現代の照明デザインでは、LED ライト ストリップは、柔軟性とエネルギー効率により、家庭、商業、プロジェクトの装飾に人気があります。 しかし、12V と 24V の 2 つの電圧仕様に直面すると、多くの消費者は混乱を招くことがよくあります。どちらがニーズに適していますか?
電圧差は、ストリップの電力と輝度の性能に影響を与えるだけでなく、伝送距離の安定性、放熱要件、および安全性にも影響を与えます。 12V LED ライト ストリップは、低電圧で最小限の電力損失で有名であるため、短距離の装飾や低電力のシナリオに最適です。 逆に、24V ストリップは電圧安定性に優れており、長距離の設置や高電力アプリケーションで優位に立っています。
このガイドでは、電圧特性や電力性能から実際のアプリケーションまで、2 つの電圧の主な違いについて説明します。これにより、理想的な照明環境を作成するための明確な選択基準が提供されます。
LED ストリップの電圧選択が重要なのはなぜですか?
LED 照明の領域では、詳細が成功または失敗を決定します。 私たちは、発光効率、演色指数、色温度に注目することがよくありますが、最も基本的なパラメータの 1 つである動作電圧を見落とす傾向があります。 12V LED ライト ストリップと 24V のどちらを選択するかは、単純な数値ゲームにはほど遠いものです。
の電圧選択 LEDストリップライト プロジェクトの信頼性とシステム コストに直接影響を与え、次の側面で明らかにします。
- 効率性: 電圧は、電力出力に直接影響します。 同じ電力定格で、24V の光ストリップは電流を引き下げ、線損失を減らし、エネルギー効率を高めます。 逆に、LED 12V ライト ストリップはより多くの電流を流すため、長距離での熱生成の増加と効率の低下につながります。
- 安定性: 24V の電圧降下が小さくなるため、均一な明るさを維持しながら、長さ 5 メートルを超える設置に最適です。 12V LED ライト ストリップは、短距離 (<3 メートル) で安定して機能しますが、端部の調光を防ぐために、長時間の実行にはセグメント化された電源が必要です。
- 安全性: 12V は安全な電圧であり、湿気の多い環境でより高い安全性を提供しますが、より高い電流ではより厚い配線が必要になる場合があります。 24V は放熱圧力が低いですが、絶縁保護に注意する必要があります。
- アプリケーション: 12V LED ライト ストリップは、家の装飾や小規模な照明に適しています。24V は、一般的に商業プロジェクトや大規模な照明アプリケーションで使用され、コストと効果のバランスをとります。
適切な電圧を選択すると、パフォーマンスが最適化され、寿命が延び、メンテナンス費用が削減されます。
12V と 24V の LED ストリップの違いは何ですか?
両方 12V LED ライト ストリップと 24V ライト ストリップ 低電圧 DC LED ストリップに該当します。 どちらも、家庭用 220V (または 110V) をストリップで必要な低電圧 DC 電源に変換する LED ドライバーを必要とします。 では、主な違いは何ですか?
