LED灯具广泛应用于商业空间、智能家居、零售展示和建筑照明项目等现代照明系统。 然而,仅仅“打开”LED灯条不再足够。 实现精确流畅的调光功能是满足各个行业的多样化照明控制要求的关键。
对于许多项目经理来说,“如何调暗 LED 灯带灯?”不是一个简单的问题。 原因在于LED灯带类型(如单色、RGB和RGBW)、不同电压规格(12V和24V)以及多种控制方法(PWM、TRIAC、0-10V、DALI和DMX),使得LED灯带调光器兼容性成为项目实施中的重大挑战。
更复杂的是,市场上有多种调光技术,例如通过 PWM 脉冲宽度调制或使用连接到传统壁挂式旋钮的 TRIAC 前端调光器实现的数字调光。 不同的技术不仅在控制效果上有很大的不同,而且影响布线方法、控制器选择,甚至影响灯带的使用寿命。 这引发了工程师和DIY爱好者的广泛搜索和讨论:“PWM与三角星光LED灯条调光——哪种解决方案更好?”
本文将借鉴SignliteLED在LED行业多年的经验和技术见解,全面解决LED灯带灯带灯光调光的核心问题,包括原理分析、调光方法、系统选择、布线指导、常见的误解和场景建议,帮助您选择最适合您的项目的调光解决方案。
LED灯条调光:基础知识
调光是指降低LED灯带亮度的过程。 调光可以降低LED灯条的光输出,让您控制灯光的亮度。 对于传统的白炽灯泡,调光很简单——只需降低电压,灯就会变暗。
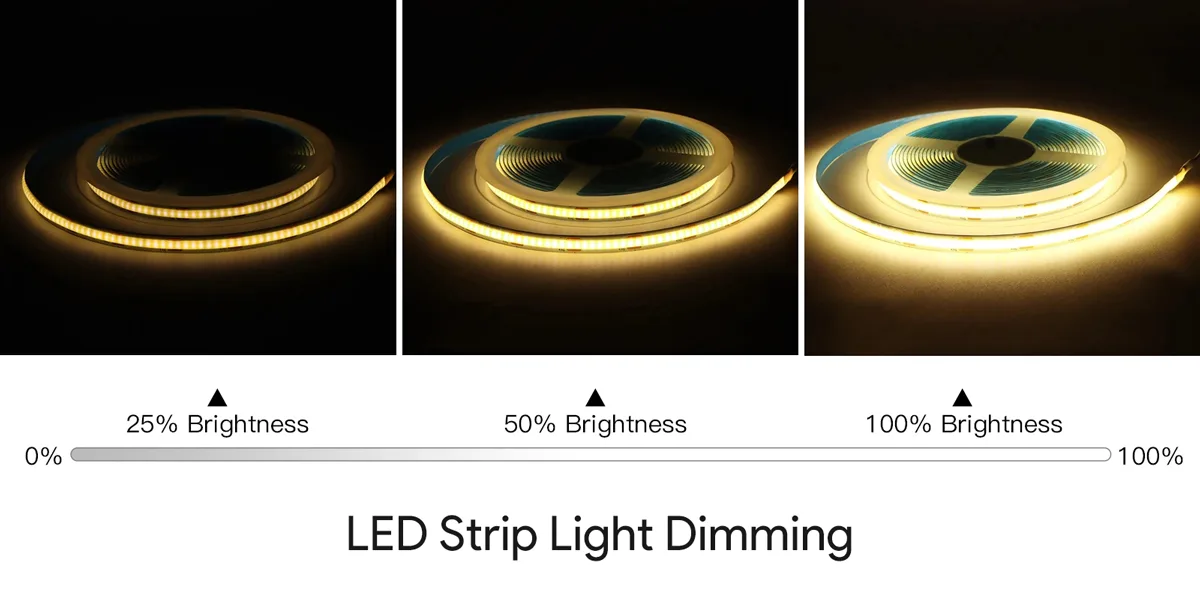
然而,LED灯条照明更复杂。 LED是需要特定电流才能有效运行的半导体器件。 因此,LED调光涉及控制提供给光源的功率,同时保持效率和性能。
在LED灯带照明系统中,调光不仅可以灵活控制亮度,还可以直接影响整体功耗和能源效率。 对于优先节能和氛围的商业空间、展示区或智能家居项目,选择适当的调光方法至关重要。
LED灯条灯光调光通常是通过脉冲宽度调制(PWM)实现的,该技术可有效控制亮度,同时保持色彩质量。 PWM调光或其他调光方法不仅延长了灯条的使用寿命并减少了能量消耗,还防止了过大的照明。 将亮度设置为 50% 将平均功耗降低到原始值的大约一半。 例如,5米24V灯带全亮度消耗60W,调光至50%亮度后,平均功耗约为30W。
此外,长时间的LED灯条操作可能会导致电压下降,影响调光的一致性。 因此,使用适当的电源和调光器至关重要。 许多 LED 灯条提供远程控制或智能家居系统集成,提供适合于内阁照明或重点照明应用的便捷无线调光选项。
能 All LED 秒绊倒 L权利是 D立即?
