電子機器製造業界では、「PCB」と「PCBA」がほぼ毎日言及されています。 ただし、これら 2 つの概念は、電子機器のバックグラウンドを持たないハードウェアの新興企業や調達チームの間でさえ、混乱を招くことがよくあります。
単に同義語であると考える人もいれば、PCBA が単に「PCB のアップグレード版」であると誤って想定している人もいます。また、見積依頼時にどのサービスが必要かについて、調達担当者が本当に必要としないと考えている人もいます。
実際には、PCB と PCBA の区別は定義を超えており、製品のコスト、配送サイクル、品質リスク、サプライ チェーンの複雑さに直接影響を与えます。 特に、エレクトロニクスが非常にインテリジェントであり、AI テクノロジが製造プロセスに深く統合されている 2026 年の状況では、PCB と PCBA の違いを正しく理解することが、企業がリスクを軽減し、効率を高めるために重要になっています。
この記事では、PCB と PCBA のコアの違いを、技術的な定義、製造プロセス、コスト構造、業界動向、調達の決定など、さまざまな側面から体系的に分析し、エンジニアや調達担当者がプロジェクトの初期段階でより多くの情報に基づいた選択を行えるようにします。
PCBとは何ですか? (プリント基板)
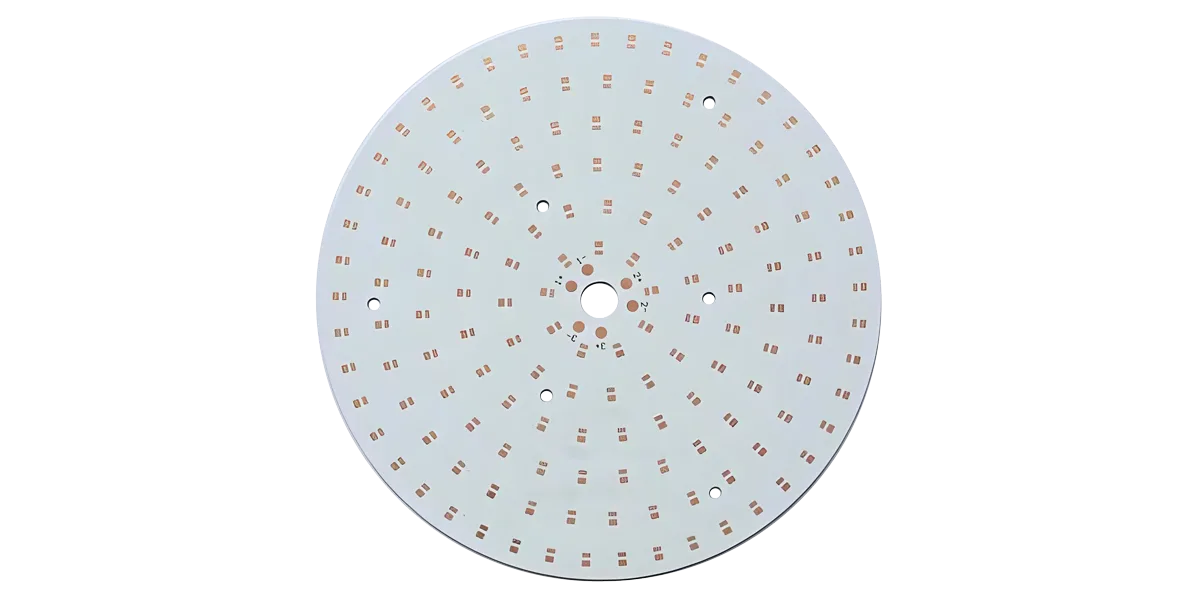

PCB (プリント回路基板) は、電子部品の基本的なキャリアとして機能し、銅箔のトレース、パッド、およびビアを介した電気接続を可能にします。 PCB は、電子部品が取り付けられていない「ベア ボード」のみを指します。 ただし、それは電子製品の物理的基礎を形成し、回路の基板を提供し、電気接続を容易にします。
PCB は、フレキシブル LED ストリップであろうと高電力 LED モジュールであろうと、すべての LED 照明システムの出発点として機能します。
LED PCB の構造部品
通常、LED PCB には次のものが含まれます。
1. ベース材
- FR-4: 低から中程度の電力 LED に適しています
