Em instalações de LED de tiras de LED de longa distância, a queda de tensão é o problema central que causa brilho irregular e vida útil reduzida. Como a corrente em tiras de LED de baixa tensão (12V/24V) diminui com o aumento da distância, a perda de tensão devido à resistência do fio afeta significativamente o desempenho da iluminação na extremidade oposta.
Sem intervenção, a queda de tensão pode causar brilho excessivo na seção frontal e obscuridade na parte traseira, potencialmente acelerando o envelhecimento do cavaco devido à sobrecorrente. Além disso, as flutuações de tensão podem desencadear reações em cadeia, como superaquecimento localizado ou falha no circuito do driver.
Portanto, o endereçamento de queda de tensão é uma abordagem multidimensional que abrange o projeto de fonte de alimentação, otimização de circuitos e seleção de equipamentos para garantir uma operação estável do sistema de iluminação LED.
O que é queda de tensão?
A queda de tensão nas tiras de LED refere-se à diminuição gradual da tensão que ocorre durante a operação devido à resistência encontrada pela corrente, pois flui através de componentes como LEDs e placas de circuito. Esse fenômeno causa brilho reduzido e iluminação irregular em toda a tira.
Em termos leigos, ele se manifesta como um brilho inconsistente entre o início e o fim da tira - com a seção próxima à fonte de energia aparecendo mais brilhante enquanto a extremidade traseira escurece visivelmente.
A queda de tensão não afeta apenas o brilho e o apelo estético das tiras de LED, mas também pode reduzir sua vida útil. Portanto, entender e abordar corretamente os problemas de queda de tensão é crucial para melhorar o desempenho das tiras de LED.
Como mostrado abaixo: Quando a tensão de entrada na faixa de LED é de 12 V, após percorrer uma distância de 5 metros, a tensão cai para 9,01 V. Essa diferença de 3 V representa a queda de tensão.
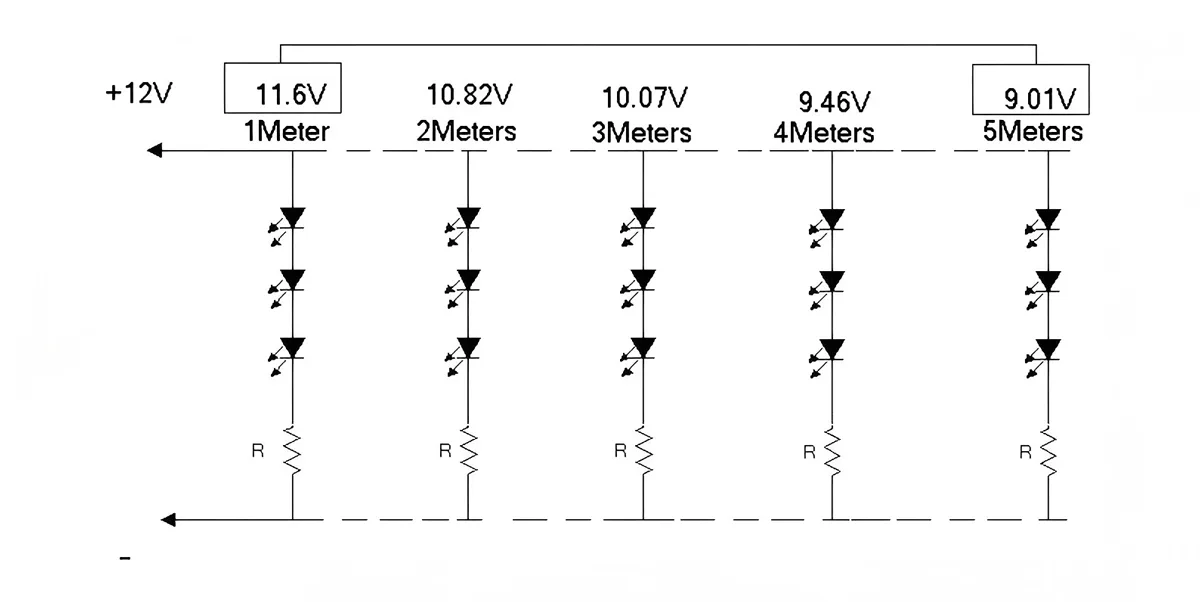
Quanto mais tempo a tira de LED, maior a queda de tensão. Uma queda de tensão superior a 5% pode reduzir a corrente de operação dos chips LED, diminuindo consequentemente seu brilho.
A queda de tensão é uma grandeza física que descreve a capacidade de um campo elétrico mover carga, também conhecida como diferença de potencial ou tensão. Quando a corrente flui através de um condutor (como fios ou resistores), a energia elétrica é convertida em calor devido à resistência do condutor, causando uma redução na diferença de potencial em seus terminais.
