In modern commercial and architectural lighting projects, LED linear modules are increasingly becoming the mainstream choice. Compared to old fluorescent tubes or light strips, LED linear modules have major benefits in brightness, how long they last, ease of installation, and energy savings. They not only provide uniform, comfortable illumination but also substantially reduce long-term maintenance costs.
For LED lighting projects or retrofit initiatives, selecting the appropriate LED linear module translates to higher project efficiency and more reliable lighting quality. Whether in offices, retail spaces, factory warehouses, or building facades and decorative lighting, linear modules offer flexible solutions tailored to diverse application requirements.
This article will guide you through the core aspects of LED linear modules, including definitions and characteristics, structural components, drive methods, performance metrics, application scenarios, and selection recommendations. Through this comprehensive guide, you can quickly learn how to choose the right products based on project requirements and collaborate with reliable suppliers to enhance the overall value of your lighting projects.
What is an LED Linear Module?
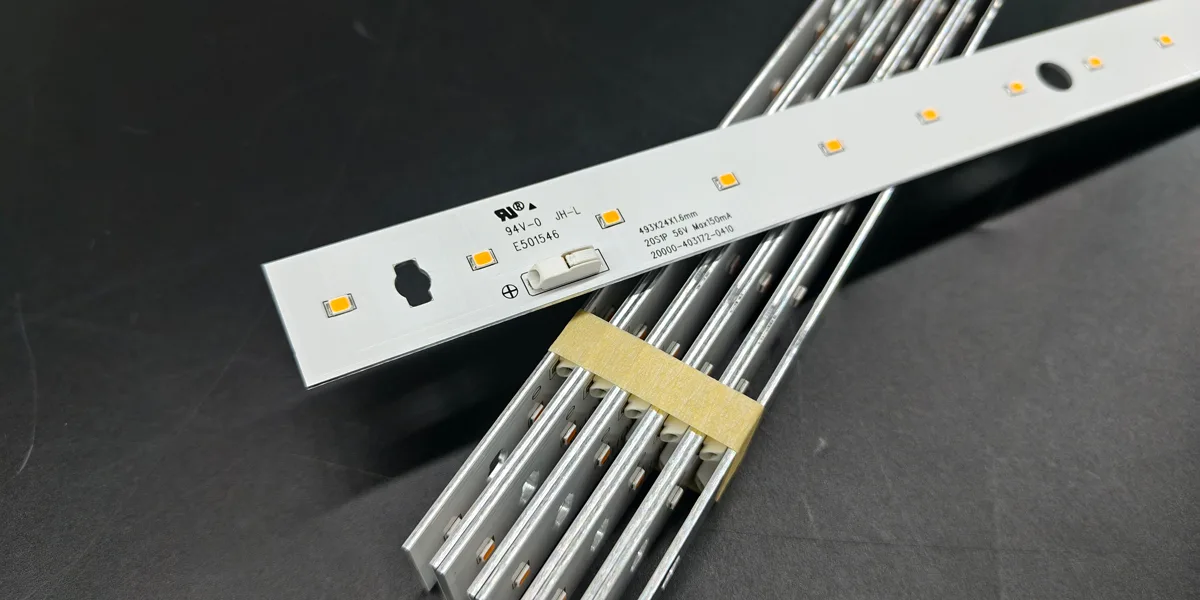

An LED linear module is a lighting component specifically designed for linear fixtures and retrofitting existing lighting systems. It consists of an LED light source, a PCB circuit board, an optical lens (optional), and necessary electrical interfaces. Compared to traditional fluorescent tubes or bulk LED light sources, linear modules feature standardized dimensions and interfaces, enabling easier integration into various lighting fixtures.
Simply put, an LED linear module acts as the “core light engine” of a luminaire. It delivers consistent luminous efficacy while ensuring the lifespan and reliability of the lighting system through optimized thermal management and optical design.
Standard LED linear module specifications typically include 140mm, 280mm, 560mm, and 1120mm lengths, enabling luminaire manufacturers to rapidly match designs. Customizable modules in both dimensions and shapes are also available to meet OEM/ODM clients’ requirements for specialized projects.
