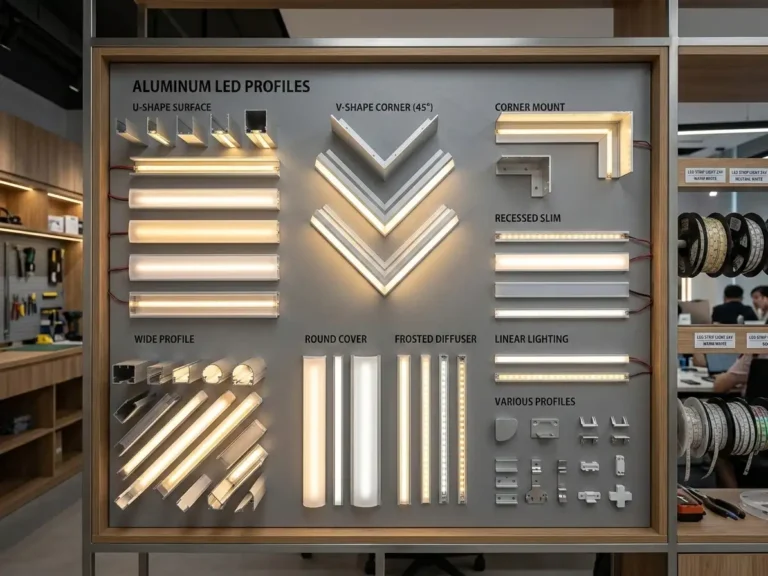
As contemporary architecture continues to favor clean lines and integrated detailing, lighting has evolved into a structural design element rather than a purely decorative feature. Linear LED lighting systems are now widely applied across residential, commercial, and architectural projects, offering visual continuity, efficiency, and flexibility. At the core of these systems is the LED aluminum profile, which determines how light is housed, managed, and sustained over time.
Often referred to as LED channels or aluminum extrusions for LED lighting, these profiles serve far more functions than simple mounting. They manage thermal performance, influence optical quality, protect LED strips, and ensure consistent installation results across a project. Without proper profile selection, even premium LED components cannot deliver reliable performance.
This guide provides a system-level overview of modern linear lighting solutions, focusing on how LED profiles interact with system components, technical parameters, application requirements, and installation constraints.
Core Components of Professional LED Profile Systems
A professional linear lighting system is defined by how its components work together. Each element must be evaluated based on its relationship with the LED profile.
Component Interaction Overview
| System Component | Relationship to LED Profile | Selection Impact |
| LED strip / tape light | Mounted directly inside the profile | Determines required profile width and thermal capacity |
| Aluminum profile / channel | Structural and thermal housing | Defines heat dissipation, mounting method, and appearance |
| Diffuser / lens | Installed within the profile opening | Affects light uniformity, glare, and efficiency |
| Power supply / driver | Electrically connected to the profile system | Influences run length, wiring space, and heat planning |
| Control system | Integrated through wiring and access points | Requires profile space for connectors and service access |
| Mounting hardware | Profile-specific accessories | Determines installation accuracy and stability |
1.LED Strips and Tape Lights
LED strips determine brightness, color quality, and power consumption, but their long-term performance depends on the aluminum housing that supports them. High-output or high-density LED tape generates significant heat, which must be transferred efficiently through the profile body.