是的,几乎 所有LED灯条 是可调光的。 只要有合适的直流信号(通常是PWM),任何LED灯条的亮度都可以自由调节。
但是,LED 灯条的设计不直接连接到电源电压(例如,120V/220V 交流墙壁插座)。 它们需要电源将较高的 AC 电压转换为较低的 12V 或 24V 直流电压。 因此,如果使用壁式调光器,则必须先将其连接到 LED 灯条的电源,然后才能使 LED 灯条变暗。
因此,可调光/非调光的问题取决于电源以及它是否可以解释墙壁调光器发送的调光信号。
LED灯条常用调光方法分析
随着LED灯带灯在商业照明、智能家居和装饰中的广泛应用,调光方法的选择和兼容性变得越来越重要。 不同的调光技术不仅影响照明效率和用户体验,还直接决定系统的稳定性。
下面,我们将系统回顾五种最流行的LED灯条调光方法,分析它们各自的优缺点、适用的应用和布线特性。
PWM调光 — 精确且广泛兼容
PWM(脉冲宽度调制),也称为恒压调光,通过快速打开和关闭灯以控制传递到灯的平均功率的工作。 通过调整每个周期内“开”和“关”时间的比率,可以调节整体亮度,而无需改变输入电压。 即使在较低的亮度水平下,这种方法也能确保一致的色温和无闪烁的性能。
PWM调光可以分为两种主要类型:
- 模拟 PWM:该方法使用模拟信号(通常为 0 至 10V)来调整占空比。 每周期内的“开启”时间越长,光输出越亮。 也可以使用 TRIAC 调光器和我们的许多恒压电源来控制此方法。
- 数字化 PWM:占空比由数字信号控制,提供高精度调光控制。 这种类型的 PWM 通常与智能系统或可编程控制器集成,以实现高级调光应用。
优势
- 高控制精度,支持0–100%亮度调节
- 最小色温偏差
- 与各种LED控制器(例如,遥控器、蓝牙、WiFi等)的广泛兼容性
缺点
- 需要高频 PWM 控制器;否则,在低亮度级别可能会出现可见闪烁
- 不适合传统壁挂式调光开关
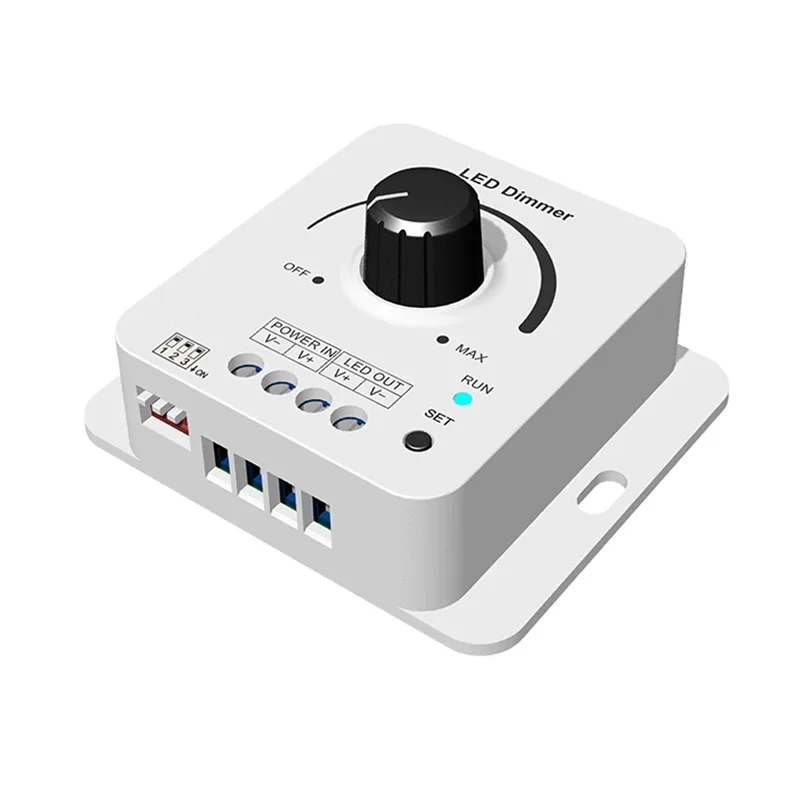

LED灯带灯PWM调光控制器
型号 一、KC
输入电压: 12-48VDC
输入电流: 8.5A
输出电压 12-48VDC
输出电流: 8A@12-24V,6A@36-48V
输出功率 96W@12V, 192W@24V, 216W@36V, 288W@48V
灰度调光: 256级
调光范围: 0-100%
脉宽频率: 500Hz、2kHz、8kHz、16kHz
认证: CE、EMC
尺寸 L66 x W59 x H32mm
IP 等级: IP20
保修单: 5 年
双向可控硅调光 — 住宅壁挂式调光的首选
TRIAC(交流电用于交流电)调光器通过改变电压波形来减少对连接设备的电源的工作。 降低输入功率会导致电源输出减少或照明灯具的流明输出减少。
三重奏调光器有两种类型:
- MLV(磁性低压)调光:也称为前沿调光或前向调光,这种方法通过切断交流波形的前沿来调光。 该操作减少了传递给负载的功率,从而实现了调光。
- ELV(电子低压):ELV调光器,也称为后沿调光或反相调光,通过切断交流波形的后缘来控制功率。 这种调光方法通常提供更平稳的性能、更少的闪烁和更安静的操作,使其特别适用于电子低压照明系统。
优势
- 与常见的壁挂式调光器(例如,Lutron、Leviton)兼容
- 用户友好,适合住宅用户
- 安装简单,配线方法与标准照明灯具一致
缺点
- 对电源驱动器的高要求,需要使用“可调光”恒压电源
- 可能会在低亮度水平下表现出闪烁或噪音