Leitura relacionada: Queda de tensão em fitas de LEDs: Causas e soluções.
Causas da queda de tensão nas luzes de tiras de LED
A queda de tensão nas luzes de tiras de LED é um problema comum que afeta a uniformidade da iluminação, decorrente de três fatores centrais: perda de resistência do fio de entrada, condutividade insuficiente da folha de cobre PCB e tensão de entrada excessivamente baixa. A seguir, analisamos esses três aspectos.
resistência do fio
A resistência do fio é uma quantidade física que mede o grau de oposição encontrado pela corrente que flui através de um condutor. Indica a capacidade do condutor de impedir o fluxo de corrente e é medido em ohms (ω). Sua magnitude depende do material do fio, comprimento, área de seção transversal e temperatura.

Metais como cobre e alumínio têm menor resistividade, enquanto ligas e materiais semicondutores exibem maior resistividade. Fios mais longos exibem maior resistência, enquanto uma área de seção transversal maior reduz a resistência. Além disso, os aumentos de temperatura podem elevar a resistência em certos materiais (por exemplo, metais).
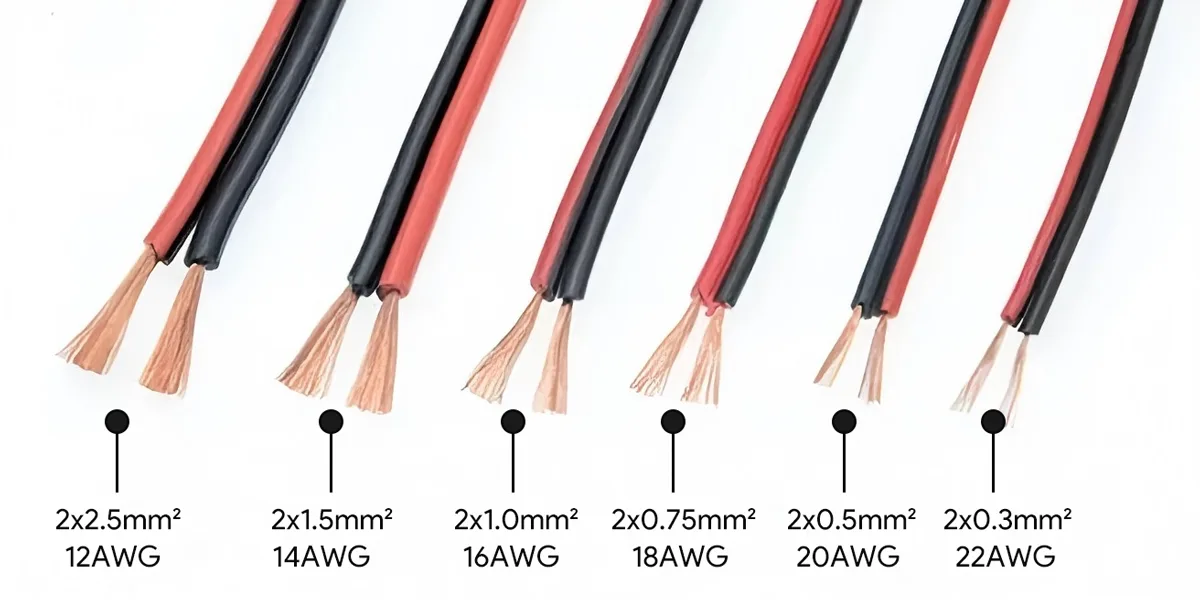
Certifique-se de que a fiação de tamanho adequado seja usada entre a fonte de energia e a tira de luz durante a operação. Fios mais grossos têm menor resistência, o que significa que eles transmitem eletricidade de forma mais eficiente. Com base na sua carga de energia (em watts) e comprimento do fio (em pés), você pode usar a tabela abaixo para selecionar o tamanho apropriado do fio para um gerenciamento conveniente de queda de tensão.