These modules find extensive applications in:
- Office and commercial space lighting
- Retail store and supermarket shelf lighting
- Industrial lighting for factories and warehouses
- Architectural decoration and linear design lighting
- Retrofit projects (replacing fluorescent tubes or light strips)
Core Components of LED Linear Modules
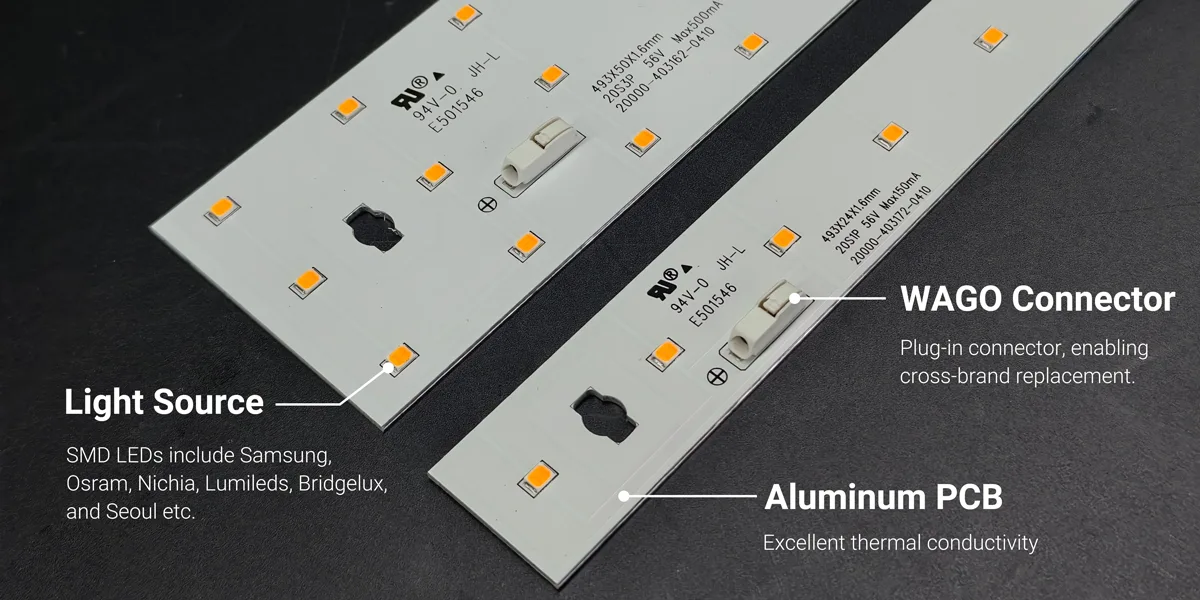
To understand the performance and reliability of LED linear modules, one must first grasp their core components. A high-quality linear module typically comprises the following parts:
1. Light Source (LED Chips)
The light source is the core of the linear module, determining brightness, luminous efficacy, color temperature, CRI, and lifespan. The most common light source type is SMD LED (Surface Mount Device): currently the most prevalent, offering high luminous efficacy suitable for most commercial and industrial lighting applications.
Common SMD LED brands include Samsung, Osram, Nichia, Lumileds, Bridgelux, and Seoul. These SMD LEDs deliver high luminous efficacy, typically reaching 160–220 lm/W. They feature excellent thermal performance, and when paired with aluminum substrates, effectively reduce junction temperature. They offer high color rendering (CRI ≥90), multiple color temperatures (2700K–6500K), and strict color tolerance control (3–5 SDCM).
2. PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
LED chips are typically soldered onto aluminum substrates or FR4 PCBs, which handle current conduction and heat dissipation.
- Aluminum PCB: Excellent thermal conductivity, commonly used in medium-to-high power modules.
- FR4 fiberglass board: Lower cost, suitable for low-power linear modules.
High-quality PCBs not only ensure stability but also extend LED lifespan. Copper thickness, trace routing, and coating processes all impact current stability and longevity.
3. Electrical Interfaces and Connections
Linear modules require reliable electrical interfaces to ensure a stable power supply and convenient installation. Standardized interfaces facilitate easier installation and maintenance:
- Common connection methods: Plug-in connectors, solder joints, and power terminals.
- Modules compliant with Zhaga specifications typically offer uniform dimensions and interfaces, enabling cross-brand replacement.
4. Optical Components (Optional)
To achieve comfortable, uniform illumination or specific optical effects, modules may optionally include:
- Diffusers: Improve light uniformity and reduce glare.
- Lenses: Control beam angles for wall-washing or accent lighting.
Effective optical design helps modules achieve low UGR (Unified Glare Rating), meeting visual comfort requirements in environments like offices and schools.

5. Thermal Management and Structural Components (Optional)
Although LEDs generate less heat than traditional light sources, effective thermal management remains essential for prolonged operation.
- Common thermal solutions: Aluminum extrusion backplates, thermally conductive adhesives, and heat sinks.
- Aluminum extrusion heat sinks: Most prevalent, balancing lightweight construction and thermal conductivity.
- Integrated module design: PCB directly bonded to the heat sink for enhanced thermal efficiency.
- Key metric: Junction temperature (Tj) must be maintained within a reasonable range (typically <85°C).