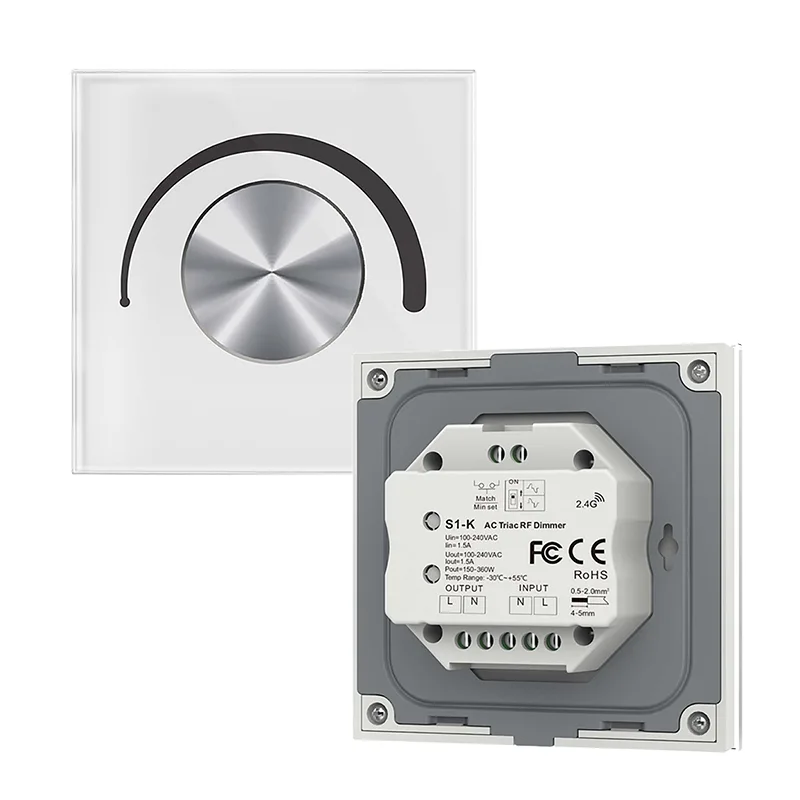

LED灯带灯三端调光控制器
型号 斯科斯克
输入电压: 交流 100-240 伏
输出电压 交流 100-240 伏
输出电流: 最大 1.5A
输出功率 150-360W
灰度调光: 256级
调光范围: 0-100%
认证: CE, FCC
尺寸 L86 x W86 x H48mm
IP 等级: IP20
保修单: 5 年
0-10V/1-10V 调光 — 工业和商业照明的标准解决方案
0-10V/1-10V 调光是一种标准化的模拟调光协议,通过调节控制信号的电压电平来调节连接的照明灯具的亮度。 随着控制电压的变化,灯具通过增加或减少其光输出来做出响应。 这种方法因其简单性和可靠性而被广泛使用,可在各种亮度级别上提供平滑、无闪烁的调光。
优势
- 高稳定性和良好的调光线性度
- 支持大规模同步控制,适合大型项目
- 与 DALI 控制系统良好的兼容性
缺点
- 需要单独安装控制线
- 控制器成本略高,调光响应较慢
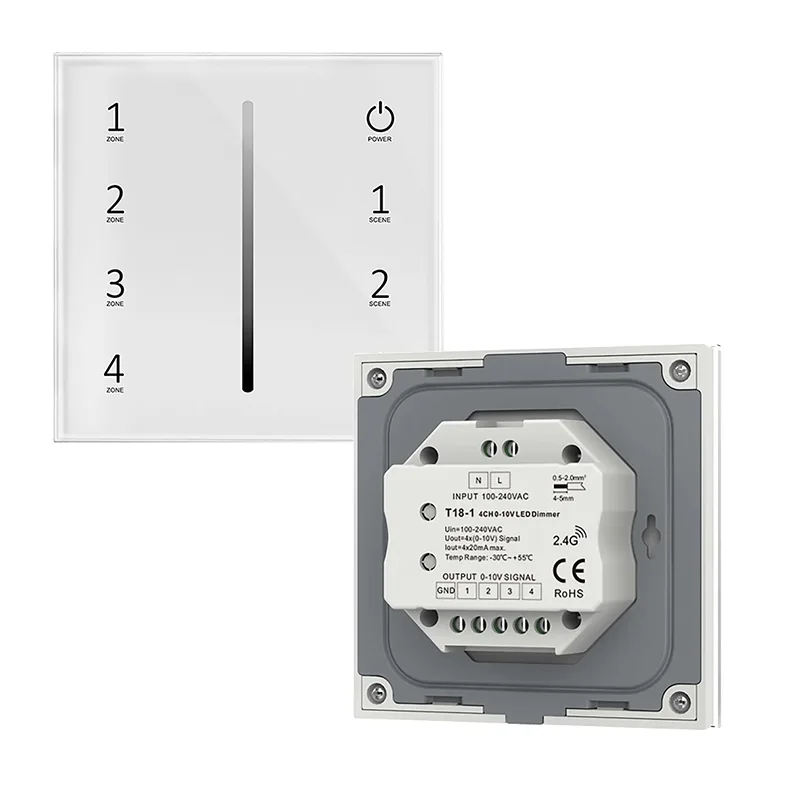

LED灯条 0-10V调光控制器
型号 18-1
输入电压: 交流 100-240 伏
输入信号 触摸键 + 2.4GHz
输出信号: 0-10V (20mA)
输出电流: 20mA/CH
灰度调光: 256级
调光范围: 0-100%
认证: CE,EMC,LVD,红色
尺寸 L86 x W86 x H33mm
IP 等级: IP20
保修单: 5 年
达利·迪明——智能建筑系统的支柱
DALI(数字可寻址照明接口)调光协议最初是作为 0-10V 系统的继承者而开发的,是一种基于数字信号通信的专业照明控制协议。 通过总线连接,可以对每个组或单个灯具进行处理和精细调光。
DALI LED 控制系统最适合大规模安装。 例如,控制系统通过中央大理调光开关管理整个建筑物的可调光 LED 灯的项目。 这不仅允许用户手动打开/关闭灯光和控制亮度,还可以在预设时间激活和运行照明程序。
优势
- 每盏灯都可以独立编程和控制。
- 远程监控和智能集成
- 全数字化,具有出色的稳定性和可扩展性
缺点
- 高成本,需要专用的 DALI 控制器和接口模块
- 复杂的安装调试,适合专业系统集成商
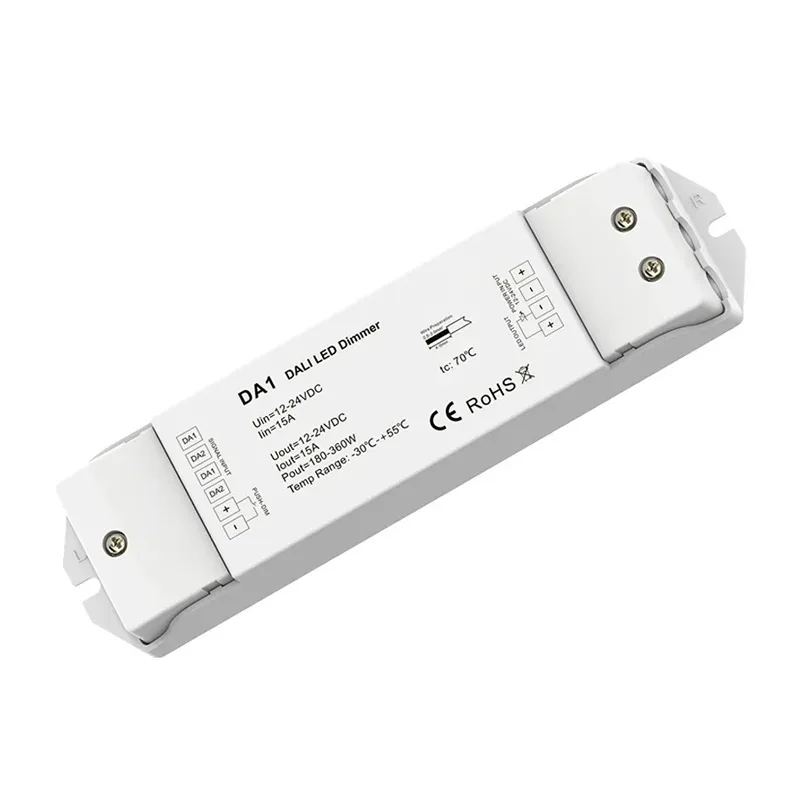

LED灯条大理调光控制器
型号 DA1
输入电压: 12-48VDC
输入电流: 最大 15A
输出电压 12-48VDC
输出电流: 15a@12/24v,10a@36/48v
输出功率 180W@12V,360W@24V,360W@36V,480W@48V
调光范围: 0-100%
认证: CE、EMC、LVD、DALI-2
尺寸 L175 x W45 x H27mm
IP 等级: IP20
保修单: 5 年
DMX 调光 — 动态照明的专用解决方案
DMX(数字复用)控制是一种非常古老的协议,最初设计用于连接不兼容的调光系统。 常用于音乐会灯光、剧院灯光、工作室照明、各种规模的建筑照明和动态照明项目,需要复杂的照明效果。
DMX LED 控制器最多可管理 512 个通道(协议的全名是“DMX 512”)。 DMX LED 条带接收机的每个通道均通过设备侧面的 DIP 开关设置,使用 9 个二进制开关。 使用这些开关,您可以将每个通道设置为最大 512。
优势
- 控制多个通道(颜色、亮度、频闪)
- 支持编程的灯光显示和动态场景转换