| Gráfico de queda de tensão de 12 volts (queda de 5%) | ||||||||||
| medidor de fio | 12 W | 24 W | 36 W | 48 W | 60 W | 72 W | 84 W | 96 W | 108 W | 120 W |
| 22 awg | 16 pés. | 8 pés. | 5 pés. | 4f. | 3 pés. | 3 pés. | 2 pés. | 2 pés. | 2 pés. | 2 pés. |
| 20 AWG | 25 pés. | 13 pés. | 8 pés. | 6 pés. | 5 pés. | 4 pés. | 4 pés. | 3 pés. | 3 pés. | 3 pés. |
| 18 AWG | 42 pés. | 21 pés. | 14 pés. | 10 pés. | 8 pés. | 7 pés. | 6 pés. | 5 pés. | 5 pés. | 4 pés. |
| 16 AWG | 75 pés. | 38 pés. | 25 pés. | 19 pés. | 15 pés. | 13 pés. | 11 pés. | 9 pés. | 8 pés. | 8 pés. |
| 14 awg | 117 4. | 58 pés. | 39 pés. | 29 pés. | 23 pés. | 19 pés. | 17 pés. | 15 pés. | 13 pés. | 12 pés. |
| 12 awg | 183 pés. | 92 pés. | 61 pés. | 46 pés. | 37 pés. | 31 pés. | 26 pés. | 23 pés. | 20 pés. | 18 pés. |
| 10 AWG | 275 pés. | 138 pés. | 92 pés. | 69 pés. | 55 pés. | 46 pés. | 39 pés. | 34 pés. | 31 pés. | 28 pés. |
| Gráfico de queda de tensão de 24 volts (queda 5%) | ||||||||||
| medidor de fio | 12 W | 24 W | 36 W | 48 W | 60 W | 72 W | 84 W | 96 W | 108 W | 120 W |
| 22 awg | 73 pés. | 37 pés. | 24 pés. | 18 pés. | 15 pés. | 12 pés. | 10 pés. | 9 pés. | 8 pés. | 7 TT. |
| 20 AWG | 117 pés. | 58 pés. | 39 pés. | 29 pés. | 23 pés. | 19 pés. | 17 pés. | 15 pés. | 13 pés. | 12 pés. |
| 18 AWG | 183 pés. | 92 pés. | 61 F+. | 46 pés. | 37 pés. | 31 pés. | 26 pés. | 23 pés. | 20 pés. | 18 pés. |
| 16 AWG | 300 pés. | 150 pés. | 100 pés. | 75 pés. | 60 pés. | 50 pés. | 43 pés. | 38 pés. | 33 pés. | 30 pés. |
| 14 awg | 475 pés. | 238 pés. | 158 pés. | 119 pés. | 95 pés. | 79 pés. | 68 pés. | 59 pés. | 53 pés. | 48 pés. |
| 12 awg | 750 pés. | 375 pés. | 250 pés. | 188 pés. | 150 pés. | 125 pés. | 107 pés. | 94 pés. | 83 pés. | 75 pés. |
| 10 AWG | 1092 pés. | 546 pés. | 364 pés. | 273 pés. | 218 pés. | 182 pés. | 156 pés. | 136 pés. | 121 pés. | 109 pés. |
Observação:
- Calcule a carga total em watts.
- Meça a distância da fonte de energia à tira de LED.
- Selecione um medidor de fio apropriado.
Minimize o comprimento de operação da faixa de LED. A melhor abordagem é alimentá-lo da seção do meio.
Por exemplo, suponha que você precise de uma faixa de 50 pés para iluminar uma sala. Recomendamos colocar a fonte de energia no meio e dividir a tira em duas seções de 25 pés correndo para a esquerda e para a direita, em vez de um comprimento contínuo de 50 pés. Ele não precisa ser dividido exatamente pela metade - se for mais conveniente, dividir em seções de 20 pés e 30 pés é aceitável.
Se não for viável colocar a fonte de alimentação no meio, a segunda opção é passar um fio de tamanho adequado (consulte o gráfico de queda de tensão) da fonte de energia até o meio da tira. Dessa forma, você mantém a energia no início da corrida, enquanto o fio de tamanho adequado (oferecendo menor resistência do que a própria tira de LED) lida com o trabalho pesado.
Limitações na folha de cobre para tiras de LED
Embora a folha de cobre ofereça condutividade térmica superior em comparação com materiais padrão, ele se oxida facilmente em ambientes de alta temperatura, reduzindo a eficiência da dissipação de calor. A operação prolongada em temperaturas elevadas pode acelerar a degradação da folha de cobre, reduzindo a vida útil da tira.
A folha de cobre é fina e quebradiça. A pressão externa ou a flexão durante a instalação ou uso podem causar fraturas, resultando em curtos-circuitos ou luzes que não funcionam.
Além disso, a folha de cobre corrói facilmente em ambientes úmidos ou de alta temperatura, exigindo tratamentos adicionais de antioxidantes (como revestimento de níquel ou revestimento de agente de acoplamento de silano) para prolongar sua vida útil.
Níveis de tensão da fonte de alimentação (12V vs 24V vs 48V)
As faixas de LED de 12, 24 V e 48 V exibem diferenças significativas no impacto da queda de tensão e na comparação de desempenho:
- As tiras de 12 V apresentam perdas de linha notáveis devido à tensão mais baixa e corrente mais alta. O brilho permanece estável em 5 metros, mas uma queda significativa de tensão ocorre além de 5 metros, causando um decaimento do brilho na extremidade traseira.
- As tiras de 24 V reduzem a corrente pela metade, reduzindo as perdas de linha e permitindo uma transmissão sem queda de tensão em 10 metros com uniformidade superior de brilho.