- 金属コア PCB (MCPCB): アルミニウムまたは銅ベースで、高電力の LED ストリップおよびモジュールで広く使用され、優れた熱性能を実現します。
- 高周波材料: スマート照明および IoT LED システムで使用
2です .銅層
銅の厚さ (1 オンス~6 オンス) は直接影響を与えます。
- 現在の収容能力
- 電圧降下制御
- LED ストリップの熱管理性能
3. はんだマスク
短絡や酸化を防ぎます。 LED 業界では、優れた反射特性のために、白はんだマスクが広く採用されています。
4.シルクスクリーン
マーキングは、LED 極性、向き、および部品番号を示し、大量生産とメンテナンスを容易にします。
LED業界で一般的なPCBタイプ
LED 業界における PCB の種類とアプリケーションは、主に次のとおりです。
| タイプ | 素材 | アプリケーション・シナリオ |
| LED フレキシブル ストリップ PCB | フレキシブルプリント回路 (FPC) | ライトスロット、キャビネット、不規則な設置環境 |
| LEDモジュールPCB | FR-4 グラスファイバー基板 / アルミ製ベースボード | 直線ライト、天井灯 (低電力用 FR-4、高出力用アルミニウム) |
| LED 剛性ストリップ PCB | アルミニウム製ベース PCB / 厚い銅製の FR-4 基板 | 線形照明、産業用照明 |
| LED カスタム PCB ボード | LED カスタム PCB ボード | ハイエンド/プロフェッショナル照明 |
PCBAとは何ですか? (プリント基板アセンブリ)
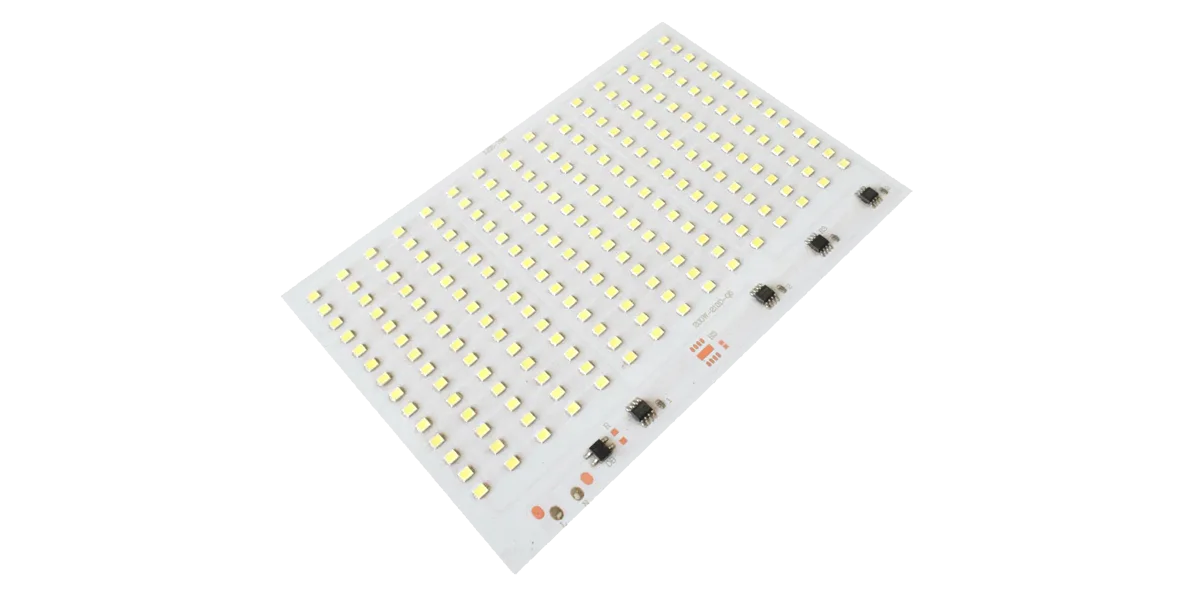

PCBA (プリント基板アセンブリ) SMT または THT プロセスを使用して、抵抗、コンデンサ、IC、LED、およびコネクタなどの電子部品を PCB に半田付けして製造された完成した回路基板を指します。 完全な電気的および機能的特性を備えています。 電子部品を半田付け、組み立て、PCB でテストした後の完成した回路システムです。