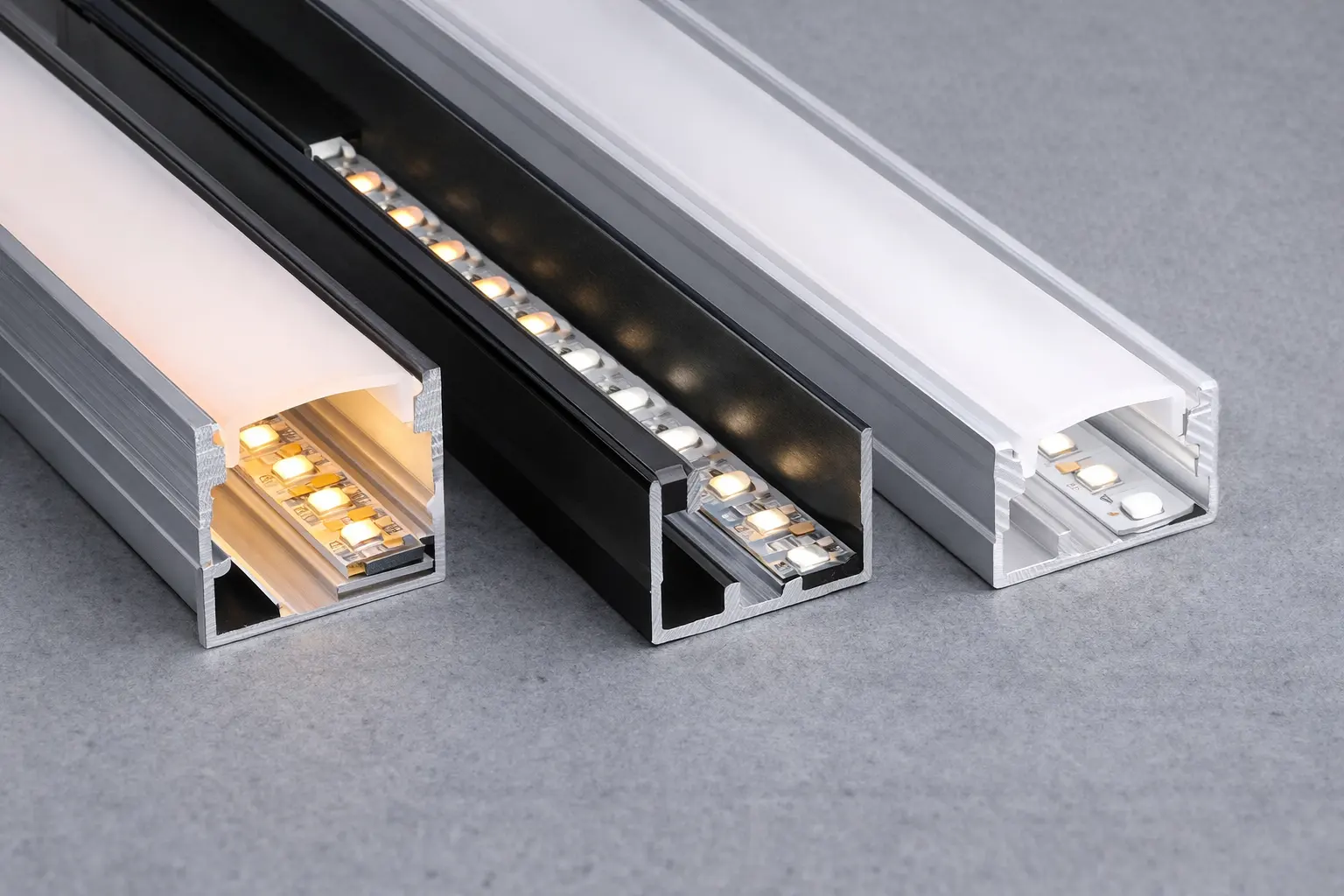

Shallow or lightweight channels may be suitable for low-power accent lighting, but they are often insufficient for continuous operation at higher wattages. Profile depth, wall thickness, and material quality directly affect thermal stability and LED lifespan. Strip width is equally critical, as the internal dimensions of the extrusion must accommodate the PCB and solder joints without compromising airflow.
2.Aluminum Profiles and Extrusion Channels
Aluminum extrusions for LED lighting form the structural backbone of linear systems. Their primary functions include heat dissipation, mechanical protection, and defining installation geometry.
Compared with plastic housings, extruded aluminum profiles provide superior thermal conductivity and dimensional stability. Surface finishes such as anodizing or powder coating enhance corrosion resistance and allow alignment with architectural finishes. Profile size and mass directly determine the amount of heat that can be dissipated during continuous operation. To explore the full range of aluminum extrusion options and their applications, see our complete LED tape light channel guide for 2025.
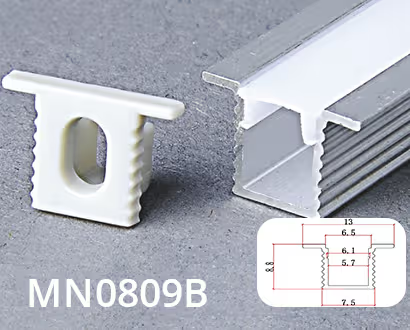
MN0809B
Weight:0.042KG
Thickness: 0.7mm
PC color: Milk white
Size: L1000*W8*H9mm
End caps/Clips: 1pair/m
Aluminiu color: Silver/Black
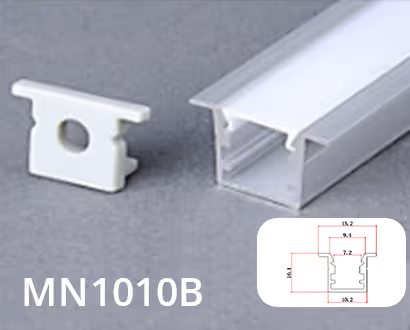
MN1010B
Weight:0.096KG
Thickness: 0.8mm
PC color: Milk white
Size: L1000*W10*H10mm
End caps/Clips: 1pair/m
Aluminiu color: Silver/Black
For standard surface-mounted linear lighting, models such as MN0809B or MN1010B are recommended. These lightweight LED profiles are suitable for residential cabinetry, furniture lighting, or light commercial display applications. They support common LED strips and, when paired with PC or PMMA diffusers, provide uniform illumination and effective glare control.
