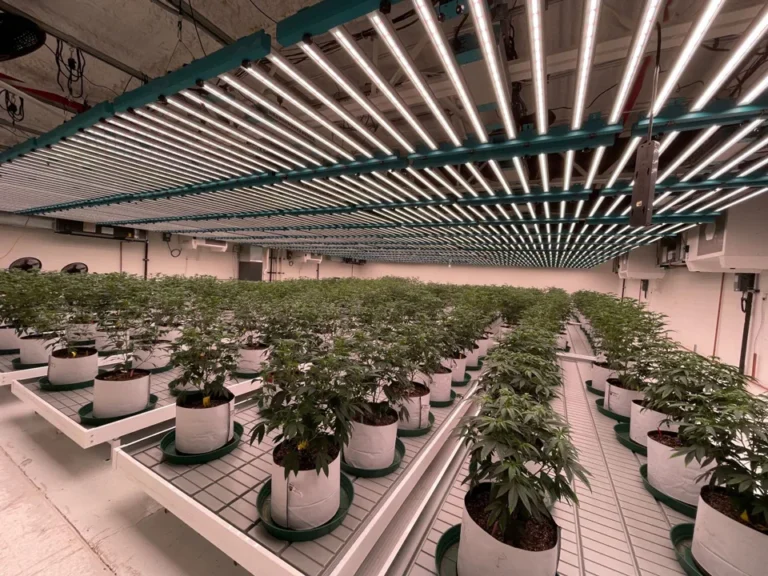
LED PCB design for horticulture lighting focuses on creating stable, long-duration lighting systems that operate reliably in controlled grow environments. Unlike general lighting, horticulture systems must support continuous photoperiods, manage sustained heat within enclosed fixtures, and deliver consistent electrical performance over entire growing cycles. The way the LED PCB is designed directly affects light reliability, uniform plant exposure, and long-term system stability in real cultivation settings.
What LED PCB Design Means in Horticulture Lighting
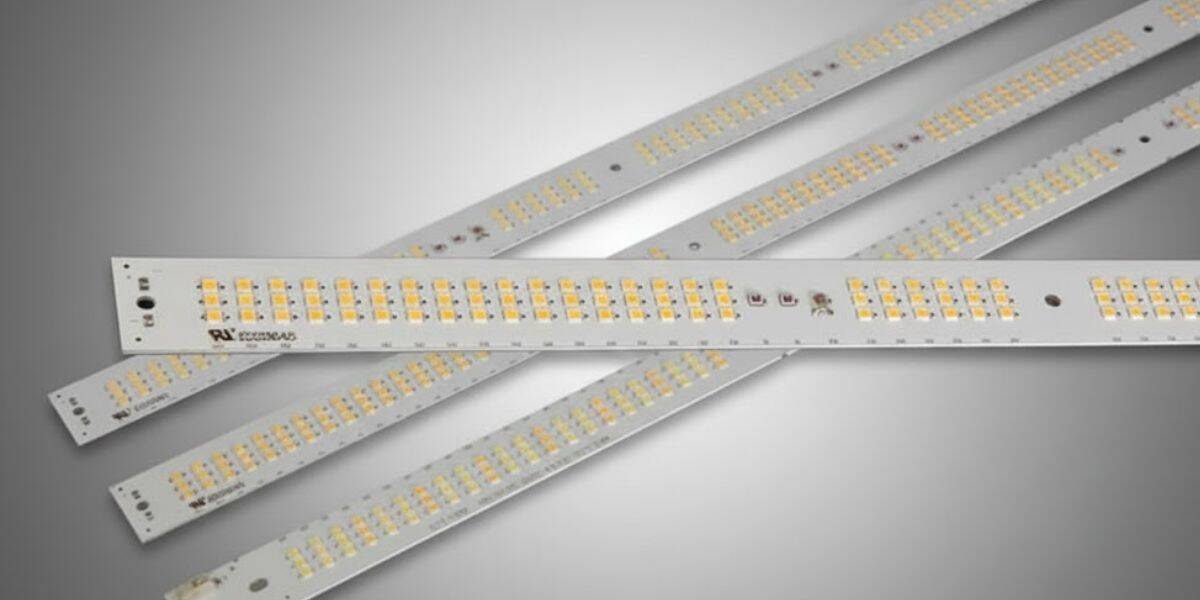

LED PCB design in horticulture lighting refers to how LEDs are electrically and physically supported to operate for plant growth applications rather than human-focused illumination. The design is not just about mounting LEDs on a board. It is about ensuring the board can handle long operating hours, environmental stress, and consistent output across growing cycles.