PCBA は、PCB を「真に機能させる」ための重要なステップです。
1. LED 製品はなぜ PCBA を受けなければならないのですか?
PCBA なし:
- LED は点灯できません。
- 定電流ドライバは、安定して動作できません。
- スマート制御と調光機能は実装できません。
PCB 上の PCBA はんだ付けされた LED チップ、抵抗器、コンデンサ、ドライバ IC、コネクタ、およびその他のコンポーネントを PCB に搭載し、それを機能的な照明システムに変換します。
2です . LED PCBA アセンブリ プロセス
- SMT (表面実装技術)
– LED ストリップとモジュールの主流プロセス
– 高度な自動化、効率性、一貫性
– 高密度 LED 配置に適しています
- THT (スルーホール技術)
– 電源インターフェースと大電流端子に使用
– 高い機械的強度と安定性
– ハイブリッド アセンブリ (SMT + THT)
– 商用および産業用 LED 器具で一般的で、パフォーマンスと信頼性のバランスをとっています。
PCB と PCBA の製造プロセスの比較 (段階的な)
製造プロセスを理解することは、それらの違いを把握するための鍵です。
PCB の製造プロセスでは、主に露出、エッチング、穴あけ、めっきなどが行われます。具体的なワークフローについては、次の図を参照してください。
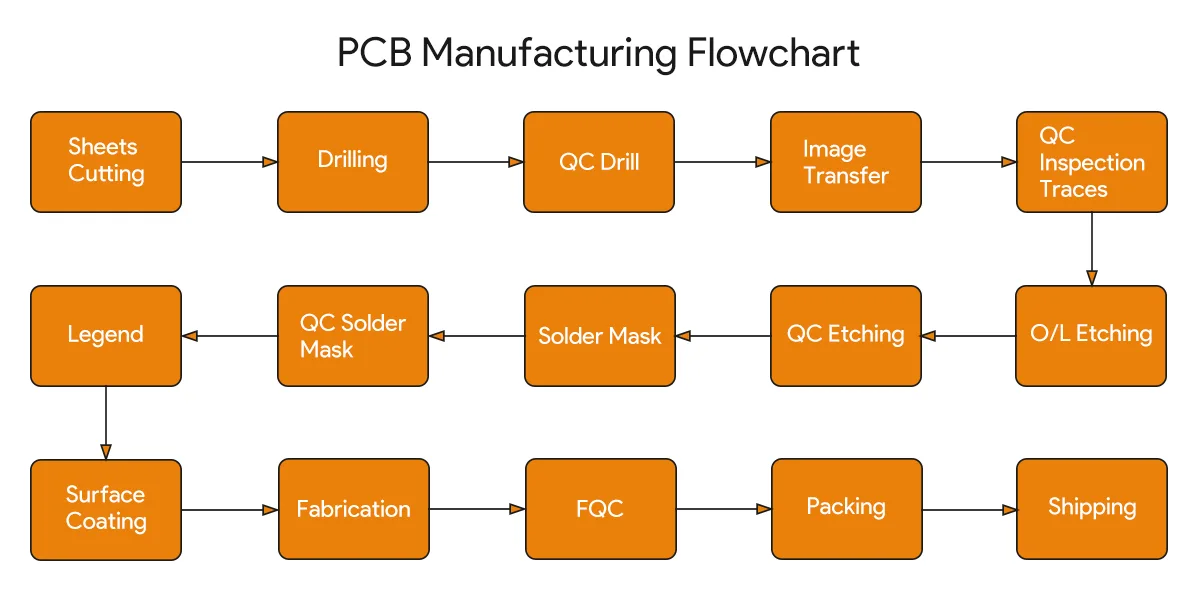
この段階では、完成した PCB は、照明や制御機能のない裸のボードのままです。
PCBA の製造プロセスには、主に SMT の配置、組み立て、およびテストが含まれます。 具体的なワークフローを下のグラフに示します。
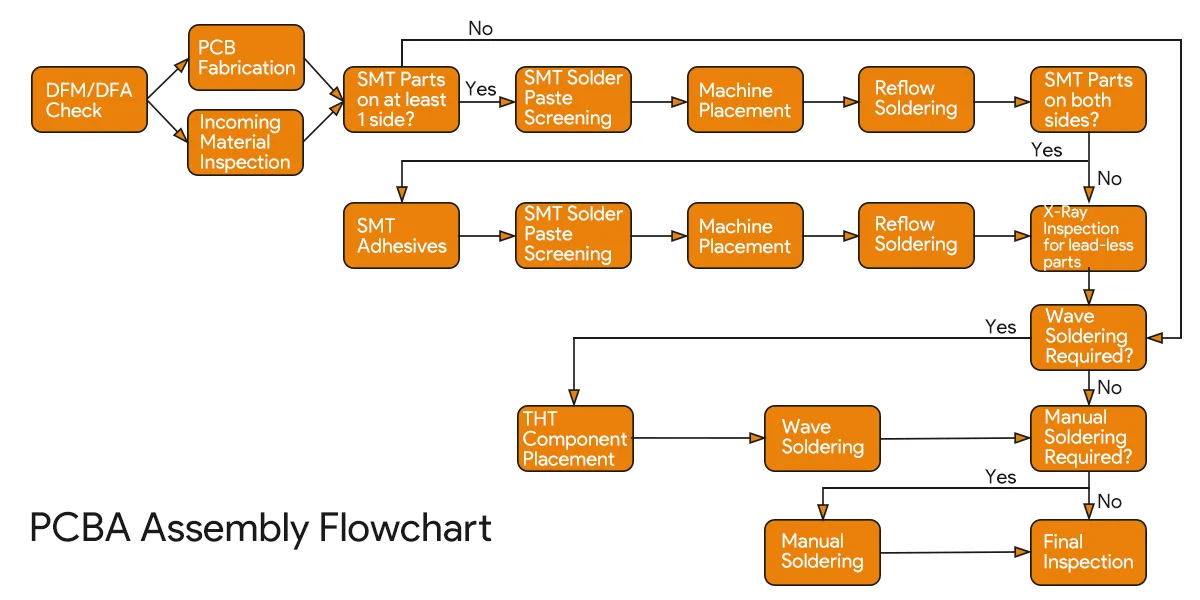
示されているように、PCBA プロセスは PCB 製造よりも大幅に長く、専門知識、機器、および管理機能に大きく依存しています。
PCB と PCBA: 主な違いを一目で把握
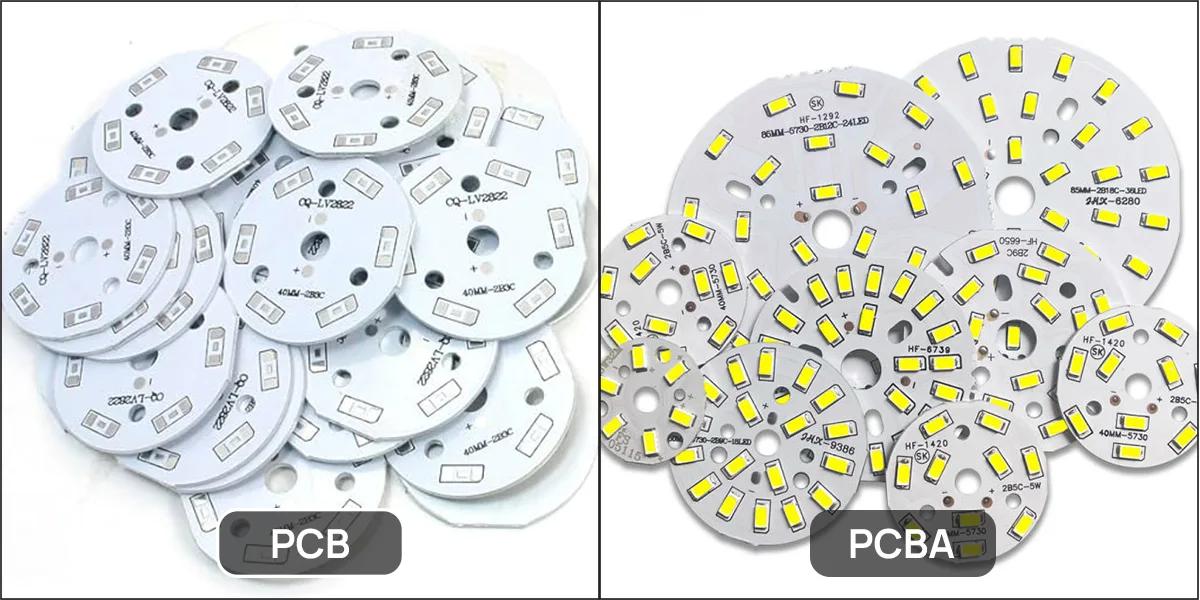