- As tiras de 48 V operam em correntes mais baixas - apenas 1/4 de tiras de 12 V com potência equivalente - minimizando a queda de tensão. Eles se adaptam a uma iluminação de ultralonga (por exemplo, mais de 30 metros), mas exigem uma fonte de alimentação estável.
Em comprimentos iguais, as tiras de 24 V normalmente oferecem maior potência e brilho do que as tiras de 12 V. As tiras de 48 V, operando em tensão mais alta, podem gerar mais chips LED para aumentar o brilho. As tiras de alta tensão (24 V/48 V) consomem menos corrente e sofrem perdas de linha inferior, tornando-as mais eficientes em termos de energia para uso a longo prazo.
As tiras de 12 V requerem uma corrente mais elevada, exigindo maior dissipação de calor e são propensas a superaquecimento em espaços confinados. 24V/48V: A corrente mais baixa reduz o estresse por calor, mas a proteção contra o isolamento em ambientes de alta tensão deve ser assegurada. As tiras de 12 V têm custos iniciais mais baixos, mas comprimentos estendidos exigem transformadores ou fiação adicionais, potencialmente aumentando as despesas gerais.
Comparação de desempenho de tiras de LED de 12 V x 24 V x 48 V
| Tipo de fita LED | DC12V | CC 24 V | DC48V |
| Atual | Mais alto | Inferior | mais baixo |
| Distância de instalação | ≤5m | ≤10m | ≤30m |
| Custo | Aumento do custo da fonte de alimentação para longas distâncias | baixo custo | relativamente econômico |
| Corte o comprimento | curta distância | distância média | distância relativamente longa |
| Segurança | Baixa tensão, relativamente seguro | seguro | Menor segurança, requer cuidados de isolamento |
| Dissipação de calor | Pobres | Bom | bastante bom |
Resumo: A seleção de tensão requer equilíbrio, brilho, custo e segurança. Opte por 12V para uso residencial de curta distância, 24V para aplicações comerciais de média a longa distância, e priorize 48V para distâncias ultra longas ou projetos de alta potência.
leia o blog “Quando escolher sistemas de tiras de LED de 12, 24 V ou 48 V? (atualizado para uso comercial)” para aprender mais.
Como calcular a queda de tensão?
Calcular a queda de tensão das tiras de LED requer considerar fatores como corrente, resistência do fio e comprimento.
Fórmula básica: queda de tensão = corrente x resistência do fio
onde:
- Corrente (A) = potência total da tira (W) ÷ Tensão de operação (V)
- Resistência do condutor (ω) = resistividade (fio de cobre: 0,0175 Ω·mm²/m) × Comprimento do condutor (M) ÷ Área da seção transversal do condutor (mm²)
Exemplo: Tira de LED de 24 V, potência de 240 W, comprimento do condutor de 40 m, calibrador de fio de 4 mm ²:
Corrente = 240 ÷ 24 = 10a
Resistência = 0,0175 × 40 ÷ 4 = 0,175Ω
Queda de tensão = 10a × 0,175Ω = 1,75 V
Em sistemas de baixa tensão (por exemplo, 12V/24V), a queda de tensão normalmente não excede 5% da tensão nominal (por exemplo, sistemas de 24V permitem ≤1,2 V). Se a queda de tensão exceder as especificações, aumente o medidor de fio ou diminua a distância da fonte de alimentação.
Não quer lidar com cálculos complicados? Em seguida, use um calculadora de queda de tensão online!
Recomendações de seleção de fios: Para corridas longas (>10 metros), priorize os sistemas de 24 V/48 V para reduzir a corrente; a fonte de alimentação de extremidade única para tiras de LED de 12 V é recomendada para ≤ 5 metros; 24 V ≤ 10 metros; uma fonte de alimentação dupla pode se estender até 20 metros.
Testes práticos: Um multímetro pode verificar o efeito de divisão de tensão dos resistores em série em circuitos LED.
Soluções práticas para evitar queda de tensão
A queda de tensão nas tiras de LED causada pela resistência do circuito e pela perda de corrente afeta diretamente a uniformidade e a vida útil da iluminação. Abaixo estão vários métodos eficazes para evitar queda de tensão.