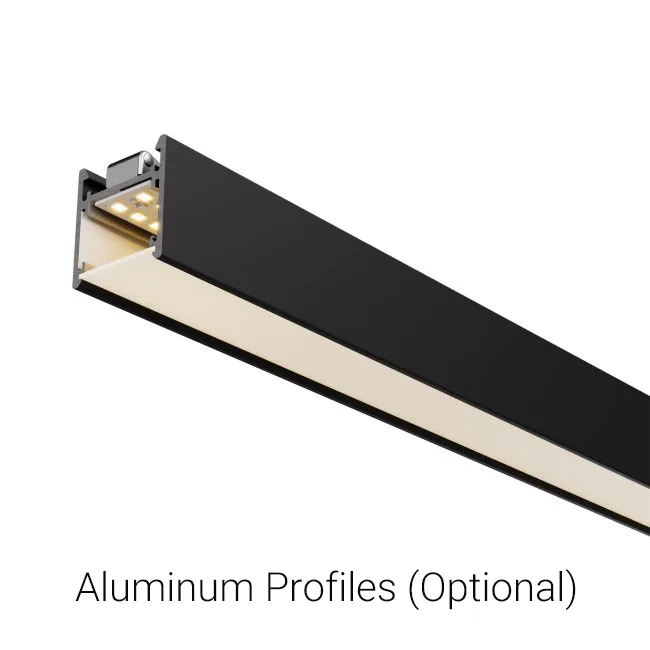

LED lifespan and performance are highly dependent on thermal design. Effective heat dissipation ensures stable luminous efficacy and prevents premature lumen depreciation or reduced lifespan caused by excessive temperatures.
LED Linear Module Drivers and Power Options
LED drivers are one of the core components of LED linear modules, directly impacting light source stability, lifespan, and compatibility with control systems. For commercial lighting, office lighting, and architectural lighting projects, selecting appropriate drivers and power supply methods can significantly enhance system reliability and energy efficiency performance.
Constant Current vs. Constant Voltage Drivers
LED linear modules primarily rely on two fundamental drive methods: Constant Current (CC) and Constant Voltage (CV) drivers.
Constant Current Drivers
By strictly controlling the current output, these drivers ensure LEDs operate under stable current conditions, delivering consistent brightness and extended lifespan. This approach is better suited for environments demanding high luminous efficacy and reliability, such as office lighting, retail lighting, and precision display lighting.
- Features: Provides stable current (e.g., 350 mA, 700 mA, 1050 mA), with voltage varying according to load.
- Advantages: Higher luminous efficacy, excellent current stability, prevents LED overdrive, and extends lifespan.
- Disadvantages: Inconvenient for parallel connection of multiple modules; wiring design requires strict control.

Constant Voltage Drivers
Typically provide fixed voltage outputs (commonly 12V, 24V, or 48V), allowing multiple LED modules to be connected in parallel for high flexibility. They are often used in lighting systems requiring modular assembly or variable lengths, such as display cabinet light strips and linear architectural fixtures. However, careful attention to current distribution is necessary during use to prevent overloading of individual modules.
- Features: Fixed output voltage (typically 12V or 24V), with current distribution handled internally by the module circuitry.
- Advantages: Simplified wiring, easy parallel expansion, suitable for low-power, modular fixtures.
- Disadvantages: Significant voltage drop over long runs, unsuitable for high-power or long-distance transmission.
In practical engineering, constant-current drivers emphasize stability and protection, while constant-voltage drivers prioritize flexibility and scalability. Selection depends on the installation environment and system design objectives of the lighting project.
Integrated Driver-on-Board (DOB) Modules
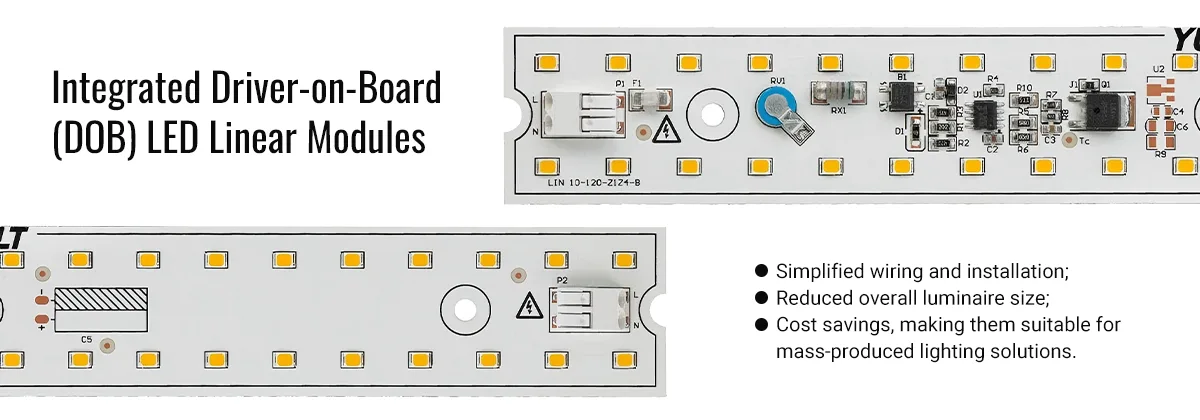
In recent years, integrated driver-on-board (DOB) modules have emerged as a trend. They integrate the driver circuit directly onto the LED module substrate, eliminating the need for an external power supply. Advantages of DOB modules include:
- Simplified wiring and installation;
- Reduced overall luminaire size;
- Cost savings, making them suitable for mass-produced lighting solutions.