PCB と PCBA の違いは正確には何ですか? 単純な例え: PCB = 建物のフレームワークや配管に似た基本的な構造; PCBA = 機能的な完成品、完全に動力を与えられた運用の建物。
LED 照明製品では、裸の PCB だけでは光を発することができません。 PCBA を完了すると、LED ストリップまたはモジュールが正しく機能するようになります。
| C破書 | PCB (プリント基板) | PCBA (プリント基板アセンブリ) |
| 定義 | 絶縁基板と導電性銅のトレースでできた裸のボードで、電子部品は使用されていません。 | 電子部品(抵抗、コンデンサ、IC など)を PCB に組み込んで作成された機能モジュール |
| 主な機能 | 電気接続経路とコンポーネントの機械的サポートを提供します | 信号処理、電力管理、制御ロジックなどの実際の電子機能を実行します。 |
| 体調 | 無人の「裸の板」 | 完全に組み立てられ、はんだ付けされた「完成したモジュール」 |
| 外観 | 目に見える銅の痕跡とパッドを備えた緑 (または他の色) はんだマスク | コンポーネント、はんだ接合部、およびリードで覆われ、機能的なレイアウトがはっきりと見える |
| 製造範囲 | ボードの製作のみ | コンポーネントの調達 + アセンブリ + テスト |
| 生産プロセス | 材質切断 → 銅積層 → 回路エッチング → ドリリング → 表面仕上げ | 受入検査 → SMT 配置 → リフロー / ウェーブはんだ付け → 検査および機能試験 |
| 主な技術的焦点 | トレース精度、インピーダンス制御、ミクロンレベルのエッチング精度 | はんだ付け品質、配置精度、歩留まり制御 (通常は 99.9% ≥99.9%) |
| 原価構成 | 原材料 + PCB 製造プロセス | 電子部品 (BOM) + アセンブリ + テスト |
| 典型的なコストレベル | 比較的低い (カスタム PCB: 約。 $0.1–$5 ボードあたり) | より高い (PCBA プロトタイプは、通常、$30 から開始します。BOM に応じて) |
| 配信出力 | 機能のない電気キャリア | 定義された機能を備えたすぐに使える電子回路 |
1. 機能の違い
- PCB: 回路経路のみを提供します