Injeção de energia de ambas as extremidades
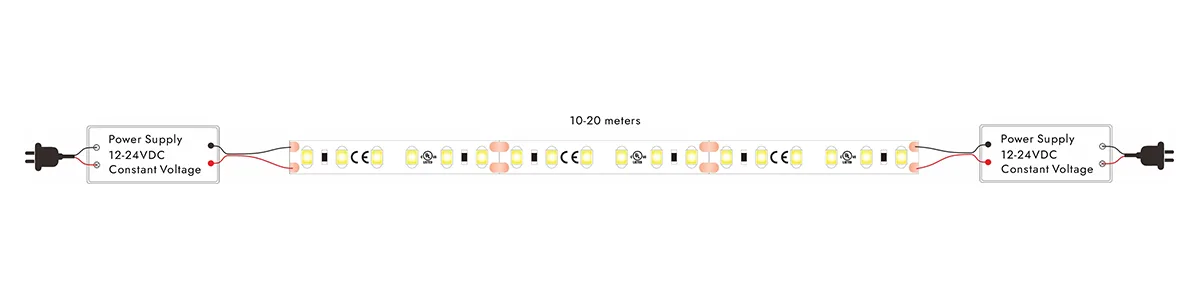
Fonte de alimentação de extremidade dupla: para tiras mais longas, implemente uma solução de fonte de alimentação de extremidade dupla conectando fontes de energia ao início e ao final da tira. Isso garante um fornecimento estável de tensão em toda a faixa, evitando o brilho desigual. Se possível, adicione pontos de potência intermediários ao longo da faixa para reduzir ainda mais a queda de tensão.
Vários pontos de injeção de energia
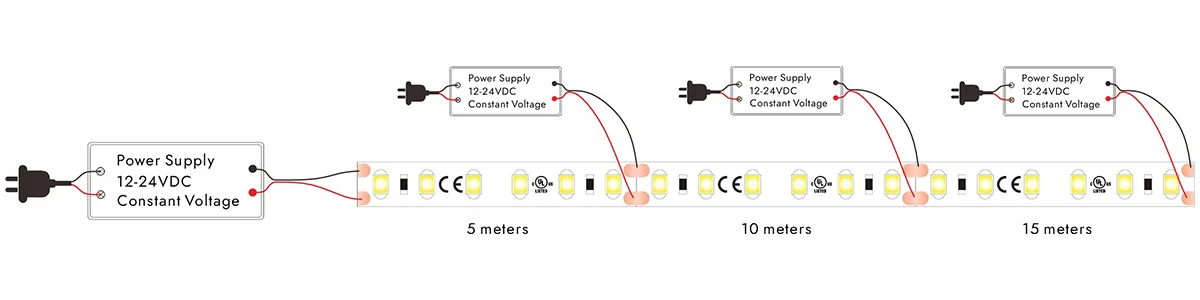
Controle segmentado: divida as tiras de LED longas em várias seções, cada uma com alimentação por um driver independente. Essa abordagem minimiza efetivamente a queda de tensão por seção, aumentando a estabilidade geral do sistema e a uniformidade do brilho.
Otimize o layout e as conexões da tira: certifique-se de que a fiação seja funcional e esteticamente agradável, evitando cabos emaranhados ou excessivamente dobrados. Ao conectar as tiras, garanta um contato seguro e confiável para evitar quedas de tensão e resistência adicionais causadas por conexões soltas ou com defeito.
Use tiras de LED de 24 V ou 48 V
O emprego de tiras de LED de 24 V ou 48 V mitiga efetivamente os problemas de queda de tensão, exibindo um impacto significativamente menor em comparação com as tiras de 12 V. Enquanto as tiras de 12v experimentam um decaimento notável do brilho além de 5 metros, as tiras de 24 V suportam comprimentos de até 10 metros sem exigir fontes de energia adicionais. Seus pontos de corte flexíveis (cada 6 LEDs) os tornam ideais para instalações de longa distância.
As níveis de potência equivalentes, as tiras de 48 V desenham apenas metade da corrente das tiras de 24 V. De acordo com a fórmula de perda de potência Q=I²R, os sistemas de 48V exibem perdas térmicas significativamente reduzidas e menores taxas de queda de tensão. Os sistemas de 48V permitem que mais acessórios sejam conectados em série, reduzindo os custos de fiação e mão de obra; as tiras de 24 V simplificam a instalação, eliminando os frequentes reforços de energia. As tiras de 24 V geram menos calor, tornando-as adequadas para operação prolongada; os sistemas de 48 V otimizam ainda mais a eficiência energética.