In horticulture environments, lighting systems are often part of a closed-loop setup that includes temperature control, humidity management, and automated schedules. The PCB becomes a foundational component that influences how reliably the entire lighting system performs over time.
Key contextual factors that define LED PCB design for horticulture include:
- Continuous lighting cycles that often run many hours per day without interruption
- Operation inside controlled grow rooms, greenhouses, or enclosed fixtures
- A functional difference from general indoor lighting where usage is intermittent and user comfort focused
- A requirement for consistency over weeks or months rather than short daily use
This scope is what separates horticulture-focused PCB LED design from standard lighting applications.
Why PCB Design Is Critical for Horticulture Lighting Systems
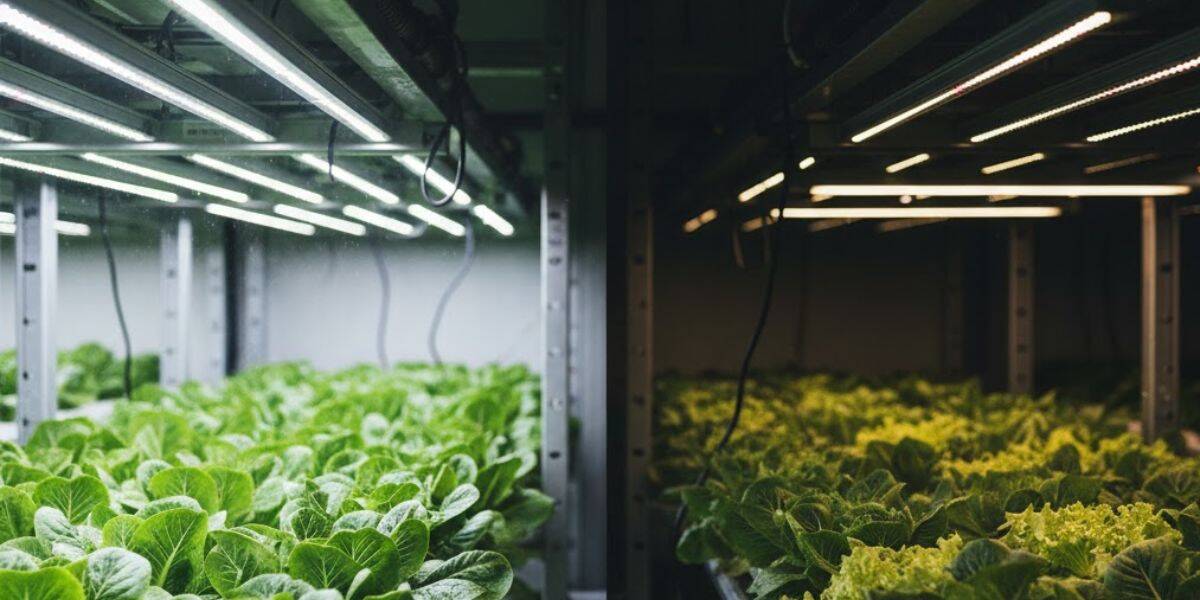

PCB design matters in horticulture lighting because plants depend on stable, predictable light exposure. Any fluctuation in output, heat handling, or electrical behavior can affect growth uniformity and system uptime. The PCB plays a central role in maintaining that stability.
Grow lights are typically operated on long photoperiods that repeat daily for entire growing seasons. This sustained use places different demands on the PCB compared to decorative or architectural lighting. The board must support reliable operation without degradation, drift, or failure under constant load.