However, since the driver and LED chip share limited thermal space, DOB modules demand higher standards for thermal materials and structural design. Additionally, their expandability for dimming and control protocols is limited, offering less flexibility than traditional external drivers. Therefore, DOB modules are better suited for compact fixtures or retrofit applications, while requiring careful consideration in high-end architectural lighting.
Dimming and Control Options
With the proliferation of smart lighting, drivers must not only supply power but also support diverse dimming and control methods:
- Traditional dimming: Such as triac dimming or 0–10V dimming, suitable for cost-sensitive projects;
- Digital control: Such as DALI or DMX512, widely used in commercial and architectural lighting requiring precise grouping and scene control;
- Wireless Control: Such as Bluetooth Mesh and ZigBee, meeting smart home and wireless building management needs.
The smoothness of dimming curves and the compatibility of control systems often directly determine the quality of the lighting experience. For instance, in venues like hotels, museums, and theaters, superior dimming performance demonstrates the value of lighting more effectively than mere luminous flux alone.
Efficiency and Power Factor Considerations
When selecting drivers, energy efficiency and power factor (PF) are equally critical metrics. High-efficiency drivers reduce electrical energy loss and lower operational costs; a power factor close to 1.0 means less grid load, avoiding additional electricity costs and compliance risks in large-scale commercial lighting. Especially in European and American markets, where countries enforce strict PF standards, high-PF drivers have become essential.
Therefore, whether selecting constant current, constant voltage, or DOB integrated solutions, enterprises should comprehensively evaluate project scale, energy efficiency regulations, control requirements, and system lifespan when choosing LED linear module drivers. This ensures the optimal balance between performance and cost for the solution.
Performance Factors to Evaluate

When selecting LED linear modules, beyond price and dimensions, it is crucial to focus on the product’s performance metrics. These indicators not only influence the final lighting effect but also determine the luminaire’s stability, reliability, and compliance with target market certification requirements. Below are several key performance evaluation dimensions:
Luminous Efficacy (lm/W)
Luminous efficacy measures the amount of luminous flux produced per unit of power consumed, serving as a core parameter for assessing an LED module’s energy efficiency. Higher efficacy translates to lower energy consumption, making it particularly suitable for large-scale commercial and industrial lighting projects.
Current mainstream LED linear modules typically achieve luminous efficacies between 150 and 190 lm/W, with premium products exceeding 200 lm/W. For project developers, selecting high-efficiency linear modules not only reduces long-term operating costs but also helps projects meet stricter energy-saving standards.
Color Temperature Options
Color temperature (CCT) directly influences a space’s ambiance and visual experience. LED linear modules typically offer a range of 2700K–6500K:
- 2700K–3000K: Warm white, ideal for hotels, residences, restaurants, and other settings requiring a comfortable ambiance;
- 4000K–5000K: Neutral white, commonly used in offices, retail spaces, and educational lighting;
- Above 6000K: Cool white, frequently employed in industrial facilities, hospitals, outdoor lighting, and other applications prioritizing brightness.
Selecting the appropriate color temperature ensures lighting solutions align with project functionality and user experience.
Color Rendering Index (CRI)
CRI measures a light source’s ability to reproduce the true colors of objects. General lighting requires CRI ≥ 80, while premium commercial spaces, retail displays, or museum lighting demand CRI ≥ 90 to ensure highly accurate color rendering.
High-CRI linear LED modules significantly enhance product presentation and visual experience, which is particularly crucial for commercial lighting in retail and exhibition settings.
Color Consistency
Color consistency is paramount in large-scale applications. Noticeable color variation among fixtures within the same space compromises overall aesthetics.
The industry commonly uses SDCM (McAdam Ellipses) to quantify color difference. Select LED linear modules with SDCM ≤ 3 to ensure consistent lighting across different batches and areas. This is especially critical for large-scale projects requiring bulk procurement (e.g., office buildings, hotels, shopping malls).
Lifetime and LM80/LM79 Testing
The LED module lifespan extends beyond rated operating hours and requires validation through standardized testing:
- LM80 Testing: Developed by the IES (Illuminating Engineering Society of North America) to evaluate LED light source lumen maintenance over extended operation;
- LM79 Testing: Assesses the optical, electrical, and thermal performance of LED luminaires or modules under real-world operating conditions.
Only products passing these tests can provide reliable lifetime data (e.g., L70, L80) and meet energy efficiency certification requirements for European and American markets.