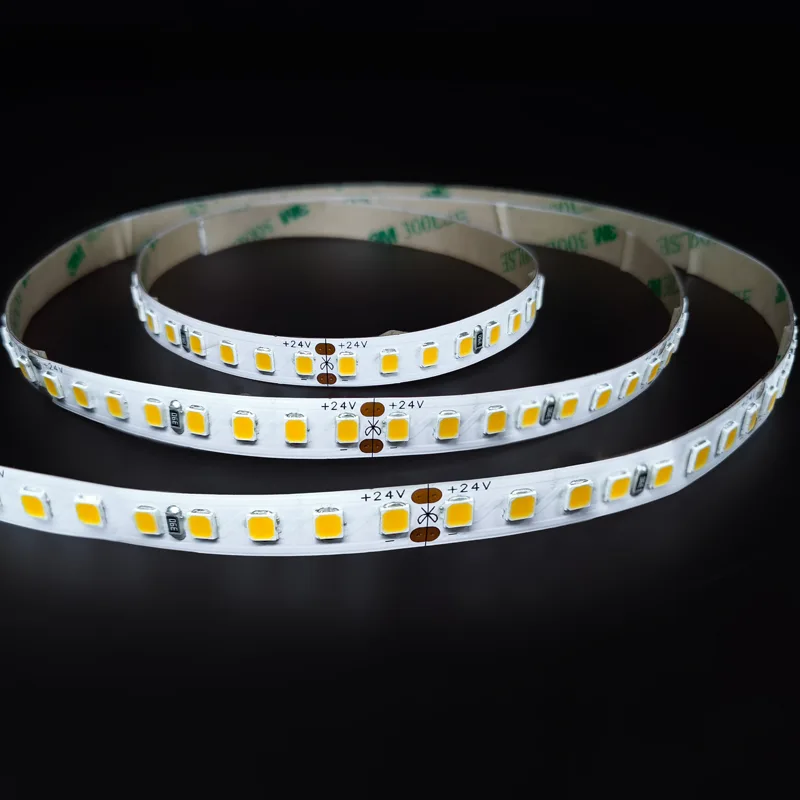

Luzes de tiras de LED DC24V 2835 de alto brilho – 180LM/Watt
Modelo: FQX10T128C
QTD. de LED por metro: 128
Largura do PCB: 10 mm
Temperatura de cor: 2700K/3000K/4000K/5000K/6500K
Tensão de entrada: CC 24 V
Potência por metro: 12W
Grau IP: IP20/IP54/IP65/IP67/IP68
Garantia: 5 anos
Acima, a função suporta a personalização.
fios mais grossos
Use fios mais grossos ou reduza o comprimento do fio: a resistência do fio é um fator importante que causa queda de tensão. Portanto, o uso de fios mais grossos pode reduzir a resistência e mitigar os problemas de queda de tensão. Além disso, minimizar o comprimento do fio entre a tira e a fonte de energia reduz efetivamente a resistência e a queda de tensão.
Use soluções de corrente constante
As tiras de LED de corrente constante resolvem fundamentalmente quedas de tensão induzidas por flutuação de tensão inerentes a faixas de tensão constantes por meio de uma regulação precisa da corrente.
Suas vantagens principais se manifestam em três aspectos: primeiro, os circuitos de corrente constante ajustam automaticamente o fluxo de corrente. Quando a impedância da linha aumenta ou a tensão da fonte de alimentação flutua, eles mantêm a estabilidade da corrente do LED em um valor definido (por exemplo, 20mA ±3%), garantindo um brilho consistente do início ao fim. Em segundo lugar, a corrente constante evita o decaimento acelerado da luz causado pelo superaquecimento localizado nos LEDs. Os testes mostram que a vida útil do LED se estende por mais de 30% em unidade de corrente constante.