Key reasons PCB design is critical in horticulture lighting systems include:
- Long photoperiod operation that stresses electrical and thermal pathways
- The need for thermal stability to avoid performance variation during extended runtime
- Electrical consistency that supports uniform plant lighting across fixtures
- Reliability over multiple seasons, reducing maintenance and system interruptions
In practice, a well-considered led pcb design reduces the risk of uneven canopy lighting and unexpected downtime in cultivation environments.
Key Design Considerations for LED PCBs in Horticulture
This section addresses the core design factors that directly influence performance in real horticulture lighting systems. These considerations are not theoretical. They reflect how PCBs behave when used in grow rooms, greenhouses, and controlled agriculture facilities.
Thermal Design in Grow Environments
Thermal management is one of the most critical aspects of LED PCB design for horticulture lighting. Grow lights often operate inside enclosed housings where heat dissipation is constrained. Over time, unmanaged heat buildup can affect both LED performance and board reliability.
In horticulture settings, thermal behavior is shaped by continuous operation and environmental conditions rather than peak brightness alone.
Key thermal considerations include:
- Heat buildup from extended operating hours rather than short bursts
- Limited airflow inside grow fixtures or sealed environments
- Interaction between PCB temperature and overall fixture lifespan
- Long-term thermal stress affecting electrical stability and light consistency
Effective thermal design supports steady output and reduces the likelihood of gradual performance decline during grow cycles.
PCB Layout Stability for Long-Hour Operation
Layout stability focuses on how electrical pathways are arranged to maintain consistent current delivery over long durations. In horticulture lighting, even minor instability can translate into visible differences across the plant canopy.
Unlike general lighting, where occasional flicker may go unnoticed, plant lighting requires uniform exposure over time. The PCB layout directly influences how evenly current is distributed across LEDs.
Important layout stability factors include:
- Maintaining consistent current flow during prolonged operation
- Reducing the risk of flicker or uneven output under continuous load
- Supporting uniform light delivery across the entire lighting module
A stable layout helps ensure that all plants receive comparable light conditions throughout the growing area.
Spectral Optimization (Plant Growth Requirements)
In horticulture lighting, LED PCB design must support spectral output that aligns with plant photosynthesis rather than human visual comfort. Different wavelengths influence plant development stages, which makes spectral planning a functional design consideration rather than a lighting preference.
Key spectral factors that influence LED PCB design include:
- Chlorophyll Absorption Peaks
Plant chlorophyll primarily absorbs light in the blue (~430–450 nm) and deep red (~660 nm) ranges. LED PCB layouts must support stable operation of LEDs tuned to these wavelengths, ensuring consistent output throughout long photoperiods without spectral drift. - Full-Spectrum Balance for Practical Grow Environments
Many horticulture systems combine red and blue LEDs with green or white channels to support balanced plant growth and allow visual inspection by growers. PCB designs must accommodate mixed LED populations without electrical imbalance or uneven aging across channels. - LED Binning and Spectral Consistency
Spectral uniformity depends on controlled LED binning and forward-voltage matching. PCB layouts that support consistent current distribution help maintain uniform light output across the panel and reduce long-term spectral variation during extended operation cycles.
By integrating spectral requirements into PCB design decisions, horticulture lighting systems achieve more predictable plant response and stable performance across full growing cycles.
Material and Structural Considerations in Context
Material and structural choices in horticulture LED PCBs are driven by operational context rather than marketing distinctions. The goal is to support reliability under constant use, heat exposure, and environmental stress.
Structural design influences how the board interacts with the fixture, mounting surfaces, and cooling elements. While material selection matters, it should always be considered within the real operating environment rather than in isolation.
At a system level, structural integrity helps maintain:
- Mechanical stability over repeated thermal cycles
- Secure mounting that supports consistent light positioning
- Long-term durability without deformation or stress-related failure
These factors collectively support dependable lighting performance over entire cultivation periods.