- 可扩展到数百种照明设备
缺点
- 需要专用的控制器和接线系统
- 陡峭的学习曲线
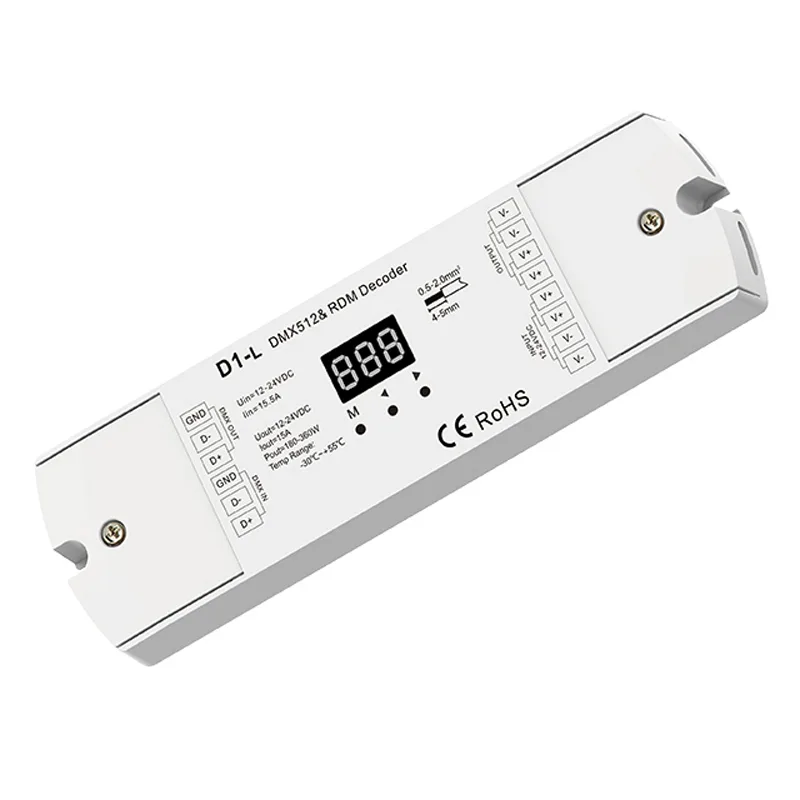

LED灯带灯DMX调光解码器
型号 1-L
输入电压: 12-24VDC
输入电流: 15.5A
输出电压 12-24VDC
输出电流: 1 通道、15A
输出功率 180-360W
认证: CE, RoHS
尺寸 L170 x W50 x H23mm
IP 等级: IP20
保修单: 5 年
还有各种用于调光LED灯带灯的方法,例如RF(射频)调光、Wi-Fi调光和在线LED调光器调光等。 每种方法都有其优点,没有“最佳”控制可调光LED灯带的方法。 最适合您的选择取决于您正在安装的项目类型。
摘 T他 M机顶盒 秒优越 D铭 M信仰
| 调光法 | 水电量 | 三亚洲 | 0-10V | 达利 | DMX |
| 机宜 | 控制 LED 开关频率 | 通过交流侧调光器控制 | 通过电压信号控制 | 数字信号协议 | 舞台/建筑物照明控制协议 |
| 优势 | 精确,无色移 | 可使用壁挂式旋钮 | 商标 | 高度集成 | 多通道可控,精确 |
| 缺点 | 对控制器的高要求 | 需要兼容电源 | 复杂的布线 | 成本高,需要专业布线 | 高度专业化 |
| 调光精度 | 高 | 中型 | 高 | 泂 | 极高 |
| 安装难度 | 低 | 低 | 中型 | 高 | 高 |
| 费用 | 低 | 中型 | 中高 | 高 | 高 |
| 适合的场景 | 低压LED灯条,RGB LED灯条 | 住宅/商业照明应用 | 工业/商业环境 | 智能建筑系统 | 户外照明、景观工程 |
在实际应用中,建议先确认灯条电压、电源驱动方式和预期控制方法,然后匹配适当的调光协议和控制器。 这不仅保证了系统的稳定运行,而且大大改善了照明环境的体验,降低了售后服务和返工的风险。
LED灯条调光系统组成和选择建议
为了实现高效、稳定、无闪烁的LED灯条调光系统,它并不像仅仅选择一个“好的调光器”那么简单。 它需要系统集成多个因素,包括电源驱动器、电压匹配、控制协议、灯条规格和应用场景。
什么组件构成了一个完整的LED灯条调光系统? 应该如何选择最合适的解决方案? 让我们一步一步地分解它。
LED灯带灯光调光系统的基本组件

无论是住宅RGB LED灯条还是商用大功率线性灯条,典型的调光系统通常都包含以下核心组件:
| 舱 | 功能 | 札记 |
| LED 灯条 | 发光元件 | 必须确认为“可调光”灯带灯,如非恒流驱动类型、支持 PWM 调光等。 |
| 发光二极管 电源/发光二极管 变压器 | 提供稳定的电压和电流 | 调光方法必须与调光器兼容,如支持 TRIAC/0-10V/PWM 等。 |
| 发光二极管 淡光 | 控制亮度变化 | 用作系统的“控制中心”,需要精确匹配输入信号、电压和灯条类型 |
| 控制信号模块(可选) | 比如遥控器、墙壁开关、APP控制器等。 | 涉及用户界面交互;智能控制需要可选的兼容协议模块 |
| 附件组件(可选) | 包括LED分流器、LED放大器、铝通道等。 | 取决于安装的复杂性和要求 |
例如,如果您计划使用 PWM 调光,系统必须包括一个与 PWM 兼容的 LED 控制器和一个不可调光的 LED 电源;如果您打算使用 TRIAC 墙壁调光器,您必须选择一个 恒压LED电源 具有 TRIAC 调光功能。
如何选择最合适的LED调光器?