3.Diffusers and Optical Covers
Diffusers should always be selected in direct relation to LED profile geometry rather than as standalone components. Shallow aluminum channels typically require higher LED density or stronger diffusion materials to minimize spotting and visible LED points. In contrast, deeper LED extrusions provide additional mixing space, allowing the use of higher transmission diffusers that improve efficiency. The correct balance between diffuser type, profile depth, and LED spacing is essential for achieving uniform light output and acceptable glare control.
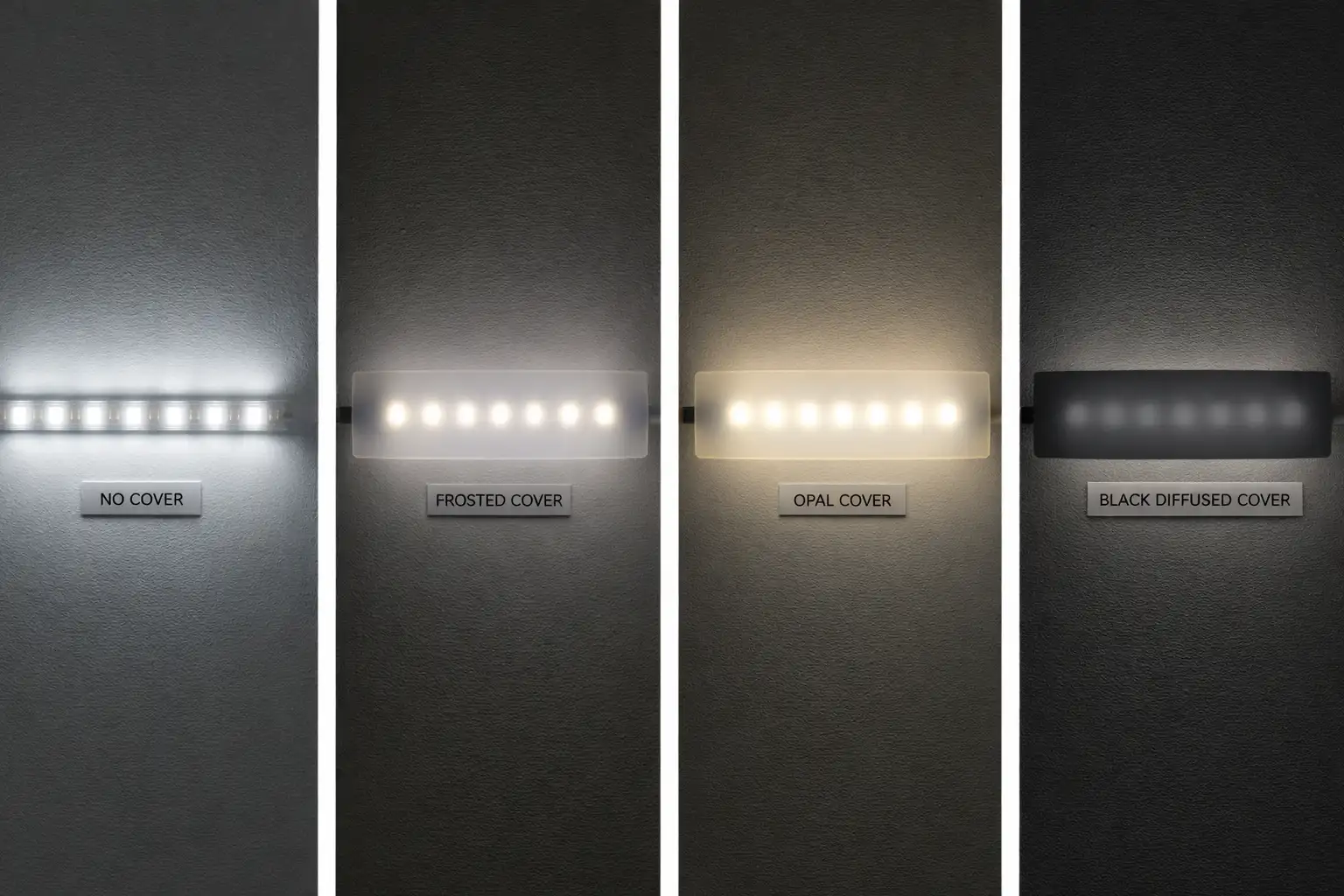

4.Power Supplies and Drivers
Although power supplies and LED drivers are not physically integrated into the LED profile, they strongly influence profile selection through wiring requirements and voltage drop management. Long linear lighting runs may require wider aluminum channels to accommodate concealed wiring, pass-through connections, or dual-feed layouts. In recessed or trimless installations, remote driver placement is often preferred to reduce heat buildup inside the profile and to maintain long-term system reliability and serviceability.