Role of LED Linear PCB Boards in Horticulture Lighting
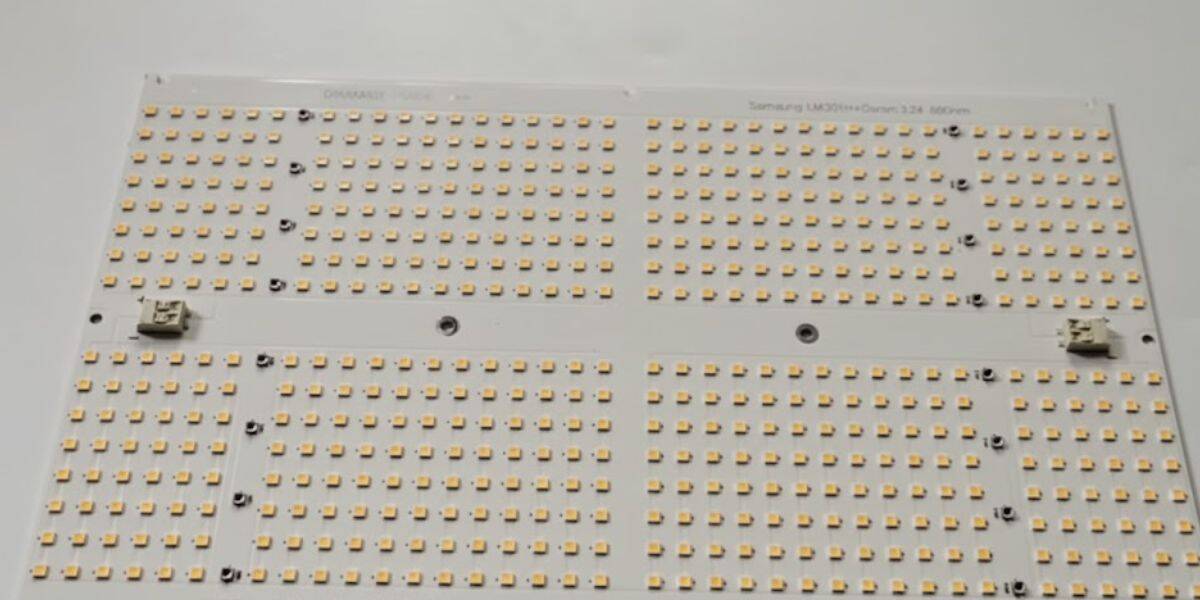
Linear PCB formats are widely used in horticulture lighting because they align well with how plants are arranged and how light needs to be delivered across growing areas. A linear led pcb board supports even distribution over plant canopies, making it easier to scale lighting systems across rows or racks.
In grow rooms and vertical farming setups, linear boards allow designers to place light sources evenly across the cultivation area. This reduces hotspots and shadowing that can occur with point-based lighting formats.
Key advantages of linear PCB designs in horticulture include:
- Broad coverage that aligns with plant canopy layouts
- Modular scalability for expanding or reconfiguring grow rooms
- Consistent light distribution across fixtures and zones
By supporting uniform coverage, linear designs help maintain consistent plant exposure throughout the growing space.
Common Design Mistakes in Horticulture LED PCB Projects
Mistakes in horticulture LED PCB projects often arise when designs are adapted directly from general lighting without accounting for grow-specific demands. These issues may not be immediately visible but can affect performance over time.
In many cases, problems appear only after extended operation, when heat, duration, and environmental factors compound.
Common mistakes include:
- Treating grow lights like standard indoor lighting with limited daily use
- Ignoring the thermal effects of enclosed fixtures and dense installations
- Designing primarily for brightness while overlooking duration and stability
Avoiding these pitfalls requires a clear understanding of how horticulture lighting operates in real environments.