回路構成の違い
下の図 1 に示すように、これは 12V LED ライト ストリップの回路図です。この図は、12V ストリップが 3 つの LED チップと 1 つの抵抗からなる「最小照明ユニット」を形成することを示しています。 このユニットは、ストリップ全体に沿って並列に繰り返されます。 それは、独立した地域がたくさんある都市のようなもので、それぞれが独自の力を生み出し、使用しています。
12V LED ライト ストリップの利点は、各 3 つの LED が、電源のプラス端子と負端子に接続された独立したユニットを形成することです。 1 つのユニットの LED が故障しても、他のユニットの照明には影響しません。 欠点は、各ユニットに抵抗が必要になることです。 抵抗が多いほど、全体的な発熱量が大きくなり、エネルギー消費量がわずかに高くなります。
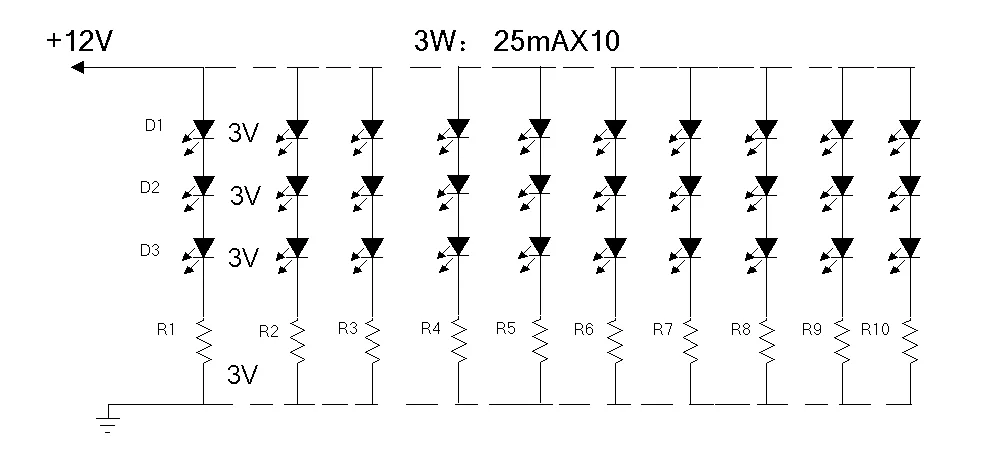
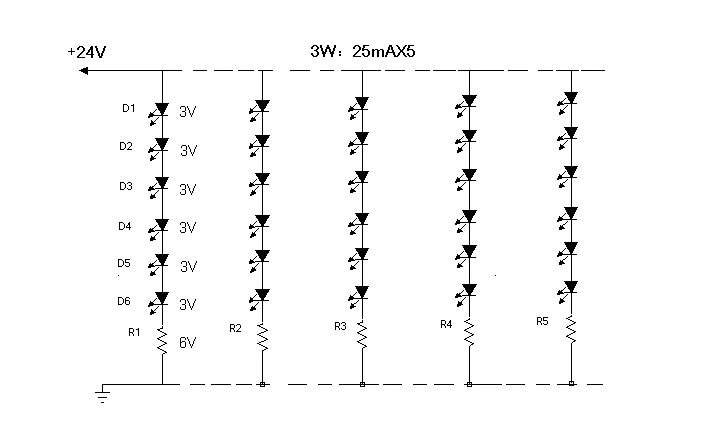
下の図 2 は、24V LED ストリップの回路図を示しています。各「最小照明ユニット」は、6 つの LED チップと 1 つの抵抗で構成されています。 このユニットは、並列に複製されます。
24V LED ライト ストリップの利点は、LED 12V ライト ストリップに比べて LED を駆動するために必要な抵抗が少ないことです。 どちらのダイアグラムも 30 個の LED を駆動します。24V ストリップは 5 つの抵抗のみを使用しますが、12V ストリップには 10 個の抵抗が必要です。 このように、24V ストリップは抵抗の使用が少なく、全体的な発熱量が少なくなり、エネルギー効率が高くなり、寿命も長くなります。
現在の強度の変化
電力計算式: 電力 (P) = 電圧 (V) × 電流 (I)。 24W LED ストリップがあるとします。
12V では、i = P / V = 24W / 12V = 2A の電流が必要です。
24V では、i = P / V = 24W / 24V = 1A の電流が必要です。
同じ出力で、24V ストリップは 12V LED ライト ストリップの半分の電流しか必要としません。 電流が小さいということは、線抵抗による発熱が少なくなり (Q=I²RT)、エネルギー損失が減少することを意味します。 これにより、24V ストリップの長距離伝送がより効率的になり、ケーブルの加熱が減り、線損失と発熱が減少し、システムの安定性が向上します。