5.Control Systems
Lighting control protocols such as 0–10V, DALI, or DMX directly affect wiring density, connector placement, and maintenance access. LED profiles specified for commercial or architectural lighting systems must provide sufficient internal space for control wiring and allow access for troubleshooting without disturbing finished surfaces. Poor coordination between control systems and profile design often leads to installation complications, limited accessibility, or visible modifications that compromise the intended architectural appearance.
6.Mounting Hardware and Accessories
Mounting clips, brackets, and suspension kits are engineered to match specific LED profile geometries and installation methods. Surface-mounted, recessed, and suspended linear systems each rely on different hardware tolerances and load requirements. Selecting an aluminum profile without its intended mounting ecosystem frequently results in misalignment, uneven spacing, or visible fasteners. Properly matched accessories ensure consistent installation quality, structural stability, and long-term performance of the linear lighting system.
Types of LED Profiles: Structural Classification
LED profiles can be classified based on installation method, geometry, and application intent.
Installation-Based Classification
| Installation Type | Typical Profile Characteristics | Common Use Cases |
| Surface mounted | Shallow channels, visible housing | Retrofit projects, cabinetry |
| Recessed | Flush alignment, drywall integration | Ceilings, walls |
| Trimless mud-in | Edge-free plaster integration | Modern architectural interiors |
| Suspended linear | Rigid extrusion with internal wiring | Offices, commercial spaces |
| Wall or corner mounted | Angled or directional geometry | Accents, indirect lighting |
Profile Shape and Geometry
| Profile Shape | Functional Advantage | Design Impact |
| Flat linear | Compact form | Minimal visual presence |
| Deep channel | Improved light mixing | Reduced glare |
| Corner / angled | Directional output | Concealed light source |
| Round or tubular | Even distribution | Decorative applications |
Corner and angled profiles provide directional output while concealing the light source. For specialized applications, explore our guide to 45° corner LED aluminum profiles.

Application-Oriented Designs
Many LED profiles are engineered for specific application scenarios such as under-cabinet lighting, cove illumination, facade accents, tile edge integration, or outdoor installations. These application-oriented designs address unique factors including environmental exposure, mounting constraints, and optical performance requirements. For example, exterior aluminum channels must consider weather resistance and sealing, while tile trim profiles focus on precise dimensions and clean visual transitions within architectural surfaces.

3. LED Profile Performance Parameters That Influence Selection
Technical specifications should guide profile selection decisions rather than serve as abstract data points.
