geeignete Lösungen basierend auf bestimmten Bedingungen auswählen, um die Leistung und die ästhetische Attraktivität ihrer LED-Streifeninstallationen zu verbessern.
Empfehlungen für Designer & Käufer
Als Kernelement des modernen Beleuchtungsdesigns wirken sich die Spannungsspezifikationen der LED-Streifenleuchten - 12 V / 24 V / 48 V - direkt auf die Ergebnisse und die Benutzererfahrung der Projektoren aus.
Das 12V-System zeichnet sich durch Sicherheit und Flexibilität aus und ist somit ideal für die Wohnkultur. Das 24-V-System schafft eine Balance zwischen Spannungsabfall und Schneidkomfort und wird zur Hauptwahl für kommerzielle Umgebungen. Das 48-V-System mit seinem extrem niedrigen Linienverlust wurde speziell für großflächige Beleuchtungsprojekte entwickelt.
Die Designer sollten anhand der Übertragungsentfernung, der Sicherheitsanforderungen und der Kostenüberlegungen ausgewählt werden. Käufer sollten den tatsächlichen Anwendungsbedarf priorisieren und vermeiden, blind höhere Spannungsspezifikationen zu verfolgen.
LED-Streifen-Spannungs-N
| Spannungs-Nennwert | Hauptvorteile | Geeignete Anwendungen | Überlegungen |
| 12V | Hohe Sicherheit (kein elektrisches Schlagrisiko), weiches Licht zum Schutz der Augen, einfache Installation (selbstklebende Rückseite) | Wohnkultur (Kinderzimmer/Treppen/Schränke), Kurzstreckenbeleuchtung (Studium/Balkon), Beleuchtung für Zusatzgeräte | Erfordert eine Leistungserweiterung über 5 Meter, um Spannungsabfall bei langen Läufen zu verhindern |
| 24V | Minimaler Spannungsabfall (unterstützt 10m ohne Leistungssteigerung), flexibles Schneiden (je 6 Leuchten), gleicht Sicherheit und Effizienz aus | Wohnkultur, Gewerbe-Vitrinen/Lightboxen, Mittelklasse-Projektbeleuchtung | Benötigt dedizierte Stromversorgung, etwas höhere Kosten als 12-V-Systeme |
| 48V | Minimaler Leitungsverlust (derzeit nur halb so hoch wie 24V), geeignet für ultralange Serienanschlüsse, hohe Projektstabilität | Große Architekturbeleuchtung, Wandwäsche für große Entfernungen, Beleuchtungsprojekte mit hoher Dichte | Erfordert professionelle Installation mit strengen Verdrahtungsanforderungen |
Empfehlungen zur Designauswahl
Szenarien für Sicherheit-Priorität (z. B. Räume für Häuser / Kinder): Entscheiden Sie sich für 12-V-Systeme für die Sicherheit und die Installation. Kombinieren Sie mit RGB-Streifen für Umgebungslichteffekte.
Kurz- bis mittlere Anwendungen: Empfehlen Sie 24-V-Streifen für ausgewogene Kosten und Leistung. Achten Sie bei der Beleuchtung der Vitrine an Schnittpunkten auf eine gleichbleibende Helligkeit.
Großprojekte: Übernehmen Sie 48-V-Systeme, um die Leitungsverluste zu minimieren. Wenn beispielsweise mehr als 50 Meter architektonische Umrissbeleuchtung in Reihe geschaltet wird, beträgt der Spannungsabfall von 48 V nur 1/4 der von 12 V.
Einkaufsführer
Wohnbenutzer: Bei der Auswahl von 12-V-Streifen priorisieren Sie die wasserdichten Bewertungen (z. B. IP65 für Balkone) und die Funktionalität der Fernbedienung. Wählen Sie eine LEDs mit hoher Dichte (z. B. 60 LEDs/Meter), um eine gleichmäßige Beleuchtung zu gewährleisten.
Projektkäufer: Überprüfen Sie für 24V / 48V-Streifen die Spannungsabfalltestdaten der Lieferanten und fordern Sie einen Vergleichsbericht für 5-m / 10-m-Helligkeit an.
Kostenkontrolle: 12V-Systeme haben niedrigere Anfangskosten, erfordern aber eine Stromergänzung für lange Auflagen, 48-V-Systeme haben höhere Stückkosten, sparen aber Verkabelung und Arbeitskräfte - bewerten Sie die Gesamtkosten des Lebenszyklus umfassend.
Wichtige Hinweise: Alle Spannungen erfordern hochwertige Netzteile, um Spannungsschwankungen zu vermeiden, die die Lebensdauer verkürzen. In feuchten Umgebungen (z. B. Badezimmern / Gärten) wählen Sie immer wasserdichte Modelle (IP65 oder höher). Spannungsabfall vor Ferninstallationen testen und bei Bedarf eine segmentierte Stromversorgung verwenden.