電流は高速道路の交通の流れのようなものです。 トラフィックが少ないということは、スムーズな流れと問題の数が減ることを意味します。 24V ストリップの電流が小さいため、長距離設置中の変圧器の数とワイヤ ゲージの小型化 (電流の低さにより細線は十分) が可能になり、全体的なコストを削減できる可能性があります。
カットの長さの違い
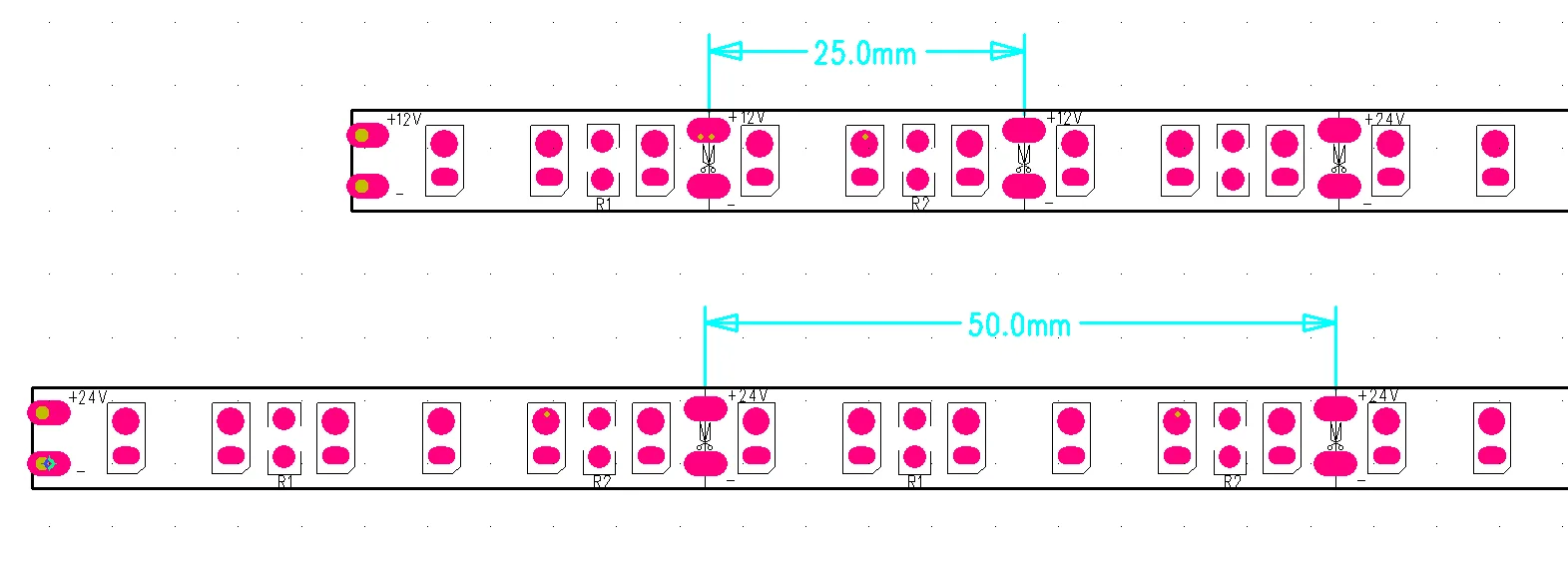
同じ数の LED で、12V LED ライト ストリップの切断点間隔は 24V ストリップの半分です。 以下に示すように、両方のストリップには 1 メートルあたり 120 個の LED が含まれています。 12V ストリップには 25mm ごとにカッティングポイントがあり、24V ストリップには 50mm ごとにカッティングポイントがあります。 これは、12V ストリップを 3 つの LED ごとにカットできるのに対し、24V ストリップは、その構造により、6 つの LED ごとにカットできるためです。 プロジェクトに多くのタイトなコーナーが必要な場合や、正確なカットが必要な場合は、12V LED ライト ストリップの柔軟性が向上します。
明るさの違い
12V LED ライト ストリップと 24V LED ストリップの間で、照明の明るさに違いはありません。 電圧は光出力を決定しません。 代わりに、LED の品質など、他の要因が明るさに影響します。
電圧降下の違い
電圧降下 低電圧 LED ストリップの最大の敵です。 電流が銅線を流れるにつれて、ワイヤ固有の抵抗により電圧損失が発生します。 これにより、電源からさらに電圧が低く、照明が減り、色の不一致が生じる可能性があります。
次の表は、SignliteLed 12V および 24V の光ストリップのランダムな電圧降下テスト データを示しています。
| 12V vs 24V 電圧降下データ テスト テーブル | ||||||||||||
| 長さ | 0m | 1m | 2m | 3m | 4m | 5m | 6m | 7m | 8m | 9m | 10m | ユニット |
| 12V LED ストリップ | 12.00 | 11.61 | 10.82 | 10.07 | 9.46 | 9.01 | 8.69 | 8.45 | 8.27 | 8.17 | 8.04 | V |
| 24V LEDストリップ | 24.00 | 23.91 | 23.42 | 22.77 | 22.02 | 21.28 | 20.59 | 19.94 | 19.38 | 18.89 | 18.46 | |
