Em projetos modernos de iluminação, a flexibilidade tornou-se tão importante quanto o brilho ou a eficiência. Designers, engenheiros e empreiteiros não estão mais satisfeitos com o controle simples de ligar/desligar - eles precisam de uma iluminação que se adapte a diferentes humores, funções e objetivos de energia. É aqui que as luzes de LED dimmíveis desempenham um papel crucial. No entanto, com vários protocolos de escurecimento disponíveis, desde opções básicas analógicas até sistemas digitais avançados, a escolha da solução certa pode ser confusa. Neste artigo, exploraremos as principais opções de luz LED reguláveis, compararemos seus pontos fortes e fracos e forneceremos orientações práticas sobre como selecionar o método de escurecimento mais adequado para o seu projeto.
Por que o escurecimento é importante na iluminação de tiras de LED
A iluminação não é mais apenas fornecer brilho suficiente para ver. Em projetos comerciais e residenciais, espera-se que crie conforto, economize energia e se adapte a diferentes tarefas. As luzes de LED dimmable oferecem aos designers e proprietários de edifícios a capacidade de ajustar a iluminação em vez de se contentar com uma abordagem de tamanho único.
Do ponto de vista da energia, o escurecimento reduz diretamente o consumo de energia. Quando as luzes são reduzidas para a saída 50%, o uso de energia normalmente cai em uma quantidade semelhante, o que se traduz em contas de serviços públicos mais baixas e uma pegada ambiental menor. Para empresas que gerenciam espaços grandes, essa eficiência pode resultar em economias significativas a longo prazo.
Conforto e atmosfera são outro motivo importante. Uma loja de varejo pode querer luz mais brilhante durante os horários de pico para destacar os produtos, enquanto um lounge do hotel pode preferir um brilho mais quente e suave à noite. As tiras dimerizáveis permitem que um sistema atenda a ambas as necessidades sem alterar os acessórios.
Há também a questão da durabilidade. A execução de LEDs com energia reduzida gera menos calor, o que pode prolongar a vida útil da tira e da fonte de alimentação. Para os gerentes de instalações, isso significa menos substituições e custos de manutenção mais baixos.
Finalmente, o escurecimento permite a integração com sistemas de controle inteligente. Os escritórios podem automatizar os níveis de luz com base na luz do dia e os locais de entretenimento podem sincronizar as faixas com música ou efeitos de palco. Este nível de controle tornou-se padrão em design moderno de iluminação, e as tiras de LED reguláveis o tornam acessível em um formato flexível e compacto.

Resumo dos métodos de escurecimento da tira de LED
Quando se trata de luzes LED dimmeráveis, não existe uma única solução “universal”. Diferentes protocolos de escurecimento foram desenvolvidos para atender às necessidades de várias aplicações, desde simples reformas domésticas até projetos comerciais de grande escala e locais de entretenimento. Cada método tem suas vantagens, limitações e requisitos técnicos.
Antes de mergulhar nos detalhes de como cada sistema funciona, é útil dar um passo atrás e olhar para o quadro geral. A tabela a seguir fornece uma comparação lado a lado das opções de escurecimento mais comuns – PWM, Triac, 0-10V, DALI e DMX – para que você possa ver rapidamente como eles diferem em termos de definição, pontos fortes, desvantagens e aplicativos típicos.
| método de escurecimento | Definição | Prós | Contras | Aplicações típicas |
| PWM (modulação da largura do pulso) | Ajusta o brilho ligando/desligando rapidamente os LEDs e variando o ciclo de trabalho. | Ampla gama de escurecimento, econômico, simples de implementar. | Pode introduzir flicker se mal projetado; limitado para grandes redes. | Residencial, varejo, iluminação geral. |
| Triac (escurecimento por corte por fases) | Usa tecnologia de corte de fase AC, requer um driver de LED compatível. | Funciona com dimmers de parede tradicionais, retrofit fácil. | Problemas de compatibilidade, menos precisos, risco de cintilação. | Upgrades domésticos, pequenos projetos. |
| 0-10 V escurecimento | Controle analógico usando um sinal de 0–10V para regular o brilho. | Confiável, amplamente adotado em ambientes comerciais. | Necessita de fiação de controle extra; recursos avançados limitados. | Escritórios, escolas, hospitais, fábricas. |
| DALI (interface de iluminação endereçável digital) | Protocolo digital com comunicação bidirecional e capacidade de endereçamento. | Inteligente, flexível, permite agrupar e controlar individualmente. | Custo mais alto, requer comissionamento. | Hotéis, escritórios sofisticados, edifícios inteligentes. |
| DMX (Digital Multiplex) | Protocolo digital projetado para iluminação de palco, suporta efeitos RGB. | Alta precisão, ideal para faixas de LED que mudam de cor. | Fiação complexa, requer uma configuração qualificada. | Teatros, clubes, entretenimento, iluminação de fachadas. |
Com essa visão geral em mente, agora podemos examinar cada método de escurecimento, explorando como ele funciona na prática, o que o torna único e onde se encaixa melhor em projetos do mundo real.