Parameter-to-Selection Relationship
| Technical Parameter | Why It Matters | Profile Selection Impact |
| Thermal dissipation | Controls LED lifespan | Determines profile depth and aluminum mass |
| Profile depth | Affects light uniformity | Influences LED density and diffuser choice |
| Color rendering | Higher CRI generates more heat | Requires enhanced thermal capacity |
| Color temperature | Warm or tunable systems run hotter | Demands conservative profile sizing |
| System efficiency | Heat affects real output | Poor profiles reduce actual performance |
| Electrical load | Voltage drop in long runs | Requires space for wiring and feeds |
Thermal Performance
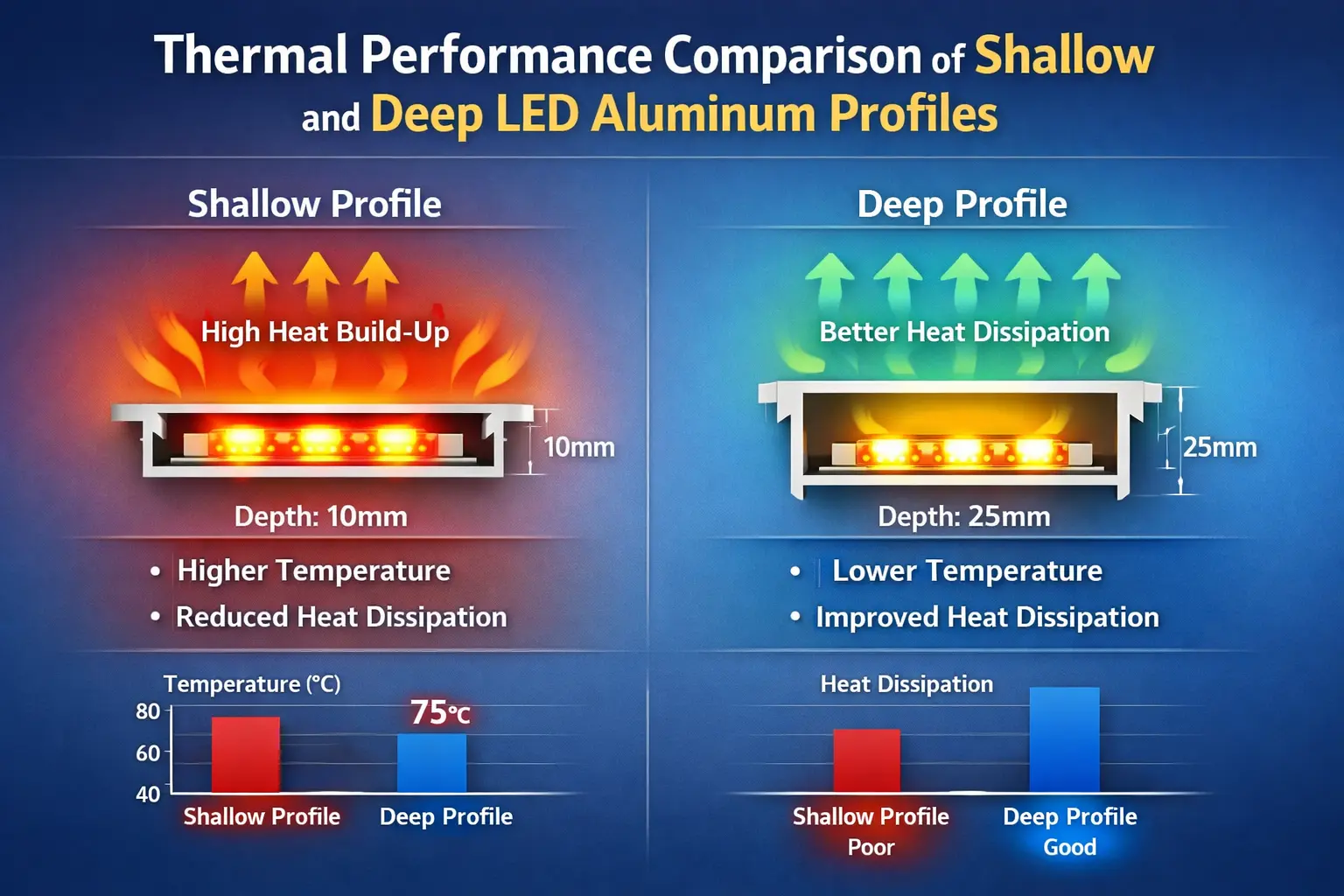
Thermal dissipation capacity defines the maximum LED strip wattage that an aluminum profile can reliably support. Deeper or heavier extruded channels provide greater surface area for heat transfer, enabling higher power densities and longer continuous operating hours. Undersized profiles, however, restrict heat flow and cause elevated junction temperatures, leading to accelerated lumen depreciation, color shift, and reduced service life within linear LED lighting systems.
When discussing thermal management and power density compatibility, profiles such as UN2015B or UN1712A provide larger channel volumes and improved heat dissipation for higher-wattage LED strips, enabling longer continuous runs without thermal stress.
For glare-sensitive spaces, the combination of a TS4022A three-sided profile with an opal diffuser improves uniform light distribution while controlling glare.
Optical Behavior
Profile depth plays a critical role in determining light uniformity and visual comfort. Deeper LED housings allow improved light blending before output reaches the diffuser, significantly reducing visible LED points and glare. This design flexibility enables the use of lower LED density strips while maintaining a smooth appearance. Shallow profiles, by comparison, demand tighter LED spacing and more aggressive diffusion to achieve comparable visual results.

Complete LED Profile Selection Guide
Effective profile selection begins with application analysis rather than product comparison.