Standards and Certifications for LED Linear Modules
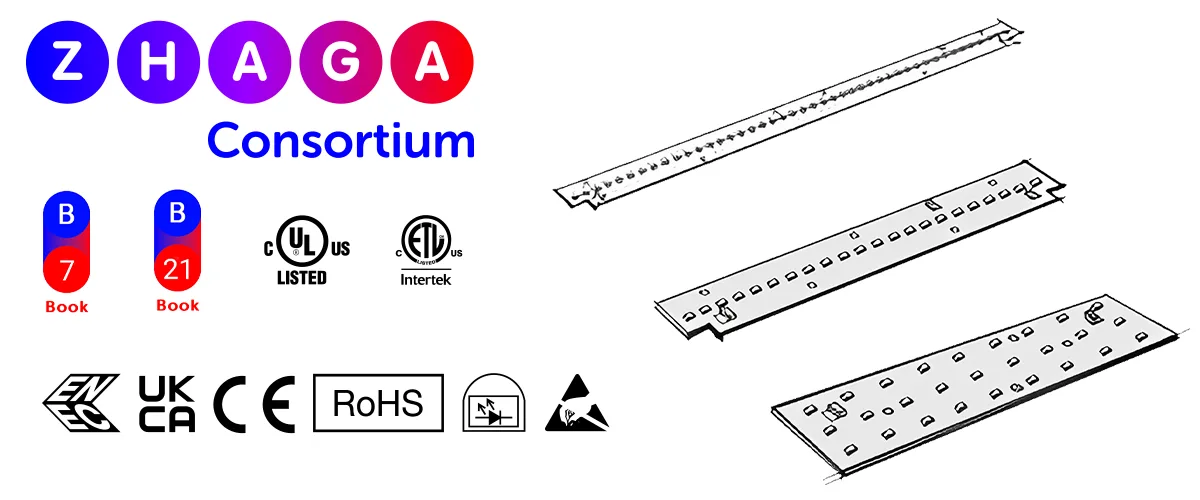
In the lighting industry, standards and certifications not only represent product safety and reliability but also directly determine whether a company can enter target markets. For LED linear modules, compliance with international and regional standards is a key consideration for project wholesalers during procurement. Below are several common certifications and standards:
International Electrotechnical Standards and Performance Testing
IES LM79 and LM80: These testing standards established by the Illuminating Engineering Society (IES) in North America verify the optical performance and long-term lumen maintenance of LED modules, respectively.
- LM79 focuses on performance metrics like luminous efficacy, color temperature, and color rendering index under real-world operating conditions;
- LM80 measures the lumen depreciation characteristics of LED chips after prolonged operation.
These tests enable customers to more intuitively assess a module’s lifespan and performance reliability.
Zhaga Standard: Interface standardization promoted by the Zhaga Consortium ensures interchangeability and compatibility among LED linear modules from different manufacturers. This is particularly crucial for project owners seeking reduced maintenance costs and flexible light source replacement.
Safety and Electrical Certifications
LED modules must guarantee electrical safety during use and comply with regional safety certifications:
- UL (US): Ensures compliance with North American electrical safety standards;
- CE (EU): Indicates fulfillment of EU safety, health, and environmental requirements;
- ENEC (Europe): High-standard certification for lighting products, enhancing market recognition;
- CCC (China): Applicable for lighting products entering the Chinese market.
These certifications serve not only as market entry requirements but also as key evaluation criteria for buyers assessing suppliers.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Certifications
- Energy Star (US): Indicates products meet high energy efficiency standards, commonly required in building and commercial lighting project bids;
- DLC (DesignLights Consortium): Especially in North American markets, many commercial and municipal projects require DLC certification for lighting products to ensure energy efficiency levels;
- RoHS (EU): Restricts the use of hazardous substances, ensuring LED modules meet environmental standards;
- REACH (EU): Emphasizes the safe management of chemical substances, particularly relevant for multinational procurement projects.
Applications of LED Linear Modules
The flexibility and high efficiency of LED linear modules make them suitable for a wide range of commercial and architectural lighting projects. Different optical designs, power configurations, and installation methods determine their advantages in various scenarios. Key application areas include:
1. Commercial Lighting
LED linear modules are widely used in offices, retail spaces, shopping malls, exhibition halls, and similar environments. They deliver uniform, comfortable illumination while minimizing glare (low UGR design), thereby enhancing employee productivity and customer shopping experiences.
- Offices: Suitable for suspended linear fixtures or recessed lighting, providing soft, even illumination.
- Retail & Malls: High CRI modules (CRI≥90) improve product display quality.

2. Industrial Lighting
In factories, warehouses, and logistics centers, LED linear modules are commonly used in three-proof lights, explosion-proof lights, and linear high-bay fixtures. Their high luminous efficacy and long lifespan reduce energy consumption and maintenance frequency, ensuring stable illumination across large areas.