上の表に示すように、ストリップは DC12V で始まりますが、10 メートルの伝送距離を経ると 8.04V まで低下します。これは、33% の電圧減衰を表します。これは、非常に顕著な電圧降下現象です。 24V ストリップは 24V で始まり、10 メートル後に 18.46V まで低下し、23% の電圧降下が発生します。 これは、24V ストリップが LED 12V ライト ストリップよりも約 10% の電圧降下を示していることを示しています。 そうでない場合、終点で目に見える調光が発生します。

LED ストリップの最適な電圧は、特定のプロジェクト要件によって異なります。 小規模なプロジェクトや短期間の実行には、12V LED ライト ストリップが適しています。 大規模なプロジェクトや長時間の実行には、電圧降下を最小限に抑え、ストリップ全体で一貫した明るさを確保するために、24V ストリップをお勧めします。
オフィス ライト コーブ、モール 周囲照明、または長距離ディスプレイ ケースなど、10 メートルを超える連続した無断光のストリップを取り付ける必要がある場合は、24V を最適に選択します。 電源アクセス ポイントの数を減らし、配線を簡素化し、統一された視覚効果を保証します。 コンパクトなキャビネット、ワインラック、またはディスプレイ ボックスなどの小規模な装飾には、長さが 5 メートル未満の場合、電圧降下の差が大きくないため、12V LED ライト ストリップと 24V ストリップの両方が適しています。
12V LED とはどのようなシナリオですか ライト ストリップに適していますか?

12V LED ライト ストリップの「最小カット長」は、通常、わずか 3 つの LED のカットなど、短く、非常に正確で小さな半径の曲げを必要とする複雑な設計でわずかな利点を提供します。 次の照明アプリケーションに最適です。
- 自動車、RV、およびマリン ライト: これらの車両はすでに 12V 電力を供給しているため、変換は必要ありません。
- コンピュータ ケースのモッド、ミニチュア モデル ジオラマ、個々の家具のアクセント照明など、小さな複雑な DIY または装飾プロジェクト。
- 短さのキャビネット、ワインラック、または本棚の照明: 通常、長さ 5 メートル未満で、最小限の切断で素早く取り付けることができます。
- アート インスタレーションは、頻繁にカットされ、非常に複雑な形状を必要とします。LED 12V ライト ストリップは、通常、より短い「カット ユニット」 (カットごとに 3 つの LED など) を備えており、カーブが狭く、正確に曲げられる複雑なデザインに有利です。
24V LED ストリップに適したシナリオは何ですか?