How LED PCB Design Supports Modern Horticulture Operations
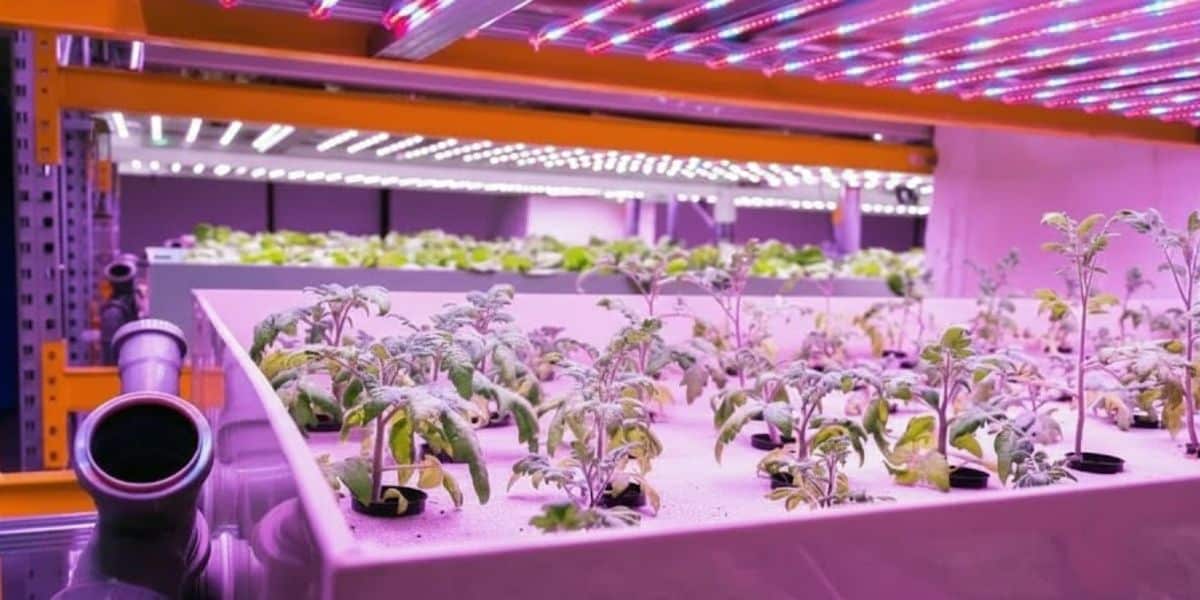

Modern horticulture increasingly relies on automated systems, scheduled lighting cycles, and scalable infrastructure. LED PCB design supports these operations by providing a stable foundation for predictable lighting behavior.
Well-designed PCBs integrate smoothly with timers, control systems, and automated grow setups. Reliability becomes especially important when lighting is synchronized with irrigation, climate control, and growth planning.
At a system level, effective led pcb light design enables:
- Reliable integration with automated lighting schedules
- Reduced risk of unexpected downtime in controlled grow systems
- Flexibility to upgrade or reconfigure lighting layouts as operations evolve
In this context, pcb led solutions are not standalone components. They are part of a broader operational ecosystem where consistency and dependability matter.
Design Factors and Practical Impact in Horticulture Lighting
| Design Aspect | Practical Impact |
| Thermal stability | Supports consistent plant exposure over long cycles |
| Layout uniformity | Promotes even canopy lighting across grow areas |
| Structural reliability | Reduces maintenance needs and downtime |
This table highlights how core design choices translate directly into real-world horticulture outcomes.
Conclusion
LED PCB design for horticulture lighting works by aligning electrical, thermal, and structural behavior with the realities of plant growth environments. Unlike general lighting, horticulture systems demand long-duration stability, consistent output, and dependable operation across entire growing cycles. When design decisions focus on reliability rather than short-term performance, the result is lighting that supports uniform plant development and predictable cultivation outcomes.
FAQs
Because grow lights operate for long periods, PCB design directly affects reliability, heat management, and consistent light delivery to plants.
Standard PCBs can function, but they may not be optimized for long photoperiods, enclosed environments, or sustained thermal load.
Thermal stability helps maintain consistent output over time, reducing fluctuations that can impact plant growth.
Linear designs provide even canopy coverage and are easy to scale across grow rooms and racks.
Unstable layouts can lead to uneven light distribution, flicker, or gradual performance drift during long operating cycles.
Yes. Reliable PCB behavior supports predictable lighting schedules and reduces disruption in automated horticulture operations.