3. Architectural Lighting
Thanks to their flexible lengths and diverse optical designs, linear modules are widely adopted in hotels, convention centers, and public buildings. Whether installed in ceiling coves, for wall washing, or as suspended decorations, LED modules deliver continuous illumination without dark zones.
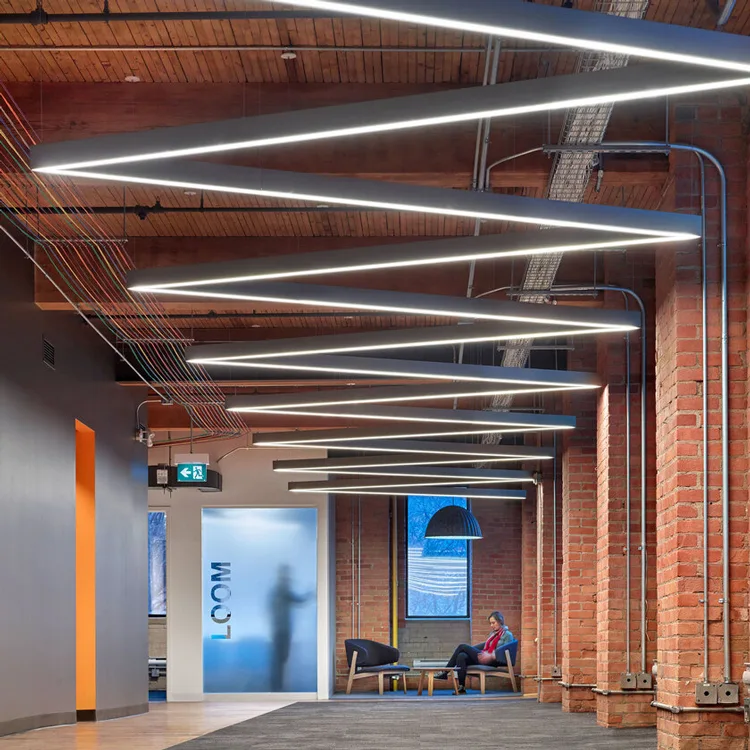

4. Specialized Applications
Certain lighting projects demand superior light quality, such as
- Museums and Galleries: Require high CRI, flicker-free modules to ensure accurate reproduction of artwork and exhibits.
- Medical Lighting: Demands high-efficiency modules with natural spectrums to create comfortable treatment environments.
- Educational lighting: Uniform, soft illumination reduces visual fatigue and enhances learning environments.

5. Fixture Manufacturing and OEM/ODM Applications
For lighting manufacturers, LED linear modules serve as core components for customized lighting products. By combining varying lengths, power ratings, and color temperatures, linear lights, panel lights, or decorative fixtures can be rapidly designed to meet market demands, significantly shortening R&D cycles.
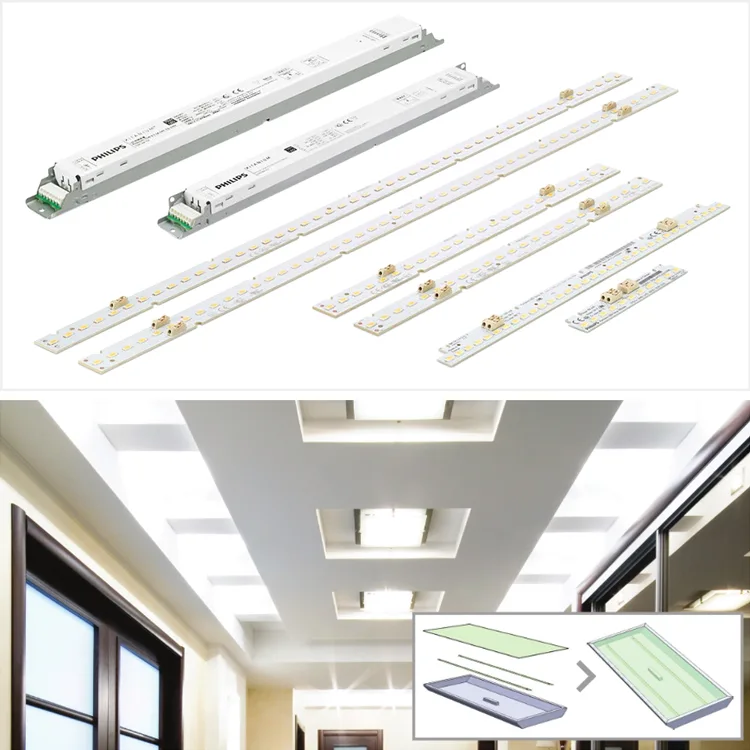

How to Choose the Right LED Linear Module
For lighting engineering firms, wholesalers, and luminaire manufacturers, selecting an appropriate LED linear module involves more than just price comparisons. It requires a comprehensive evaluation of performance, compatibility, application requirements, and certification compliance. The following considerations can help B2B customers make more informed decisions.