24V ライト ストリップは、抵抗が低く、発熱が少なくなります。 動作温度が低いということは、LED と電子部品がより好ましい環境で機能し、光の減衰を遅くし、自然に寿命を延ばすということを意味します。 照明シナリオに最適:
- 商業空間の照明: オフィス、モール、ホテル、レストランなどの間接照明コーブなど。 長距離カバレッジ、シームレスな連続性、均一な明るさが求められます。
- 超長時間ディスプレイ ケースの照明: ジュエリー カウンター、博物館の展示、小売りのアパレル ディスプレイ。 品質を際立たせるために、商品の一貫した照明を保証します。
- 建築概要照明: 建物のファサード イルミネーションと広告看板。 24V が効果的に電圧降下に対抗し、故障点を減らす長距離および複雑な環境に適しています。
- 極端な寿命と安定性を要求するプロジェクト: 24 時間年中無休のコンビニエンス ストア、工場の組み立てラインの照明など。
- 総所有コストの削減を目指すプロジェクト: 配線を節約し、電源を削減し、設置作業を最小限に抑えることで、全体的な予算を最適化します。
なぜ 24V LED ストリップ ライトを選ぶのですか?
- ケーブル代: 24V システムの電流が小さいため、同じ伝送距離と出力で同じゲージ配線を使用できます。 これは、低電圧ケーブルの調達を大幅に節約し、取り付けを容易にすることになります。
- 電源のコスト: 24V 電源は、12V の電源よりもユニットあたりわずかに安価になる場合があります。 24V の電源が 1 つあれば、ストリップにより電力を供給できるため、必要な電源の総数が減り、全体的な電源コストが削減されます。
- 設置の複雑さ: 24V ストリップでは、長さが長いため、必要な電力接続が少なくなります。 これにより、配線が簡単になり、人件費と時間のコストを節約できます。
補足: 高電圧 AC 110/220V LED ストリップ ライト
この記事では低電圧システムに焦点を当てていますが、次の存在に注意することが重要です。 高電圧 110/220V ストリップ ライト。 特殊なカプセル化により、これらは 110/220V AC 電源に直接接続できます。
メリット: 電圧降下が最小限で、個々のストリップは最大 100 メートルに達します。 建物のファサードや大きな屋外の看板など、設置の利便性が必要な超長距離およびアプリケーションに最適です。
デメリット: 設置には専門的な電気的知識が必要で、電気ショックの危険性があり、任意にカットできず、限られた柔軟性を提供し、より目立つ LED の粒状性を示します。
LED ストリップ購入の重要な考慮事項
- 正しいドライバー電源を一致させる: の出力電圧 電源 ストリップの電圧と一致する必要があります。 12V LED ライト ストリップと 12V 電源装置、24V 電源装置を備えた 24V ライト ストリップをペアリングします。 電源容量は、ストリップの総消費電力の 1.2 ~ 1.3 倍にして、マージンを考慮に入れる必要があります。
- ケーブル断面積: 24V システムでも、長距離伝送距離に適したワイヤ ゲージ (AWG 値) を計算して選択します。細いケーブルに無差別に優先順位を付けないでください。
- コントローラと調光システムの互換性: 調光または色制御が必要な場合は、コントローラー (DMX512 デコーダ、トライアック調光器、0-10V コントローラーなど) が選択したライト ストリップの電圧をサポートしていることを確認してください。
- プロフェッショナ: 評判の良いサプライヤーは、単に価格を引用するのではなく、プロジェクトの詳細について積極的に問い合わせ、電圧の推奨事項を含む包括的なソリューションを提供する必要があります。
結論
LED 照明の詳細な領域では、知識は力と利益の両方です。 大多数のプロジェクトでは、 24V LED ライト ストリップ より安定したパフォーマンス、長寿命、全体的なコストの削減、および優れた光出力につながります。 これは徐々に業界の標準であり、コンセンサスになっています。
この包括的なガイドが、強力な意思決定ツールとして役立つことを願っています。 プロジェクトの図面や照明に関する要件がある場合は、技術専門家チームにご連絡ください。 電圧選択や製品マッチングからソリューション実装まで、エンドツーエンドのサポートを提供し、すべてのプロジェクトが見事に輝けるようにします。