Escurecimento do PWM (modulação da largura do pulso)
Definição
PWM, ou modulação por largura de pulso, é uma das formas mais comuns de controlar o brilho das luzes LED. Em vez de diminuir a tensão para os LEDs, o PWM funciona ligando e desligando rapidamente a luz em uma frequência muito alta. Ao alterar a proporção de tempo livre para tempo de desligamento (conhecido como ciclo de trabalho), a saída média da luz parece mais brilhante ou mais escura para o olho humano.
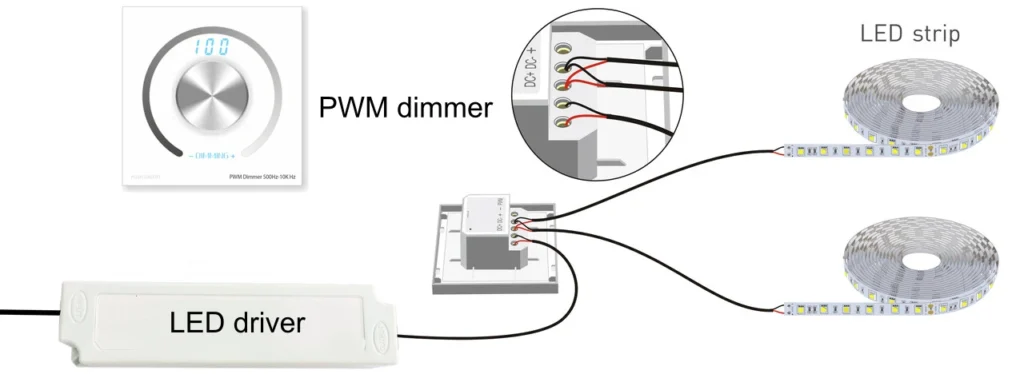
Caraterísticas
Uma das características principais do PWM é sua ampla faixa de escurecimento. Os LEDs podem ser ajustados de forma suave, desde o brilho total até níveis muito baixos, sem uma mudança significativa de cor, tornando-o uma opção versátil para muitos projetos.
Outro recurso é a compatibilidade. O escurecimento PWM é suportado por uma ampla variedade de drivers e controladores de LED, desde controles remotos simples até sistemas avançados inteligentes. Isso o torna um ponto de entrada fácil para usuários residenciais e pequenas instalações comerciais.
Custo-benefício também é uma característica importante. Em comparação com os protocolos digitais mais avançados, os sistemas de escurecimento PWM são relativamente acessíveis e exigem equipamentos menos especializados.
Prós e contras
A principal vantagem do PWM é a sua flexibilidade. Ele oferece uma qualidade de luz consistente em diferentes níveis de brilho e pode ser usado em tiras LED de cor única e ajustáveis em branco e RGB. Seu custo mais baixo também o torna uma escolha prática para projetos com orçamentos apertados.
Por outro lado, os sistemas PWM mal projetados podem introduzir um piscar de olhos visível, especialmente em níveis de escurecimento muito baixos ou quando gravados por câmeras. Embora o PWM de alta frequência possa reduzir esse efeito, requer um design cuidadoso do driver e do sistema de controle. O PWM também é menos adequado para redes de grande porte, onde protocolos de comunicação analógica ou digital oferecem mais estabilidade.
Aplicações
O escurecimento PWM é amplamente utilizado em iluminação residencial, como tiras de armário, iluminação de destaque ou instalações decorativas. Em ambientes de varejo, ele pode fornecer ajuste de brilho flexível para destacar produtos em diferentes horários do dia. Projetos comerciais menores, como cafés ou boutiques, também se beneficiam de sua acessibilidade e facilidade de uso.