1. Define Application Scenarios and Lighting Objectives
Different lighting projects demand vastly different optical and structural specifications:
- Commercial & Office Lighting: Requires high luminous efficacy, low UGR, and effective glare control to ensure long-term lighting comfort;
- Retail & Display Lighting: Emphasizes high Color Rendering Index (CRI≥90), consistent color temperature, and light color to enhance product presentation;
- Industrial and Warehouse Lighting: Emphasizes high brightness, durability, and low maintenance costs;
- Architectural and Decorative Lighting: Often requires diverse size specifications and compatibility with dimming and smart controls.
Before selecting products, B2B clients must first define the project’s lighting objectives to filter suitable module parameters.
2. Core Performance Metrics
Performance forms the foundation of selection, with key focus on:
- Luminous efficacy (lm/W): Selecting high-efficiency modules reduces energy consumption, helping projects meet green building or energy-saving regulations;
- Color temperature and CRI: Different color temperatures create distinct atmospheres; high-CRI products are better suited for premium displays and retail;
- Color consistency (SDCM): Recommended ≤3 to avoid color variation issues in large-scale installations;
Lifespan and Test Data: Prioritize modules certified by LM80/LM79 testing to ensure longevity and consistent optical performance.
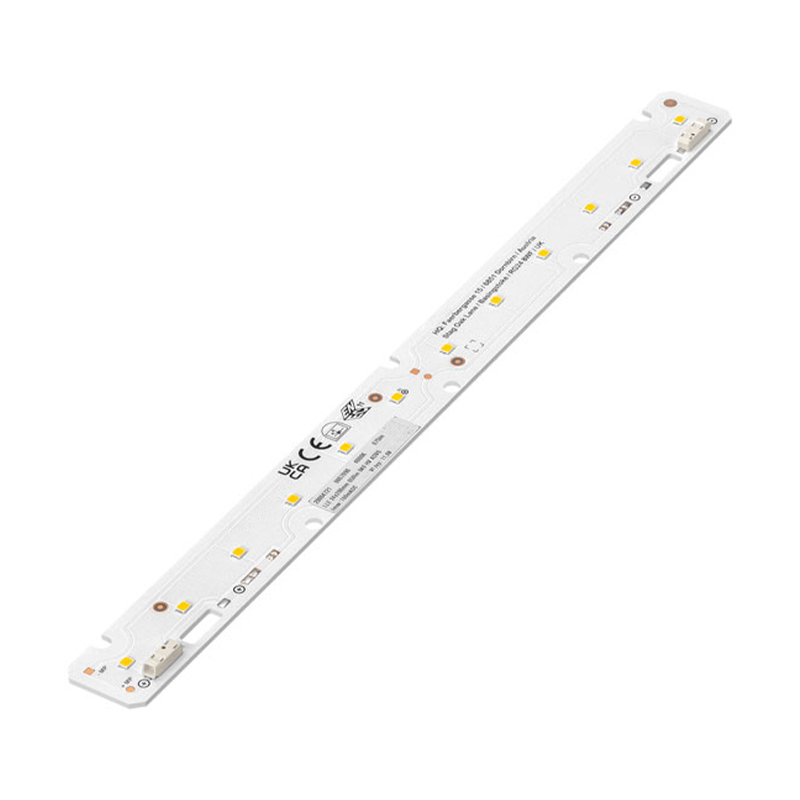

280x24mm 1100lm LED Linear Module
Input Voltage: 20.9-22.7VDC
Input Current: 275mA
Input Watt: 6.1W
Lumens: 1098-1241 lm
Luminous Efficacy: 183-205 lm/W
LED Types: SMD3030/SMD2835
LED Chip: Samsung/Osram/LUMILEDS/Bridgelux/Seoul
LED QTY: 24pcs
Color Temperature: 2700K/3000K/4000K/5000K/6500K
CRI: 80/90
Dimension: 279×23.6×1.6mm
PCB Material: Aluminum/FR-4
Certification: CE, RoHS
Warranty: 5 Years
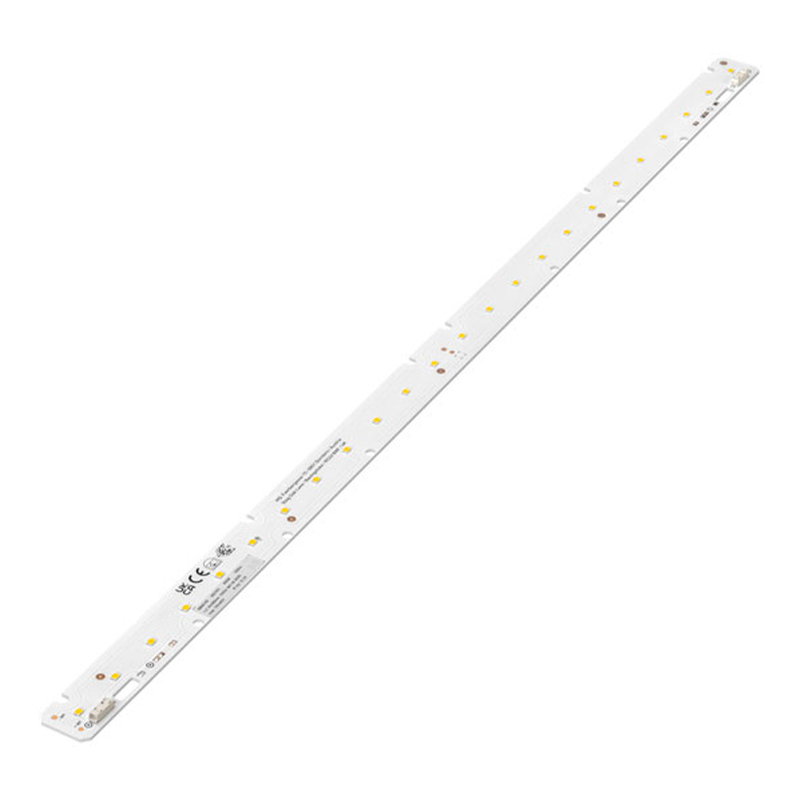

560x24mm 2200lm LED Linear Module
Input Voltage: 41.8-45.4VDC
Input Current: 275mA
Input Watt: 12.1W
Lumens: 2195-2482 lm
Luminous Efficacy: 183-205 lm/W
LED Types: SMD3030/SMD2835
LED Chip: Samsung/Osram/LUMILEDS/Bridgelux/Seoul
LED QTY: 48pcs
Color Temperature: 2700K/3000K/4000K/5000K/6500K
CRI: 80/90
Dimension: 559×23.6×1.6mm
PCB Material: Aluminum/FR-4
Certification: CE, RoHS
Warranty: 5 Years
3. Drive Type and System Compatibility
Drive selection directly impacts installation flexibility and future maintenance:
- Constant current drivers: Ideal for applications requiring high stability;
- Constant voltage drivers: Suitable for lighting systems requiring parallel connection of multiple modules;
- DOB integrated modules: Suitable for retrofit projects with limited space or requiring rapid installation.
