Introduzione: Perché l'illuminazione acustica sta diventando il nuovo argomento caldo nel settore dell'illuminazione?
I moderni spazi per uffici, gli edifici commerciali, le istituzioni educative e gli ambienti sanitari appongono sempre di più al "controllo del rumore" come priorità di progettazione, alla pari con l'illuminazione. Uffici a pianta aperta, spazi condivisi e traffico pedonale ad alta densità significano che gli apparecchi tradizionali non possono più affrontare adeguatamente le crescenti sfide acustiche, soddisfacendo al contempo i requisiti di illuminazione.
È in questo contesto che l'illuminazione acustica ha rapidamente guadagnato popolarità. Non solo fornisce l'illuminazione, ma migliora anche efficacemente gli ambienti acustici interni attraverso la progettazione strutturale e i materiali fonoassorbenti. Eppure, per acquirenti, designer e appaltatori, rimane una domanda fondamentale: queste luci acustiche sono state davvero sottoposte a test professionali affidabili?
Questo articolo esamina sistematicamente il framework di convalida dietro l'illuminazione acustica da più dimensioni di test critici. Aiuta i clienti a ottenere informazioni più chiare sul valore del prodotto fornendo al contempo motivi credibili per le decisioni di approvvigionamento.
Cos'è una luce acustica? Come si ottiene la riduzione del rumore?

Luci acustiche Non sono semplicemente infissi con "uno strato di materiale aggiunto" sulla loro superficie. Sono prodotti compositi che integrano profondamente il design acustico con l'ingegneria del luminoma.
I loro principi fondamentali includono
- Utilizzando materiali fonoassorbenti altamente efficienti (come fibre acustiche, fibre di poliestere, materiali microporosi, ecc.)
- Aumentare i percorsi di diffusione sonora e assorbimento attraverso la struttura dell'apparecchio
- Ridurre i riflessi sonori a un tempo di riverbero inferiore (RT)
A differenza delle normali lampade acustiche decorative, le lampade acustiche autentiche richiedono la convalida attraverso test acustici standardizzati per dimostrare le loro effettive capacità di assorbimento del suono, non semplicemente "design concettuale".
Certificazione di prodotto: conformità UL e CE: barriere legali all'ingresso nel mercato

Nel quadro di conformità tecnica per le lampade acustiche, le certificazioni UL (USA), CE (UE) e TÜV (Germania ed Europa) non sono solo elementi di test di routine. Costituiscono prerequisiti obbligatori o autorevoli per l'accesso al mercato in diverse regioni, formando collettivamente una rete di garanzia della conformità che copre il Nord America, l'Europa e i principali mercati globali.
Certificazione UL
Rilasciata da Underwriters Laboratories (UL), questa certificazione non è obbligatoria a livello federale ma funge da standard di accesso de facto per l'illuminazione degli spazi commerciali e pubblici in Nord America. Il marchio UL indica la verifica indipendente di terze parti della sicurezza elettrica, delle prestazioni termiche, della resistenza alla fiamma e dell'affidabilità a lungo termine di un prodotto, rendendolo un simbolo di fiducia fondamentale per rivenditori, architetti e proprietari di edifici durante l'approvvigionamento.
Certificazione CE
Un marchio di conformità obbligatorio per i prodotti che entrano nel mercato dell'Unione europea, che copre le direttive di base tra cui LVD (Direttiva Bassa Tensione), EMC (Direttiva sulla Compatibilità Elettromagnetica) e RoHS (Restrizione di sostanze pericolose). Come dispositivi compositi acustici-ottici alimentati elettricamente, gli apparecchi acustici devono essere conformi alle norme di sicurezza della serie EN 60598 e ai requisiti di compatibilità elettromagnetica EN 55015/61547. Il marchio CE funge da prova diretta della loro conformità legale.
Certificazione TÜV
Rilasciata dalla TÜV (Associazione Tecnica di Ispezione), questa certificazione è un'autorità eccezionale nel mercato europeo, rinomata per i suoi rigorosi standard in materia di sicurezza e dettagli di qualità. Gli aspetti chiave di certificazione includono:
- Test di sicurezza completi: che coprono la resistenza meccanica, la resistenza all'invecchiamento dei materiali e l'estrema adattabilità ambientale.