Application-Based Evaluation Matrix
| Project Condition | Recommended Profile Direction |
| High output requirement | Deep aluminum extrusion |
| Limited installation depth | High-density LED with shallow channel |
| Glare-sensitive environment | Deeper profile with opal diffuser |
| Long continuous runs | Profile with wiring space and joint system |
| Wet or outdoor area | Sealed, IP-rated aluminum housing |
Matching LED Strip Specifications
LED strip specifications must be carefully matched to the internal dimensions and thermal capacity of the selected aluminum extrusion. Strip width determines channel compatibility, while power density influences required profile mass for adequate heat dissipation. LED spacing affects diffuser performance and uniformity. Mismatched combinations often result in overheating, poor light quality, or installation difficulties, underscoring the importance of selecting strips and profiles as a coordinated system.
Kitchen Cabinet Lighting
Kitchen under-cabinet lighting typically favors slim surface-mounted LED channels that provide sufficient task illumination while maintaining controlled glare. Profiles must fit within limited installation clearances and allow easy access for maintenance or replacement. Diffuser selection is equally important, as excessive brightness or visible hotspots can reduce visual comfort. A well-chosen aluminum profile balances form factor, optical performance, and practical installation requirements in residential cabinetry.

Environmental Conditions
LED profiles installed in outdoor or damp environments require sealed aluminum housings with appropriate IP ratings to prevent moisture ingress. Beyond water protection, factors such as UV exposure, corrosion resistance, and thermal expansion must be evaluated. Coastal or high-temperature environments place additional stress on materials and finishes. Selecting profiles specifically designed for these conditions ensures durability, electrical safety, and consistent performance in demanding applications.
Linear Lighting Applications and Profile Selection Logic
Different environments impose distinct requirements on profile selection.
Application-to-Profile Logic
| Application Scenario | Key Requirements | Typical Profile Choice |
| Kitchen task lighting | Glare control, slim form | Surface-mounted shallow channel |
| Living space cove lighting | Soft indirect output | Deep recessed profile |
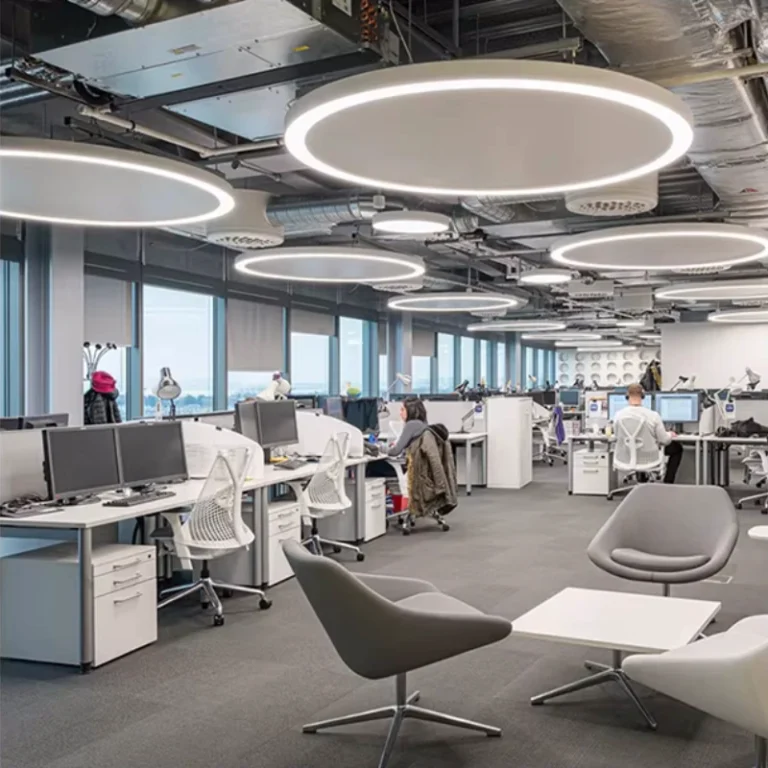
| Office environments | Uniformity, visual comfort | Suspended or recessed linear system |
| Retail displays | Directional flexibility | Adjustable or angled channel |