- PCBA: 完全に動作する LED システムで電源を投入する準備ができています
2. 製造範囲
- PCB: 回路基板の製造
- PCBA: コンポーネントの調達 + アセンブリ + テスト
3. 必要な書類 (よくある調達に関する質問)
PCB 製造には次のものが必要です。
- ガーバーファイル
- NC ドリル ファイル
PCBA が必要とするもの:
- BOM (部品表)
- ピック アンド プレイス (座標ファイル)
- ステンシルファイル
4. テストと品質管理
PCB:
- 電気導通試験
- 目視検査
- 銅の厚さ測定
- インピーダンス試験
PCBA:
- SPI はんだペースト検査
- 葵自動光学検査
- X 線 (BGA、ドライバー IC はんだ接合点検査)
- ICT/機能テスト (明るさ、電流、安定性)
- 老化と信頼性のテスト
- 光束と電気性能試験
5. パッケージングとロジスティクス
- PCB: 真空防湿包装
- PCBA: 静電気防止パッケージ (ESD)、カスタム トレイ
なぜ PCBA が PCB よりもかなり高価なのですか?

これは、調達担当者から最もよく寄せられる質問の 1 つです。 PCBA のコストの上昇は、単に「処理手数料の増加」によるものではなく、複数の要因によるものです。
- コンポーネントのコスト: チップ、抵抗、コンデンサ、LED、ドライバ IC、およびその他のコンポーネントが、多くの場合、PCBA コストの最大の部分を占めています。
- 労力と設備投資: 高速ピック アンド プレース マシン、リフロー オーブン、AOI システム、および試験装置はすべて高価値の資産です。
- 利回りとリスクのコスト: はんだ付けの欠陥、材料の欠陥、および設計上の問題はすべて、再加工やスクラップのリスクを伴います。
- サプライ チェーン管理のコスト: 材料不足、コンポーネントの代替品、および配送スケジュールの変動には、追加の調整が必要です。
ビジネスの観点から見ると、PCBA は基本的に「システム エンジニアリング サービス」であり、単なる製造プロセスではありません。
2026 年の業界動向: AI は PCB/PCBA をどのように変革しますか?