- Supervisione regolare dei sistemi di qualità in fabbrica per garantire la coerenza della produzione di massa. Sebbene non sia obbligatorio nell'UE, il marchio TÜV migliora significativamente la competitività dei prodotti nei mercati europei. Serve come simbolo vitale di qualità e affidabilità, in particolare nei progetti commerciali di fascia alta e nelle applicazioni industriali.
Test ambientali SGS: la base della conformità, della sostenibilità e della fiducia
Nel mercato internazionale B2B, il test SGS è virtualmente sinonimo di "sostegno affidabile di terze parti". Per le lampade acustiche, i test ambientali SGS si concentrano principalmente sui seguenti aspetti:
- Conformità ambientale dei materiali: aderenza a regolamenti come RoHS e REACH
- Limitazione di sostanze pericolose: metalli pesanti, alogeni ed emissioni di COV
- Consistenza della produzione: stabilità e tracciabilità del lotto di materiale
Questi test non solo si occupano della responsabilità ambientale, ma determinano anche direttamente se i prodotti possono entrare nei mercati europei e americani e superare le revisioni della conformità per i grandi progetti. Per gli acquirenti, un rapporto SGS indica una riduzione dei rischi di conformità e una maggiore sicurezza del progetto.
Test delle prestazioni di assorbimento acustico: misurazione della riduzione del rumore effettiva

Lo standard internazionale per la gamma di frequenza del parlato umano si riferisce tipicamente allo standard di larghezza di banda della trasmissione vocale nelle comunicazioni telefoniche digitali, che vanno da 300 Hz a 3400 Hz. Il nostro discorso quotidiano si basa principalmente sulla gamma di frequenza da 500 Hz a 3000 Hz, che contiene la maggior parte delle informazioni sull'energia e sulla chiarezza nel parlato, fondamentale per comprendere il linguaggio. La gamma uditiva umana va da 20 Hz a 2000 Hz, ma la stragrande maggioranza delle informazioni vocali è concentrata all'interno della banda di frequenza 300–3400 Hz più stretta.
La capacità di assorbimento acustico dei pannelli acustici deve essere quantificata attraverso test di laboratorio acustici professionali, principalmente utilizzando strumenti come l'indagine B&K 2270, l'amplificatore di potenza 2716, l'altoparlante omnidirezionale 4292 e il microfono 4189.
Le metriche di test comuni includono:
- Coefficiente di assorbimento acustico (SAC)
- Coefficiente di riduzione del rumore (NRC)
- Prestazioni di assorbimento acustico tra le bande di frequenza (bassa frequenza/mid-frequenza/alta frequenza)
- Standard di prova: Basato su EN ISO 354:2003 / ISO 354 “Acustica—Misurazione dell'assorbimento acustico in una stanza di riverbero”
Per ottenere l'assorbimento acustico e la riduzione del rumore, i materiali rilevanti devono possedere proprietà di “sound-sound-sound-sounding”. Di seguito è riportato il rapporto di prova per il materiale primario utilizzato nei prodotti di illuminazione acustica di SignLiteled, pannelli acustici in fibra di poliestere, presentati per l'ispezione:
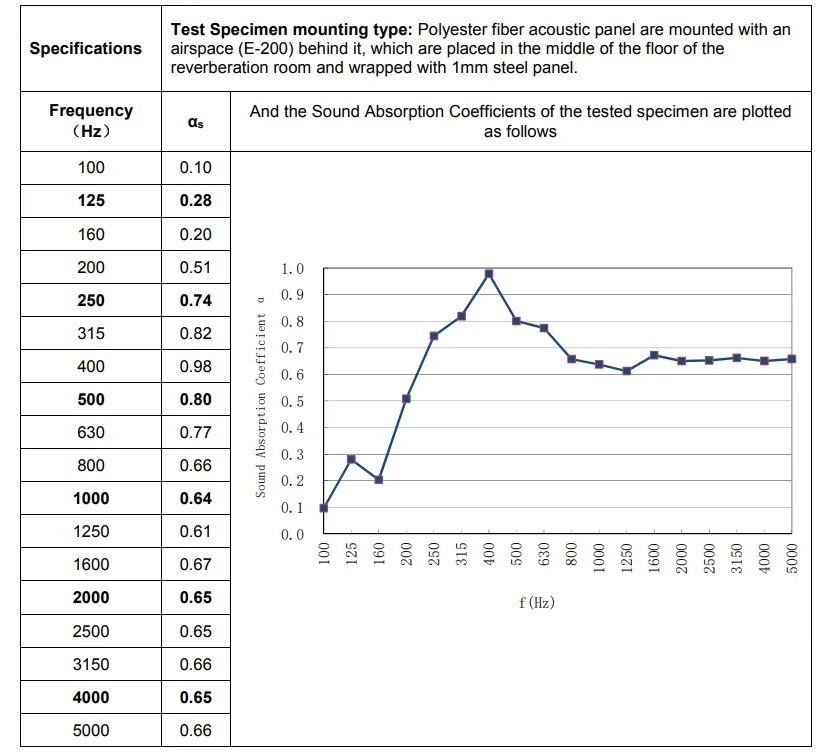
Come mostrato sopra, i pannelli in fibra di poliestere testati mostrano coefficienti di assorbimento acustico costantemente al di sopra di 0,74 attraverso il parlato core e la gamma di frequenza del rumore comune di 250 Hz-1250 Hz, con valori di picco a 250 Hz e 800 Hz. Ciò indica un eccellente assorbimento del linguaggio umano, dello squillo del telefono e del rumore delle apparecchiature per ufficio, il che lo rende altamente adatto per migliorare l'intelligibilità del parlato in uffici, sale conferenze e scuole.
Al di sotto di 125 Hz, il coefficiente di assorbimento acustico è inferiore (<0,3), una caratteristica tipica dei materiali sottili e porosi. Per affrontare il rumore a bassa frequenza (ad es. ronzio del condizionatore d'aria, rombo del traffico), sono generalmente necessari materiali più spessi o strutture di assorbimento specializzate a bassa frequenza.
I rapporti indicano che questo pannello acustico in fibra di poliestere eccelle nell'assorbimento del rumore da medio ad alta frequenza (in particolare 250-1250 Hz), ottenendo prestazioni leader del settore a frequenze specifiche. Se utilizzato in apparecchi di illuminazione acustica, questo materiale offre una notevole riduzione del rumore per il linguaggio umano. L'applicazione effettiva dovrebbe fare riferimento a questi dati in base a specifici spettri di rumore e condizioni di installazione.
Gli ambienti di test standardizzati riflettono accuratamente le capacità di riduzione del rumore dell'illuminazione acustica negli spazi reali. Tali dati sono particolarmente cruciali per i progettisti di acustica architettonica e gli integratori di sistemi, fungendo da differenziatori chiave tra l'illuminazione acustica e gli apparecchi convenzionali.
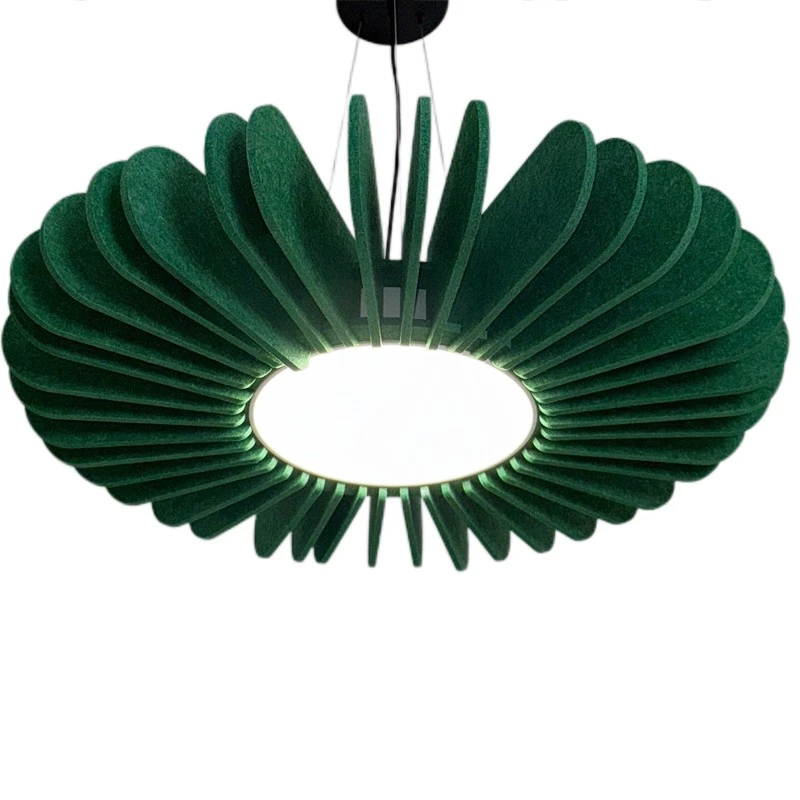

Lampada a sospensione a LED acustica rotonda ultrasottile
Tensione di ingresso: AC100-277V / AC220-240V,50-60Hz
Dimensione dell'alloggio: 120 mm
Direzione emettendo: in giù
Taglia (DXH): 500x80mm
CCT: 3000K / 4000K / 6000K
Potenza: 15W
Flusso luminoso: 100-110 lm/w
CRI: >90
PF: >0.90
Flicker gratuito: Sì
Angolo del fascio: 120°
Grado IP: IP20
Garanzia: 5 anni
Opzione colore del pannello acustico: Rosso / Verde / Blu / Grigio Più di 48 colori Opzione
Test delle prestazioni antincendio: sicurezza negli spazi pubblici e commerciali