Além disso, esta solução apresenta baixa sensibilidade à resistência da linha. Mesmo com fios finos (por exemplo, 28 AWG) ou fiação de longa distância, a compensação de queda de tensão dinâmica se ajusta dinamicamente às perdas de linha de deslocamento. Este design é particularmente adequado para cenários que requerem fiação flexível, como tiras de luz decorativas de longa distância, garantindo um brilho consistente da tira LED.
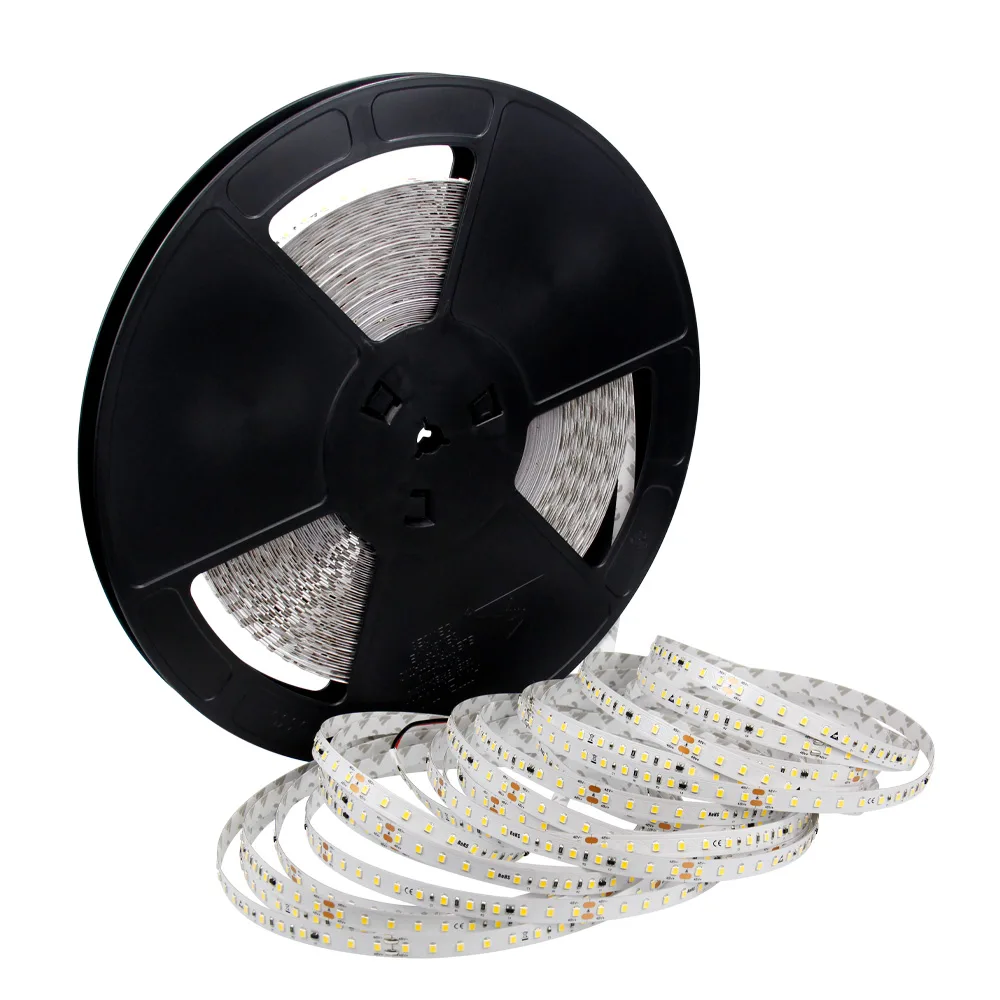

DC24V/DC48V Corrente Constante Luzes de LED de longa duração
Modelo principal: FQW10T120D
Tipo de LED: SMD2835
QTD. de LED por metro: 120
Largura do PCB: 10mm/12mm
Comprimento: 10m/15m/20m/30m/40m/50m
Tensão de entrada: DC24V/DC48V
Potência por metro: 10W/7.2W
Temperatura de cor: 2700K/3000K/4000K/5000K/6500K
Grau IP: IP20/IP54/IP65/IP67/IP68
Garantia: 3 anos
Acima, a função suporta a personalização.
Use amplificadores/repetidores na faixa RGB/RGBW
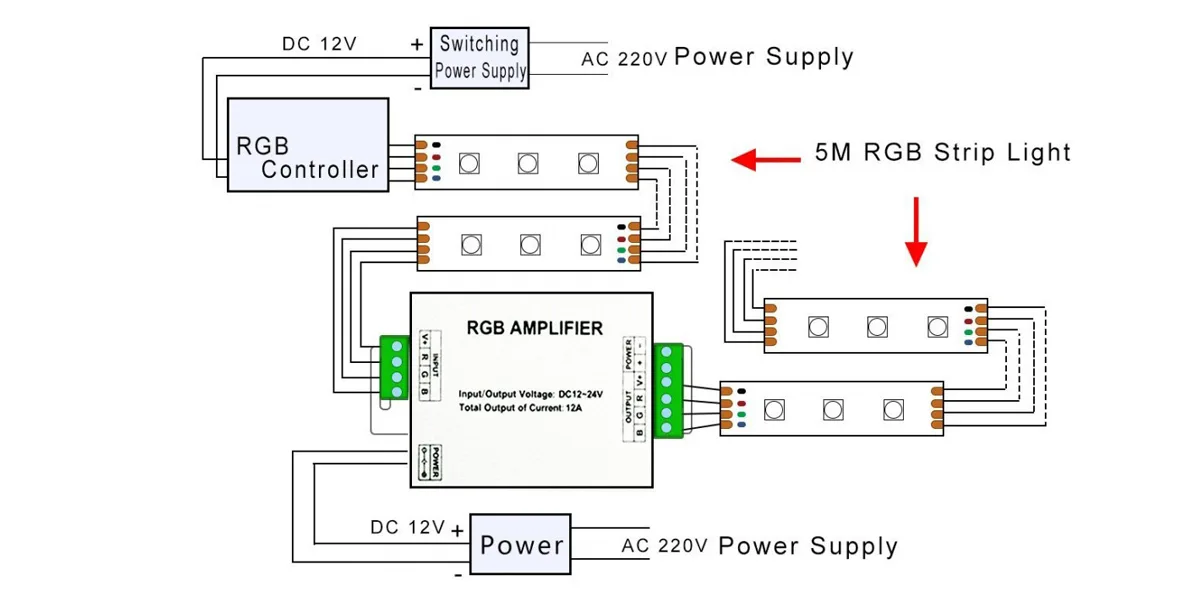
Durante a transmissão de longa distância de tiras RGB/RGBW, os sinais se degradam devido à resistência e interferência, causando brilho irregular ou distorção de cor na extremidade da tira. Para tiras de 12V (normalmente ≤5 metros), os amplificadores/repetidores permitem um controle estável em distâncias maiores (por exemplo, 30+ metros). As tiras de alta tensão (por exemplo, 24 V/48 V) têm menor consumo de corrente e redução da queda de tensão, minimizando a dependência de amplificadores/repetidores. Ao usar tiras de 12 V, instale um repetidor a cada 10 metros para compensar a queda de tensão.