2026 年までに、人工知能は概念的な段階を超えて、PCB と PCBA の生産に深く統合され、高度に統合されたインテリジェントな製造業への業界の変化を加速させました。
主な傾向は次のとおりです。
- AI 支援 DFM 分析: 製造前に製造上の問題を予測して、試行の実行を減らします。
- AI による AOI の欠陥検出: 深層学習による冷間はんだ接合部やミスアライメントなどの複雑な欠陥を特定し、判断ミス率を下げます。
- インテリジェントなスケジューリングと材料予測: 配送の不確実性を減らしながら、容量の使用率を最適化します。
- 閉ループ品質データ: データ分析により、継続的に歩留まりと一貫性が向上します。
将来的には、AI 対応の PCBA ファクトリーは、納期、品質管理、およびコスト管理において大きな利点を得るでしょう。
ベア PCB またはワンストップ PCBA を選択する必要がありますか?
万能な答えはありません。プロジェクトの種類によって完全に異なります。
経験豊富な電子機器チームと信頼できる SMT リソースがあり、裸のボードだけが必要な場合、PCB はより大きな柔軟性を提供し、より費用対効果が高くなる可能性があります。
調整コストを削減し、品質リスクを最小限に抑え、市場投入までの時間を短縮することを目指している場合、通常、ワンストップ PCBA が最適です。
LED ライト ボードなどの製品の場合、 LED モジュール、スマート ライティング、PCBA は一貫性と配信の信頼性を大幅に向上させます。
PCB/PCBA の一般的な調達の落とし穴
実際のプロジェクトでは、次のエラーがよく発生します。
- 不完全または未検証のデザイン ファイルを提供する
- 実際の設計との BOM の不一致
- 単価のみに焦点を当てながら、テスト要件を無視する
- 複雑な PCBA プロジェクトを PCB サプライヤーに割り当てる
これらの問題は、引用時には見過ごされがちですが、大量生産中のリスクを増幅します。
調達決定ガイド: どのように選択すればよいですか?
選択を確定する前に、次の要因を評価することに優先順位を付けます。
- プロジェクトの複雑さとバッチ サイズ
- 社内のエンジニアリングおよびサプライ チェーン機能
- リードタイムと一貫性の要件
- 長期安定したパートナーの必要性
最適な選択は、必ずしも最低の見積もりではなく、全体的なリスクが最も低いソリューションです。
結論
要約すると、PCB と PCBA は、エレクトロニクス製造において、異なる補完的な役割を果たします。 PCB は基本的な構造と電気接続を提供し、PCBA は製品に完全な機能と商業的価値を提供します。
LED 照明メーカーにとって、PCB と PCBA の違いを理解することは、技術的な考慮事項を超えています。これは戦略的な決定です。 適切な製造および組立ソリューションを選択することで、コストを削減し、品質を高め、グローバル市場での製品の発売を加速します。 製品の統合が進むにつれて、エンジニアリング機能と品質管理の利点を備えた PCBA ソリューションは、グローバルなエレクトロニクスおよび LED 照明市場でますます重要な役割を果たすでしょう。
よくある質問
いやー 。 PCB は単なるキャリアであり、コンポーネントがないと、どのような機能も実行できません。
通常、コンポーネントのリード タイムとテスト要件に応じて、7 ~ 15 日です。
PCB は、RoHS/REACH に準拠する必要があります。 PCBA には、機能テストと環境認証 (鉛フリーはんだ付けなど) が必要です。通常は、コンポーネントのリード タイムとテスト要件に応じて、7 ~ 15 日です。
AI アルゴリズムは、テスト データをリアルタイムで分析し、潜在的な障害を予測し、手動による再作業コストを削減します。
SMT の配置とリフローはんだ付けは依然として優勢ですが、レーザー溶接と 3D プリント技術は徐々に勢いを増しています。