I pannelli acustici a soffitto sono ampiamente utilizzati in controsoffitti, aree pubbliche e spazi ad alta occupazione, rendendo la resistenza al fuoco una considerazione fondamentale. È quindi essenziale il test di ignifugo dei materiali. In ambienti pubblici e commerciali, i materiali acustici per pannelli devono soddisfare sia i requisiti di impermeabilizzazione che di resistenza al fuoco. Secondo lo standard americano ASTM E84, le valutazioni al fuoco sono classificate in tre livelli: A, B e C. Il livello B (FSI 26-75) rappresenta il requisito di base, garantendo una diffusione controllata di fiamma durante un incendio e un indice di fumo non superiore a 450, salvaguardando così l'evacuazione sicura. La norma europea EN 13501-1 richiede materiali per ottenere almeno la classe B (equivalente a B1). Questa valutazione valuta la diffusione della fiamma e il rilascio di calore attraverso un test di combustione a corpo singolo, garantendo un basso rischio di incendio.
In sintesi, Materiali per l'illuminazione a Deve soddisfare le classi di fuoco B1 ASTM E84 di classe B o EN 13501-1 e possedere una resistenza all'acqua di base per soddisfare i requisiti di sicurezza degli spazi pubblici.
Resistenza al fuoco USA ASTM E84 e EU EN 13501-1 Rating Cconfronto Tcapace
| vessillo | Metodo di prova e base di valutazione | Definizione di classificazione dei voti | Principali mercati applicativi |
| USA ASTM E84 | Prova del tunnel di Steiner – Valuta la diffusione della fiamma superficiale e la generazione di fumo. – Indicatori chiave: Indice di diffusione della fiamma (FSI), Indice di sviluppo del fumo (SDI). – Il risultato è intuitivo, valuta solo le caratteristiche di combustione superficiale. | Classe A: FSI ≤ 25, SDI ≤ 450. Classe B: 26 ≤ FSI ≤ 75. Classe C: 76 ≤ FSI ≤ 200. La classificazione si basa direttamente sul valore FSI, senza un meccanismo di degradazione complesso. | Mercati nordamericani (Stati Uniti, Canada) Ampiamente usato nei codici edilizi come NFPA, IBC. |
| EU EN 13501-1 | Valutazione completa di test multipli 1. EN 13823 (Test a bruciatura singola, SBI): valuta la propagazione della fiamma e il rilascio di calore. 2. EN ISO 11925-2 (prova di accensione a fiamma piccola): valuta l'accendibilità. valuta contemporaneamente la generazione di fumo (S1/S2/S3) e la gocciolina fusa (D0/D1/D2). | 7 gradi principali (A1 → A2 → B → C → D → E → F): A1 è il grado non combustibile più alto. Grado B: Il materiale è “difficile da accendere” con valutazioni aggiuntive di fumo e goccioline (ad es. B-S1, D0). regola rigorosa "nessuna degradazione inversa". | Mercati dell'UE e riconosciuti a livello globale Obbligatorio per la marcatura CE e i regolamenti edilizi dell'UE |
Classificazione della resistenza al fuoco ASTM E84 (USA)
Le classificazioni sono le seguenti:
| classificazione | fiamma dividere indice, FSI | fumo-Devoluto indice, sdi |
| Classe A | 0-25 | 0-450 |
| Classe B | 26-75 | 0-450 |
| Classe C | 76-200 | 0-450 |
Appendice: EN 13501-1 Classificazione antincendio (UE)
Tabella 1: Classi di reazione alle prestazioni di fuoco per i prodotti da costruzione escluse le pavimentazioni e i prodotti di isolamento termico per tubi lineari.