| Bathrooms / spas | Moisture resistance | IP-rated aluminum housing |
| Facades / exteriors | Durability, weather resistance | Outdoor-rated extrusion |
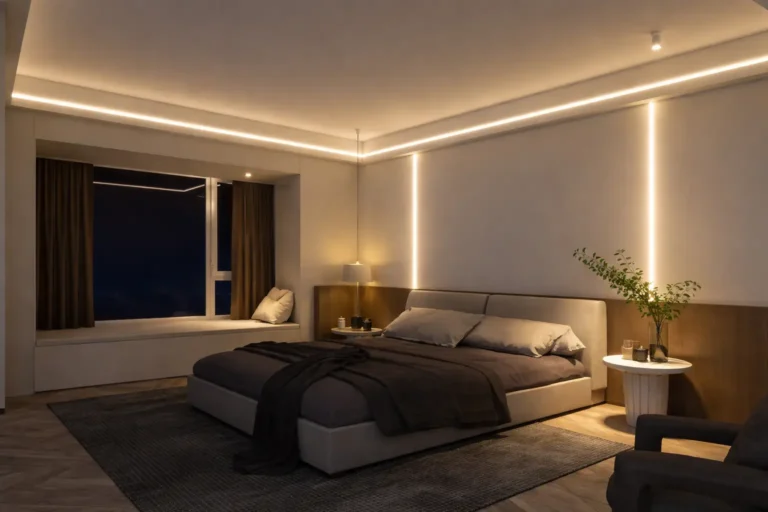
Residential Spaces
Residential lighting applications place strong emphasis on proportion, integration, and environmental suitability. Kitchens typically prioritize compact, surface-mounted LED profiles that fit within limited cabinet clearances while delivering focused task illumination. Living areas often favor deeper aluminum channels designed for indirect linear lighting, enabling softer ambient effects and reduced glare. In bathrooms and utility spaces, moisture-resistant LED housings with appropriate sealing are essential to ensure electrical safety, durability, and long-term performance within residential lighting systems.

UN1509B Recessed aluminium profile
Weight:0.092KG
Thickness: 0.8mm
PC color: Milk white
Size: L1000*W15*H9mm
End caps/Clips: 1pair/m
Aluminiu color: Silver/Black
For living room indirect lighting or linear track-style applications, profiles similar to the UN1509B offer a larger cross-section that improves light diffusion and internal light mixing. The increased profile depth allows LED points to blend more effectively behind the diffuser, creating softer ambient illumination while reducing glare in residential living spaces.
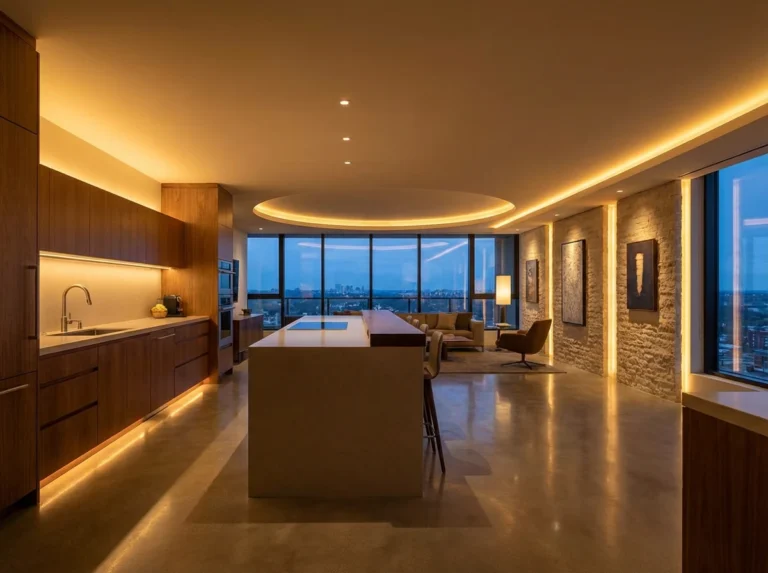
Commercial and Architectural Spaces
Commercial and architectural environments demand LED profiles that support consistent illumination, visual comfort, and scalable installation. Office spaces require linear lighting systems optimized for uniform light distribution and low glare to support prolonged visual tasks. Hospitality, retail, and public spaces prioritize continuous runs, seamless transitions, and refined architectural finishes that integrate with ceilings or walls. In these settings, aluminum profiles must balance optical performance, installation efficiency, and aesthetic continuity across large-scale lighting layouts.

TS4022A Three side light aluminium profile
Weight:0.232KG
Thickness: 0.8mm
PC color: Milk white
Size: L1000*W40*H22mm
End caps/Clips: 1pair/m
Aluminiu color: Silver/Black
For exhibition spaces, display cabinets, or retail showcase lighting, three-sided luminous profiles similar to the TS4022A or TS5022A enable enhanced multi-angle illumination. These profile designs distribute light across multiple surfaces simultaneously, improving product visibility, depth perception, and overall visual impact in commercial display environments.