选择调光器时,最常见的问题是“购买的调光器无法控制灯光”——这通常是由于 LED 灯条调光器的兼容性问题,因为并非所有调光器都与 LED 灯条兼容。 因此,在选择调光器时,请考虑以下几点:
1。 确保与调光方法的兼容性
- 12V/24V 单色 LED 灯条:推荐的调光方法包括 PWM/TRIAC 调光、恒压 PWM 调光器或壁挂式旋钮调光器。
- RGB/RGBW LED灯条:推荐的调光方法是 PWM 调光,带有 RGB 控制器(带遥控器或 APP)。
- 大功率工程灯带:推荐的 0-10V/DALI 调光,商用 0-10V 面板/DALI 中央控制器
- 最重要的因素不是选择昂贵的调光器,而是选择与您的电源和灯条兼容的一种。
2. 检查电压和功率容量
- 调光器必须支持灯条使用的电压,如 DC12V、DC24V 或 DC48V。
- 总功率不得超过调光器的额定容量;建议使用 20% 的余量。
- 对于大功率灯带,使用恒流电源+放大器进行辅助调光。
3。 调光控制方法
- 墙壁开关控制:适用于 0-10V、PWM 或 TRIAC 调光
- 远程控制/应用控制:建议使用支持RF或WiFi协议的智能PWM调光器
- 场景预设和远程调整:可选的 DALI 或 DMX 协议
总之,最适合您项目的调光方法取决于两个主要因素:
你的项目有多大?
如果您的项目很小并且仅使用一种 LED 电源,则无需能够管理多个区域(例如 DALI 或 DMX LED 灯带控制器)的可调光 LED 调光器控制器。 您可以使用简单的电源供电调光电源或内联 LED 调光器或射频 LED 调光器。
但是,对于大型项目(例如数十个可调光LED灯条,每个灯条,每个灯带),您将需要更灵活的LED调光器,例如0-10V、DALI或DMX 512系统。
您想要什么类型的调光器界面?
选择如何管理可调光LED灯条时,类型 LED调光器控制单元 你喜欢是至关重要的。 例如,如果您想要一个时尚的无线触摸屏调光器,您可以立即排除所有有线 LED 调光器。
如何将调光器连接到 LED 灯条