| classe | Metodi di prova | Criteri di classificazione | Classificazione aggiuntiva | |
| a1 | EN ISO 1182 a E | △T≤30℃, e △M≤50%, e tf=0(cioè no fiammata fiammata) | – | |
| EN ISO 1716 | Pz≤2.0MJ/kg a E Pz≤2.0MJ/kg b C E Pz≤1,4mj/m² D E Pz≤2.0MJ/kg E | – | ||
| a2 | EN ISO 1182 a o | E | △ T≤50℃, e △M≤50%, e tf≤20 s | – |
| EN ISO 1716 | Pz≤3,0MJ/kg a E Pz≤4,0mj/m² b E Pz≤4,0mj/m² D E Pz≤3,0MJ/kg E | – | ||
| EN 13823 | Figra≤120W/s e lfs<bordo di esemplare e thh600≤7,5 MJ | produzione di fumo f E Goccioline/particelle fiammeggianti sol | ||
| B | EN 13823 e | Figra≤120W/s e lfs<bordo di esemplare e thh600≤7,5 MJ | produzione di fumo f E Goccioline/particelle fiammeggianti sol | |
| EN ISO 11925-2 io Esposizione=30s | FS≤150mm entro 60 s | |||
| C | EN 13823 e | Figra≤250W/s e lfs<bordo di esemplare e thh600≤15MJ | produzione di fumo f E Goccioline/particelle fiammeggianti sol | |
| EN ISO 11925-2 io Esposizione=30s | FS≤150mm entro 60 s | |||
| D | EN 13823 e | Figra≤750W/s | produzione di fumo f E Goccioline/particelle fiammeggianti sol | |
| EN ISO 11925-2 io Esposizione=30s | FS≤150mm entro 60 s | |||
| E | EN ISO 11925-2 io Esposizione=15s | FS≤150mm entro 20 s | Goccioline/particelle fiammeggianti h | |
| F | EN ISO 11925-2 io Esposizione=15s | FS>150 mm entro 20 s | – | |
Il superamento dei test antincendio assicura che gli apparecchi e i loro materiali acustici non diventino pericolosi di incendio anche in condizioni anomale. Questo è un requisito obbligatorio per progetti come ospedali, scuole e complessi commerciali.
Test delle prestazioni ottiche: rumore Reduzione Sprendere No CQualche a Tlui Expense di Lorizzonte Qualità

Un'eccellente luce che riduce il rumore deve trovare un equilibrio tra prestazioni acustiche e ottiche.
Il test ottico chiave si concentra su:
- Flusso luminoso ed efficacia luminosa: La selezione dovrebbe essere basata sulla dimensione e sullo scopo dello spazio. Ad esempio, una camera da letto tipica può richiedere 800-1500 lm, mentre un Area di lavoro d'ufficio Potrebbe essere necessario 3000-5000 lm.
- consistenza della temperatura del colore: Non esiste uno standard rigido, ma il principio fondamentale è selezionare in base alle funzioni dello spazio e ai requisiti di utilizzo. Tipicamente che vanno da 2700K a 5000K, dando priorità a comfort e praticità.
- Indice di resa cromatica (CRI): Ra≥80 garantisce una riproduzione del colore accurata.
- Controllo abbagliamento (UGR): tipicamente mantenuto a UGR ≤ 19, uno standard universale per l'illuminazione interna che garantisce un comfort visivo e riduce l'affaticamento degli occhi.
Questi test garantiscono che le luci di insonorizzazione migliorino gli ambienti acustici, offrendo al contempo un'illuminazione confortevole, stabile e di alta qualità, evitando la trappola di soluzioni "silente ma inefficace".