Installation Best Practices
Successful installation of LED profiles relies on accurate planning, correct mounting hardware selection, and close coordination with electrical layouts. Recessed and trimless LED channels must be installed before final surface finishing, as their integration depends on precise alignment with drywall, plaster, or architectural panels. Surface-mounted systems, while more flexible, still require careful positioning to maintain straight lines and visual continuity across long linear runs. Suspension and corner profiles introduce additional considerations related to load distribution, anchoring points, and consistent spacing. Proper installation sequencing ensures that aluminum channels perform as intended while preserving the design integrity of the linear lighting system.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Many installation and performance issues originate from selecting undersized LED profiles that cannot adequately dissipate heat. Insufficient thermal planning often leads to premature lumen depreciation and reduced system lifespan. Other common mistakes include using incompatible mounting accessories, neglecting wiring space, or failing to plan for maintenance access. These issues are best avoided by specifying the lighting system at a holistic level rather than treating LED strips, profiles, and drivers as isolated components. System-level coordination improves reliability, simplifies installation, and minimizes long-term operational risks.

Quality Standards and Professional Support
High-quality LED profile manufacturers provide comprehensive technical documentation to support specification and project execution. This typically includes photometric reports, thermal testing data, material certifications, and detailed CAD drawings. Warranty coverage and compliance with recognized lighting standards further indicate product reliability. Access to sample programs allows designers and contractors to verify fit, finish, and optical performance before full deployment. Equally important is responsive technical support, which assists with profile selection, layout optimization, and installation guidance throughout the project lifecycle.
Future Trends in LED Profile Technology
LED profile technology continues to evolve alongside broader advancements in lighting systems. Smart controls, human-centric lighting concepts, and digital connectivity increasingly influence profile design and internal space requirements. Sustainable aluminum sourcing and recyclable materials are gaining importance as environmental standards tighten. Optical engineering improvements enable slimmer profiles with enhanced light uniformity, while rising LED efficacy shifts greater responsibility to intelligent thermal and structural solutions. As these trends converge, LED profiles will play an even more critical role in delivering efficient, adaptable, and future-ready linear lighting systems.

Conclusion
LED aluminum profiles form the structural and functional foundation of modern linear LED lighting systems. When specified as part of an integrated system, they ensure thermal stability, visual comfort, and long-term performance.
Professional lighting solutions require more than high-quality LEDs. They demand coordinated selection of profiles, optics, controls, and installation methods. As linear lighting continues to define contemporary spaces, the role of the LED profile remains central to successful lighting design.
FAQ
An LED profile, also known as an LED aluminum profile or LED channel, is a housing designed to hold LED strips securely while improving heat dissipation, light diffusion, and installation consistency. In linear lighting systems, LED profiles protect LED strips, enhance visual comfort, and ensure long-term performance by managing thermal and optical conditions effectively.
Choosing the right LED aluminum profile depends on application type, LED strip power density, installation method, and desired lighting effect. Shallow profiles are suitable for compact or decorative lighting, while deeper extrusions support higher wattage strips and better light mixing. Environmental conditions, mounting constraints, and glare control requirements should also be considered as part of a complete linear lighting solution.
Surface-mounted LED profiles are installed directly onto ceilings, walls, or furniture surfaces and are ideal for retrofit projects or limited installation depth. Recessed LED profiles are integrated into drywall, ceilings, or cabinetry to achieve a flush, seamless appearance. Recessed installations often require earlier planning but provide cleaner architectural results in modern linear lighting designs.
Profile depth directly influences light uniformity and glare performance. Deeper LED profiles allow better internal light mixing, reducing visible LED dots and improving diffusion. This enables the use of lower LED density strips without compromising visual quality. Shallow profiles typically require higher LED density or stronger diffusers to achieve comparable glare control in linear lighting applications.
Indirect and ambient lighting applications benefit from LED profiles with larger cross-sections that support soft, evenly distributed light. Deeper aluminum profiles enhance light blending behind the diffuser, creating smooth illumination with minimal glare. These profiles are commonly used in living rooms, hospitality spaces, and architectural cove lighting where visual comfort and atmosphere are priorities.
Common mistakes include choosing undersized profiles that cannot dissipate heat effectively, ignoring LED strip power density, selecting incompatible diffusers, and failing to plan for maintenance access. Treating LED profiles as standalone components rather than part of an integrated linear lighting system often leads to performance issues. Proper system-level specification helps avoid premature failure and visual defects.