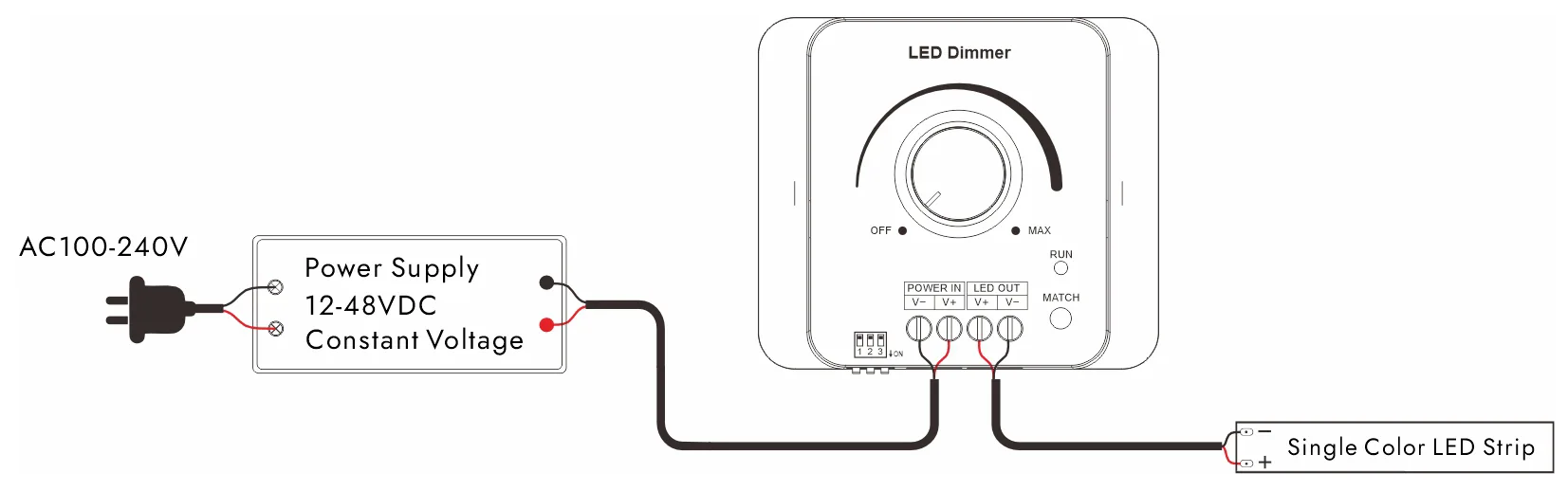
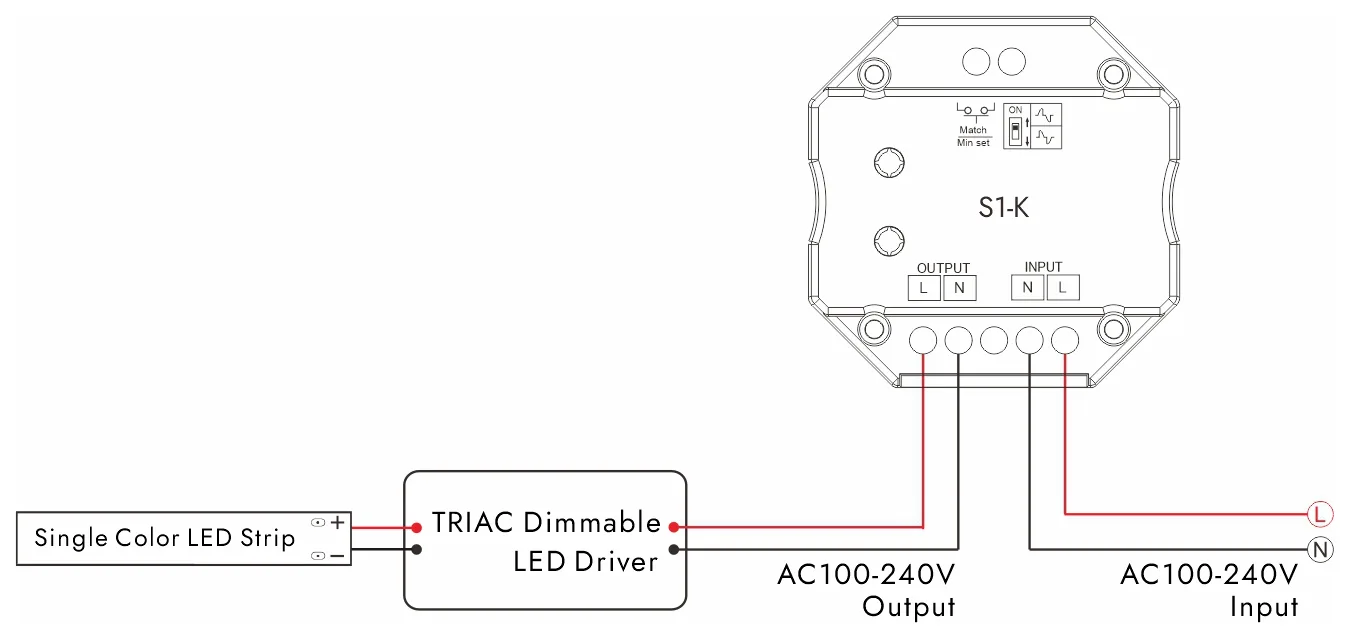
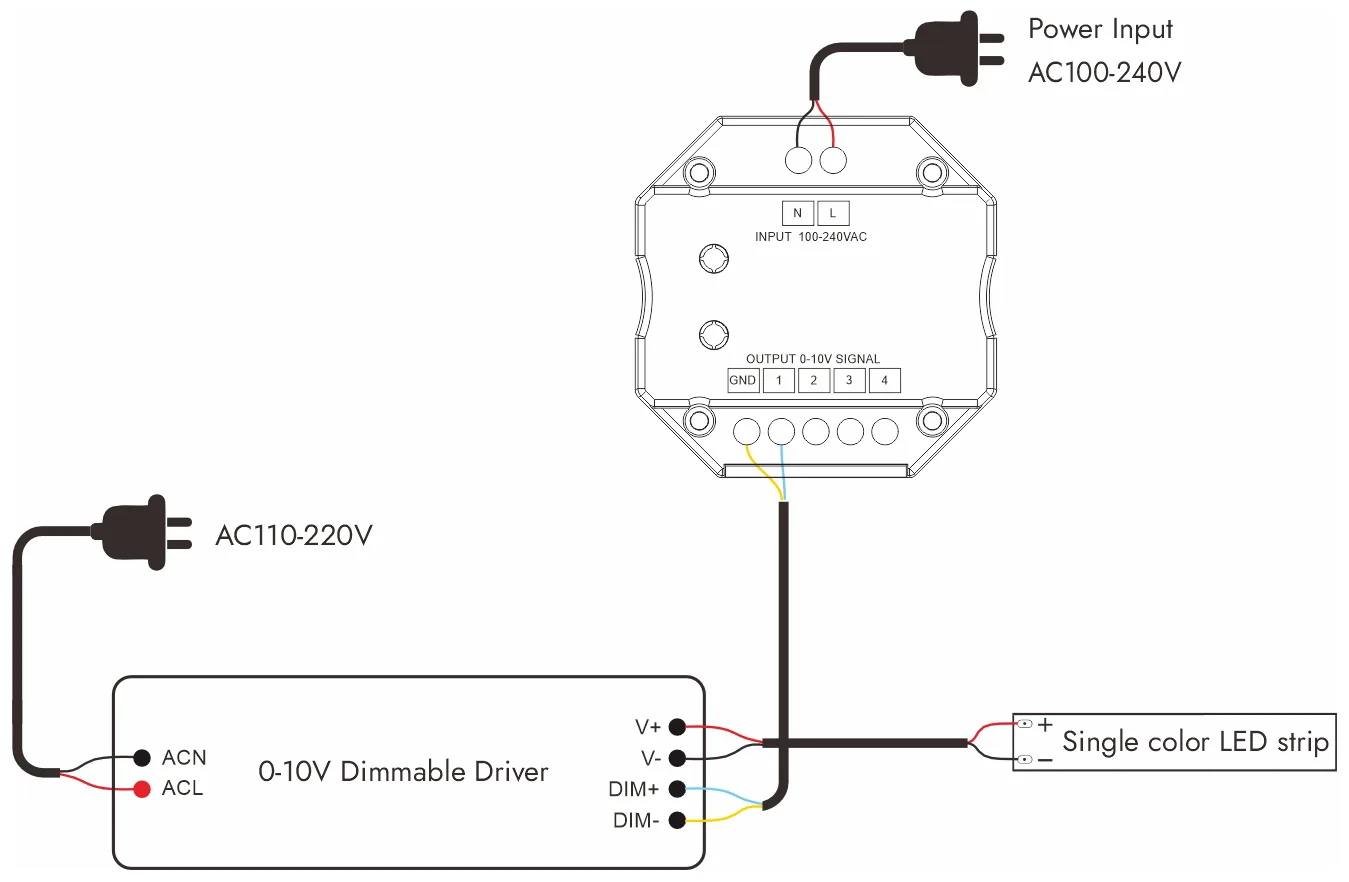
LED灯带调光系统的连接方法取决于调光器的类型。 下面是几个常见的连接图。
PWM调光连接图:
三端双向调光连接图:
0-10V调光连接图:
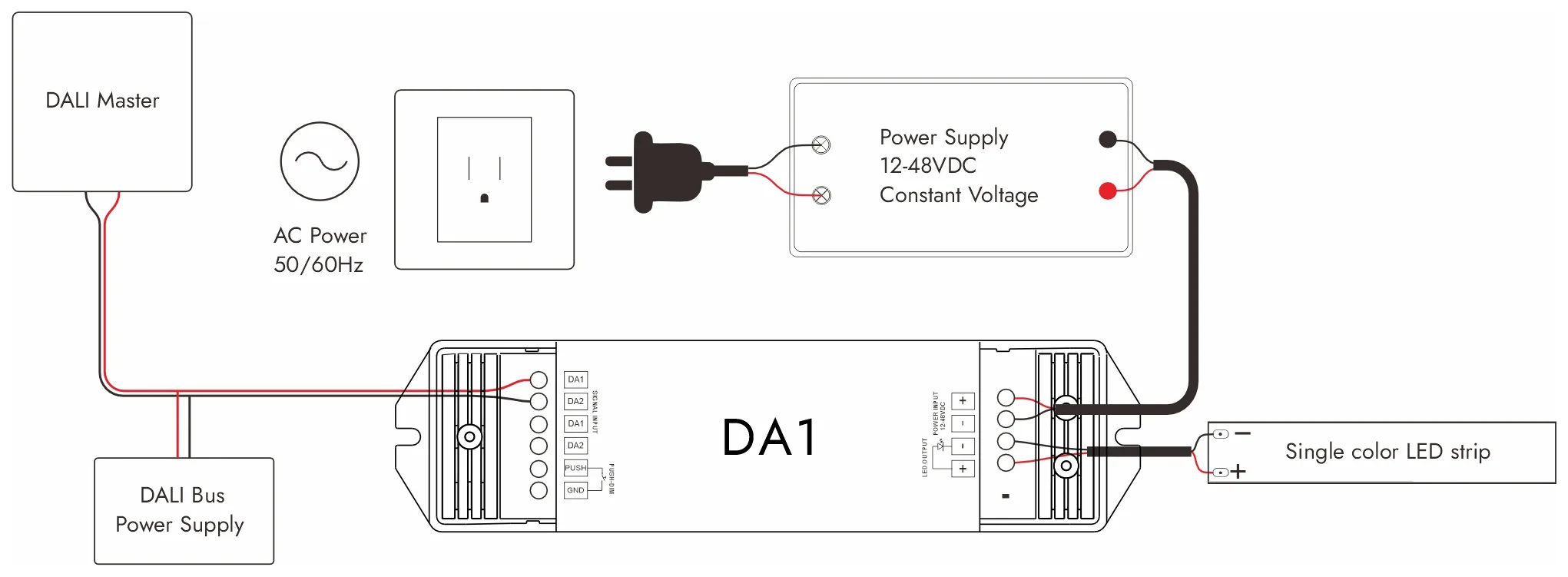
大理调光连接图:
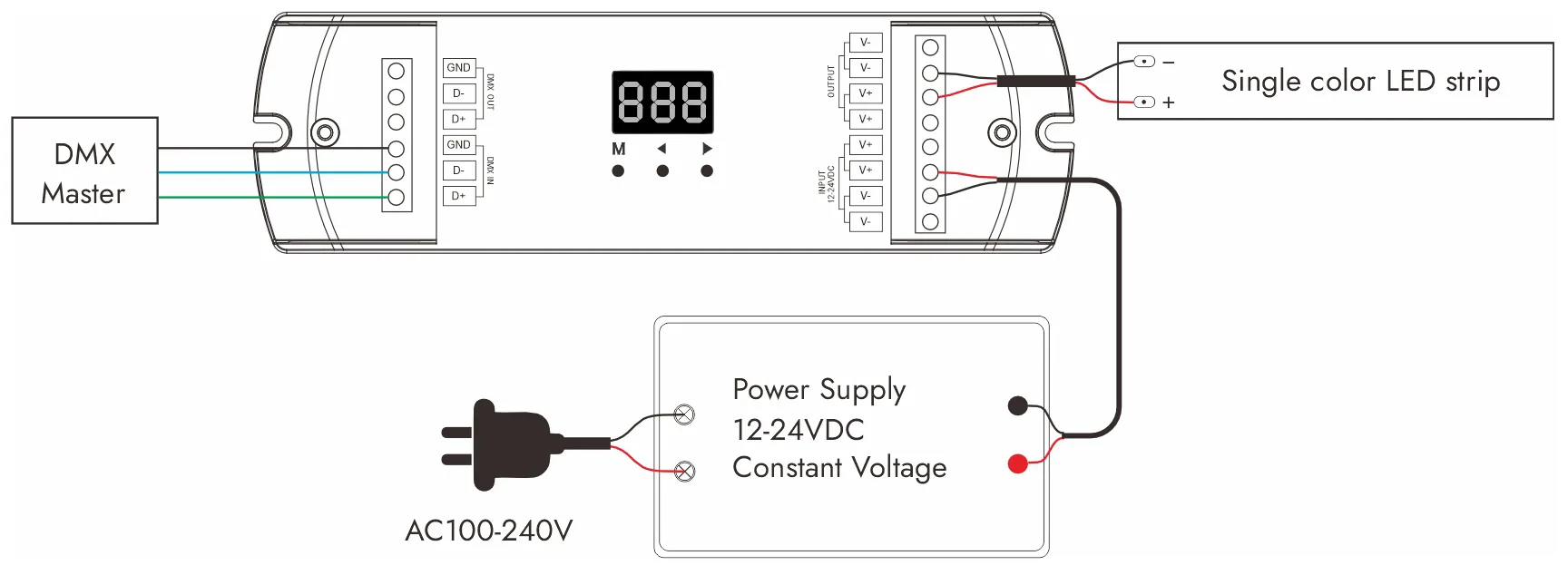
DMX调光连接图:
LED灯条调光的常见问题和解决方案
即使在使用适当的LED调光器和LED灯条组合时,在实际安装和使用过程中也可能出现各种意外问题,例如光闪烁、异常亮度、有限的调光范围或控制故障。 这些问题不仅影响照明性能,还可能导致客户误解或退货/交换。
有关更多 LED 灯带灯问题和解决方案,请阅读博客“LED 灯条常见故障及解决指南“.