Test di sicurezza elettrica: misure di base per la protezione del personale e del sistema
Indipendentemente dagli scenari applicativi, la natura fondamentale degli apparecchi di illuminazione come prodotti elettrici rimane invariata. Per garantire la sicurezza e l'affidabilità delle apparecchiature di illuminazione come le plafoniere acustiche, è necessario implementare un sistema di test di sicurezza elettrico completo che copre i seguenti aspetti critici:
Prove di prestazione dell'isola
Valuta le prestazioni di isolamento tra parti sotto tensione e componenti metallici accessibili. La tensione di prova è tipicamente 500 V CC, richiedendo valori di resistenza di isolamento non inferiori a:
- 2MΩ (isolamento di base)
- 4MΩ (isolamento rinforzato)
resistere ai test di tensione
Condotte secondo standard diversi:
- Standard europeo: tensione di prova di 1000Vac o 1414Vdc, sovrapposta a 2 volte la tensione nominale. La corrente di dispersione non deve superare i limiti specificati (ad es. 5mA) durante il test.
- UL STANDARD (US): Gli apparecchi fissi devono resistere a un test di tensione di 1500 V per 1 secondo con una corrente di dispersione non superiore a 1,0 mA. Apparecchi portatili: La corrente di dispersione non deve superare 0,5 mA.
Test di corrente di messa a terra e di dispersione
- Prova di continuità del suolo: Gli apparecchi acustici sono utilizzati principalmente all'interno e tipicamente classificati come apparecchi di classe II (progetto a doppio isolamento), eliminando la necessità di messa a terra. Pertanto, i test di continuità del suolo non sono obbligatori.
- Test di corrente di dispersione: Per gli apparecchi di classe II, i requisiti di corrente di dispersione sono più severi, imponendo una corrente di dispersione non superiore a 0,25 mA per garantire la sicurezza dell'utente.
Significato e valore
Questi test costituiscono un componente fondamentale degli standard di illuminazione internazionali (ad es. IEC60598, UL1598). Simulando condizioni di funzionamento estreme, convalidano l'affidabilità a lungo termine degli apparecchi, prevenendo efficacemente i rischi di scosse elettriche, cortocircuiti o rischi di incendio. Ciò fornisce doppie protezioni per la sicurezza del personale e il funzionamento stabile dei sistemi edili.
Test di durata e durata della vita: garanzia delle prestazioni a lungo termine
La longevità del prodotto è critica quanto i costi di manutenzione. I dati affidabili sui test sulla durata della vita consentono cicli di manutenzione prevedibili, riducendo significativamente il costo totale di proprietà.
Ambito di prova e metodi:
Test di invecchiamento della sorgente luminosa a LED
- Test di invecchiamento accelerato: Condotto secondo IEC 62506 Norma: 6.000 ore di funzionamento continuo a 85°C e 85% di umidità, simulando 15 anni di normale utilizzo.
- Monitoraggio del decadimento del flusso luminoso: Misurato ogni 500 ore utilizzando un fotometro a sfera integrante per garantire una velocità di decadimento ≤30% (per potenza nominale ≥10W) e una variazione CRI (RA) ≤5%.
- Analisi della modalità di errore: fenomeni di degradazione del documento come ingiallimento incapsulante a LED e distacco dello strato di fosforo per prevenire guasti improvvisi.
Test di durata della vita dell'alimentatore del conducente
- Invecchiamento di tensione costante/costante: funzionamento continuo a 1,2 volte Corrente nominale per 3000 ore a 40°C di temperatura ambiente, monitorando la fluttuazione della tensione di uscita ≤ ±5%.
- Prova del ciclo di commutazione: Simulare frequenti scenari di accensione/spegnimento con 10.000 operazioni di commutazione a intervalli di 10 secondi, verificando che non si rompa il condensatore o il burnout IC.
- Verifica della protezione da sovraccarico: Quando la tensione di ingresso oscilla ±15%, l'alimentazione deve attivare meccanismi di protezione entro 0,1 secondi per prevenire danni da sovracorrente del LED.
Verifica della stabilità di alta temperatura e umidità
- Test doppio 85: Dopo 500 ore a 85°C/85% RH, la resistenza di isolamento dell'apparecchio deve rimanere ≥100MΩ senza perdite o cortocircuiti.
- prova di shock termico: resiste a 100 cicli da -40°C a 85°C, verificando nessuna degradazione della resistenza all'incollaggio tra schiuma acustica e telaio in metallo.