Additionally, verify module support for dimming and control protocols like 0–10V, DALI, DMX, and Bluetooth Mesh to ensure compatibility with existing systems.
4. Standards and Certification Compliance
Certification compliance is critical for export projects or multinational engineering:
- UL, ETL (North American market);
- CE, ENEC, RoHS, REACH (European market);
- DLC, Energy Star (energy efficiency standards);
- Zhaga interface standard, ensuring interchangeability between modules from different manufacturers.
Selecting modules with comprehensive certifications not only reduces project risks but also enhances customer trust.
5. Cost and Long-Term Value
While price is important in project procurement, it is not the sole criterion. A balanced assessment of procurement costs, operational energy consumption, and maintenance expenses is essential to truly evaluate a product’s cost-effectiveness. For example, high-efficiency modules may have a higher initial price but can significantly reduce long-term electricity expenses. Certified modules also minimize post-sales issues and quality disputes.
6. Supply Chain and Customization Capabilities
Finally, the supplier’s capabilities are key to selection:
- Does the supplier support OEM/ODM customization to meet diverse size, power, and optical requirements?
- Does the supplier maintain stable delivery capabilities to ensure bulk supply for large-scale projects?
- Does the supplier provide technical support and after-sales service to facilitate rapid installation and commissioning?
For long-term project partners, selecting a reliable LED linear module supplier often holds greater value than the individual product itself.
Conclusion
LED linear modules have become indispensable core components in modern lighting projects. Whether for commercial lighting, industrial illumination, architectural decoration, or OEM/ODM luminaire manufacturing, linear modules deliver efficient, flexible, and cost-effective solutions. By accurately evaluating optical performance, drive methods, durability, and customization requirements, project developers and wholesalers can more easily select products suited to their specific projects.
Looking ahead, rapid advancements in smart lighting, eco-friendly materials, standardized interfaces, and differentiated customization will unlock further application opportunities for LED linear modules. For lighting engineering firms, wholesalers, and luminaire manufacturers, now is the prime moment to seize market upgrades and enhance competitiveness.
If you’re seeking a reliable LED linear module supplier, contact SignliteLED. We offer a diverse range of high-efficiency, low-UGR, and high-CRI linear modules, with OEM/ODM customization support. We help your projects launch quickly, reduce costs, and ensure superior lighting quality.