Em resumo, o endereçamento da queda de tensão da faixa de LED requer uma abordagem multifacetada, incluindo a melhoria dos métodos de alimentação, otimizando a fiação e o layout e a utilização de equipamentos auxiliares. Os usuários podem selecionar soluções adequadas com base em condições específicas para melhorar o desempenho e o apelo estético de suas instalações de LED.
Recomendações para designers e compradores
Como elemento central do design moderno de iluminação, as especificações de tensão das luzes LED Strip—12V/24V/48V—imultam diretamente os resultados do projeto e a experiência do usuário.
O sistema de 12V é excelente em segurança e flexibilidade, tornando-o ideal para decoração de casa. O sistema de 24 V atinge um equilíbrio entre queda de tensão e conveniência de corte, tornando-se a principal escolha para ambientes comerciais. O sistema de 48V, com perda de linha ultrabaixa, foi projetado especificamente para projetos de iluminação em grande escala.
Os designers devem selecionar com base na distância de transmissão, nos requisitos de segurança e nas considerações de custo. Os compradores devem priorizar as necessidades reais da aplicação e evitar que busquem cegamente especificações de tensão mais altas.
Comparação de classificação de tensão de tira de LED
| Classificação de tensão | Principais vantagens | Aplicações adequadas | considerações |
| 12V | Alta segurança (sem risco de choque elétrico), luz suave para proteção dos olhos, fácil instalação (suporte autoadessivo) | Decoração da casa (quartos/escadas/cabinetes) para casa (quartos infantis), iluminação ambiente de curta distância (estudo/vazio), iluminação de equipamentos auxiliares | Requer uma extensão de potência além de 5 metros para evitar queda de tensão em corridas longas |
| 24V | Queda de tensão mínima (suporta 10m sem aumento de energia), corte flexível (corte a cada 6 luzes), equilibra segurança e eficiência | Decoração da casa, vitrines/luzes comerciais, iluminação de projeto de médio alcance | Requer fonte de alimentação dedicada, custo ligeiramente superior ao dos sistemas de 12 V |
| 48V | Perda mínima de linha (corrente apenas metade de 24 V), adequada para conexões em série ultralonga, alta estabilidade do projeto | Projetos de iluminação arquitetônica em grande escala, lavagem de longa distância, projetos de iluminação de alta densidade | Requer instalação profissional com requisitos rígidos de fiação |
Recomendações de seleção de design
Cenários com prioridade à segurança (por exemplo, casas/espaços infantis): opte por sistemas de 12V para segurança e facilidade de instalação. Emparelhe com tiras RGB para efeitos de iluminação ambiente.
Aplicações comerciais de curto a médio alcance: Recomendam tiras de 24 V para equilibrar o custo e o desempenho. Para iluminação da caixa de exibição, assegure-se de um brilho consistente nos pontos de corte.
Projetos em grande escala: Adote sistemas de 48V para minimizar as perdas de linha. Por exemplo, ao conectar mais de 50 metros de iluminação de contorno arquitetônico em série, a queda de tensão de 48V é de apenas 1/4 de 12V.
Guia do comprador
Usuários residenciais: Ao selecionar as faixas de 12 V, priorize as classificações à prova d'água (por exemplo, IP65 para varandas) e a funcionalidade de controle remoto. Escolha LEDs de alta densidade (por exemplo, 60 LEDs/metro) para garantir uma iluminação uniforme.
Compradores de projetos: Para tiras de 24 V/48 V, verifique os dados de teste de queda de tensão dos fornecedores e solicite relatórios de comparação de decaimento de brilho de 5 m/10 m.
Controle de custos: os sistemas de 12 V têm custos iniciais mais baixos, mas exigem suplementação de energia para corridas longas; os sistemas de 48 V têm custos unitários mais altos, mas economizam na fiação e no trabalho - avalie os custos totais do ciclo de vida de forma abrangente.
Notas importantes: Todas as tensões exigem fontes de alimentação de alta qualidade para evitar flutuações de tensão que reduzem a vida útil. Em ambientes úmidos (por exemplo, banheiros/jardim), selecione sempre os modelos à prova d'água (IP65 ou superior). Teste a queda de tensão antes de instalações de longa distância e use uma fonte de alimentação segmentada quando necessário.