问题一:LED灯条调光时出现严重闪烁
问题表现:
- 调光至低亮度时频繁闪烁
- 在智能手机相机下,闪烁可能特别明显。
- 长时间使用后偶尔闪烁
原因分析:
- 使用低频 PWM 控制器(频率低于 1 kHz)
- 不稳定的电源输出或与调光器不兼容
- LED 灯条电流负载接近或超过电源的额定功率
- 驱动程序不支持调光功能,但连接到调光器不正确。
解决方案:
- 更换高频 PWM 控制器(推荐在 1 kHz 以上)
- 验证电源是否是“调光兼容”的恒压驱动器。
- 确保至少 20% 功率裕度以防止过载
- 确认电源和控制器调光协议之间的兼容性
问题 2:LED 灯条不能调暗或响应缓慢
问题表现:
- 墙壁调光器不工作
- 智能手机应用调光器滑块没有响应
- 调光范围不完整,仅达到一半亮度
原因分析:
- 控制器电压、电流或信号类型不兼容
- 使用非可调光电源(或默认的常亮度输出)。
- 壁式调光器不支持电流负载类型(例如,LED 调光需要 ELV 或 TRIAC 兼容调光器)。
解决方案:
- 验证电源、灯条和控制器是否兼容。
- 更换支持 TRIAC 或 0-10V 的恒压电源
- 如果使用应用程序,请检查 WiFi 或蓝牙信号强度和应用版本。
问题 3:变暗后色温或颜色变化
问题表现:
- RGB 灯条在调光后显示不一致的颜色。
- 单色灯带在调光期间表现出向较冷或较暖色调的色温变化。
- 多个灯条显示不一致的颜色变化
原因分析:
- 不同的光带通道在调整期间没有精确同步。
- 正在使用与 RGB 灯条不兼容的单通道控制器。
- 控制器的调光算法不支持色温或 RGB 映射。
解决方案:
- RGB 灯条必须配备 RGB 专用 PWM 控制器。
- 调光必须通过三通道或更高的控制器(例如,DMX)实现,以进行精确匹配。
- 使用支持色温记忆/校正的高端控制器,例如 DALI 或高级 PWM 解决方案。
打 4:调光期间出现嗡嗡声或电气噪声
问题表现:
- 低频嗡嗡声在调光灯带后发生。
- 调光器或电源附近会发出轻微的电气噪声。
- 噪声在特定的亮度范围内更为明显。
原因分析:
- 使用非专门为 LED 设计的过时调光器(例如,用于白炽灯泡的 TRIAC 调光器)
- 调光器和 LED 电源之间的兼容性问题
- 低调光频率或不稳定负载导致驱动器内部线圈共振
- 在 PWM 调光中,调光器和 LED 电源之间的频率冲突导致电磁干扰。
解决方案:
- 更换专为 LED 设计的调光器
- 检查调光器和电源的负载范围,以确保电源负载在推荐的工作范围内。
- 优先考虑高频 PWM 控制器(≥1.5 kHz),以避免可听频率范围内的振荡。
- 如果使用 TRIAC 控制系统,请确保 TRIAC 可调电源与 LED 兼容,以避免兼容性问题。
问题 5:调光器无法照亮灯带/灯带的最小亮度太高
问题表现:
- 当调光器设置为最小值时,灯带根本不亮。
- 灯带无法启动,只能在高亮度范围内正常运行。
- 将调光器设置为最小值后,灯条不能重新启动(死区)。
原因分析:
- LED灯条的启动电压超过调光器的输出下限,防止其点亮。
- 控制器/驱动器的最小亮度控制不精确或不可调节。
- 调光器不支持平滑启动,导致死区或突然亮度变化。
- LED芯片具有相对较高的电压驱动阈值。
解决方案:
- 将 LED 电源更换为低启动电压和宽电压输出范围的 LED 电源。
- 使用支持调光启动电压校准的控制器,例如带有“最小电平调整”调节功能的 PWM 调光器。
- 避免使用廉价的调光器;选择具有精确亮度控制的品牌产品。
- 考虑系统设计期间的 LED 驱动器电压范围,以避免在低亮度水平下出现功能问题。
问题 6:多个灯条之间的不一致调光/同步故障
问题表现:
- 连接到同一控制器的灯带会出现异步亮度变化。
- 由不同电源供电的灯带会出现延迟或突然的调光响应。
- 在调光期间,一些灯条变亮,而另一些灯条保持关闭或闪烁。
原因分析:
- 多个灯条之间的信号路径不一致或布线长度不均
- 不同品牌或批次的灯条之间的电气参数存在显着差异,影响调光响应
- 控制器输出负载超过上限,导致通道输出电压不平衡。
- 无同步放大器用于信号重新对齐
解决方案:
- 尽可能使用同一品牌和批次的灯条和控制器。
- 分支调光信号输出时添加信号放大器或同步模块,以确保一致性
- 对于长距离控制,使用 DMX 或 DALI 协议实现精确的分段控制。
- 确保控制器的总输出功率至少比所有灯条的总功率大 20%。
结论
随着LED照明技术的不断成熟和智能家居系统的快速发展,LED灯带灯光调光不再仅仅是调整亮度,而是将美学、智能控制和能源管理结合起来的集成系统。
本文对LED条形灯光调光、覆盖调光方法、系统组成、产品选择和常见问题的解决方案进行了全面分析。 它不仅旨在回答“如何调暗LED灯带灯?”的问题。 同时也帮助您为您的项目选择最合适的LED灯条调光解决方案:
- 确定 LED 灯条的电压、电流、调光要求和应用场景。
- 根据LED灯条的调光方法选择电源+控制器+控制信号模块。
- 确保三个组件在协议、电压和负载方面的完全兼容性。
- 避免使用非调光电源与调光控制器结合使用。
- 最好使用高频 PWM 调光器或智能调光器来最大限度地减少闪烁问题。
最后提醒:调光≠兼容性;事先测试是关键。
许多用户发现之后 采购LED灯条 两者不兼容的调光器,导致资源浪费和不必要的安装返工。 因此,我们建议将调光要求纳入灯条的初始选择中,即在选择灯光之前明确调光方法和控制系统要求。
有了正确的知识,调光不再是一项艰巨的任务。 如果您正在寻求 LED 灯条调光解决方案——无论是改造现有灯具还是设计新的照明方案——咨询专业人员并做出最明智的决定至关重要。 SignliteLED 团队可以根据您的特定空间需求提供定制解决方案,确保您选择最符合您要求的照明。