I dispositivi che superano questi test raggiungono una durata di vita L70 (tempo a 70% Manutenzione del flusso luminoso) di 50.000 ore, equivalenti a 15 anni di funzionamento esente da manutenzione in spazi commerciali. L'alimentatore del driver MTBF (tempo medio tra guasti) è ≥50.000 ore, con un tasso di guasto inferiore a 0,5%.
Test di stabilità sismica e meccanica: adattato agli ambienti del mondo reale
Durante il trasporto, l'installazione e l'uso a lungo termine, gli apparecchi sopportano vibrazioni, urti e sollecitazioni di sospensione. I test sismici garantiscono sicurezza e affidabilità in progetti commerciali (ad es. aeroporti, metropolitane) e spazi pubblici.
Testo e metodi di test:
Verifica della resistenza strutturale dell'apparecchio
- Simulazione della tabella delle vibrazioni per il trasporto: per ISTA 3A standard, test di vibrazione casuale a 5 Hz-500 Hz di frequenza con picco di accelerazione di 5G, della durata di 2 ore.
- test di impatto: Test di caduta libera da 1,2 metri su una superficie in cemento. L'alloggiamento dell'apparecchio non deve presentare crepe, con spostamento del componente interno ≤2 mm.
Affidabilità di fissaggio dei componenti interni
- Prova di vibrazione sinusoidale: vibrare a 0,75 mm di ampiezza tra 10 Hz e 55 Hz per 30 minuti per verificare l'assenza di allentamento del modulo LED o delle viti della scheda di alimentazione.
- prova di coppia: Applicare una coppia di 50 N·m sulla staffa di sospensione per 10 minuti senza deformazione plastica.
Sospensione a lungo termine e sicurezza sulle vibrazioni
- prova affaticata: Simula le condizioni di vibrazione della metropolitana con 10 cicli con accelerazione 2G. Nessun distacco si verifica alla connessione tra il cotone fonoassorbente e il corpo della lampada.
- Prova di carico del vento: Resiste a 30 minuti a velocità del vento di 15 m/s (equivalente a venti di forza 7). Angolo di inclinazione della lampada ≤5°, senza rischio di caduta.
Conclusione: perché le "luci fonoassorbenti testate" valgono l'investimento
Le luci fonoassorbenti dovrebbero trascendere l'essere semplicemente un "nuoto prodotto concettuale" e rappresentare invece una soluzione di sistema rigorosamente convalidata. Dai test ambientali SGS all'assorbimento acustico, alla resistenza al fuoco, alle prestazioni ottiche, alla sicurezza elettrica, alla durata e alle valutazioni della resilienza sismica: ogni convalida riduce i rischi e crea fiducia. Questi test non solo dimostrano il progresso tecnologico, ma migliorano anche la fiducia dei consumatori.
In mezzo all'aumento dell'inquinamento acustico, l'illuminazione acustica si distingue nel settore attraverso un design innovativo e una qualità affidabile. Scegliere in modo completo Apparecchio di illuminazione acustica Significa selezionare tranquillità, salute e longevità per il tuo spazio. Per i professionisti dell'approvvigionamento, optare per un'illuminazione acustica completamente testata si traduce in:
- Tassi di approvazione del progetto più elevati
- Ridotti costi di manutenzione e conformità
- Un'esperienza utente più stabile e sostenibile
Domande frequenti
si. Se testate in condizioni acustiche standardizzate, le lampade certificate di riduzione del rumore dimostrano un assorbimento acustico misurabile che migliora l'acustica generale della stanza.
SGS è riconosciuto a livello globale. I suoi test confermano la sicurezza dei materiali, la conformità ambientale e l'affidabilità del prodotto, che è particolarmente importante per i progetti internazionali.
non se adeguatamente progettato. I test ottici assicurano che la luminosità, la qualità del colore e il comfort visivo rimangano costanti nonostante l'uso di materiali fonoassorbenti.
si. I test di resistenza al fuoco, sicurezza elettrica e durata sono condotti specificamente per soddisfare i requisiti di sicurezza degli spazi pubblici e commerciali.
I produttori affidabili forniscono rapporti ufficiali sui test da laboratori accreditati, che possono essere rivisti durante la valutazione del progetto o l'approvvigionamento.