Dimerização TRIAC
Definição
Triac Escurecimento, também conhecido como escurecimento por corte de fase, é um método originalmente projetado para lâmpadas incandescentes e halogênicas. Funciona cortando uma parte da forma de onda CA antes de atingir a fonte de luz, reduzindo efetivamente a quantidade de energia fornecida. Quando aplicado à iluminação LED, um driver AC/DC compatível é necessário para traduzir esse sinal em uma alimentação DC estável para os LEDs.
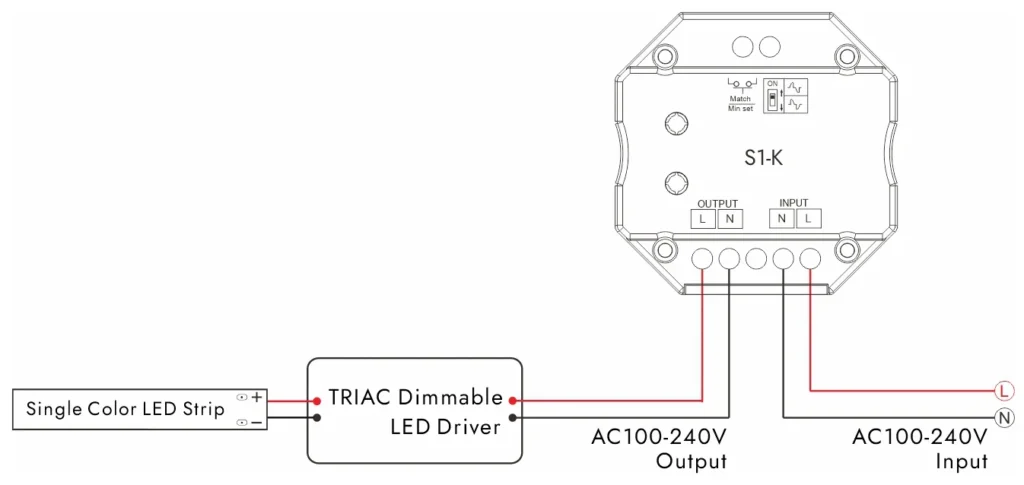
Caraterísticas
A característica mais notável do Triac Dimming é sua compatibilidade com os dimmers tradicionais de parede. Isso o torna uma solução atraente para projetos de retrofit, onde já existem fiação e interruptores existentes. Os usuários geralmente podem manter seus antigos interruptores dimmer enquanto atualizam para a tecnologia LED.
Outro aspecto importante é a sua simplicidade. Como funciona diretamente com a entrada CA, o escurecimento Triac não requer fiação de controle adicional. Para proprietários ou instaladores que procuram uma atualização simples, isso pode economizar tempo e custos durante a instalação.
Finalmente, o escurecimento Triac está amplamente disponível. Por ser usado há décadas na indústria de iluminação, os drivers e dimmers compatíveis com Triac são fáceis de obter na maioria dos mercados.
Prós e contras
A principal vantagem do escurecimento Triac é a conveniência. Ele permite uma transição suave de tecnologias de iluminação mais antigas para LEDs sem a necessidade de reconectar completamente um sistema. Também é relativamente acessível em comparação com os protocolos de controle digital.
Por outro lado, o escurecimento do Triac pode apresentar problemas de compatibilidade. Nem todos os drivers de LED respondem bem aos sinais de corte de fase, o que pode resultar em cintilação, alcance limitado de escurecimento ou ruídos de zumbido. Sua precisão também é menor do que protocolos como DALI ou 0-10V, tornando-o menos adequado para projetos que exigem um controle fino.
Aplicações
O escurecimento Triac é mais comumente usado em iluminação residencial, principalmente em projetos de renovação, onde os proprietários desejam tiras de LED dimerizáveis sem alterar sua infraestrutura elétrica. Também é adequado para pequenos espaços comerciais, cafés ou restaurantes que preferem um dimmer tradicional montado na parede para controle básico de iluminação.

0-10 V escurecimento
Definição
O escurecimento de 0 a 10 V é um dos métodos mais antigos e amplamente adotados para controlar a iluminação LED em ambientes comerciais. Ele usa um sinal de baixa tensão, normalmente entre 0 e 10 volts, para regular o brilho. A 10V, a faixa de LED funciona com brilho total, enquanto em 0V a luz está em seu nível mínimo ou completamente desligada, dependendo do design do driver.
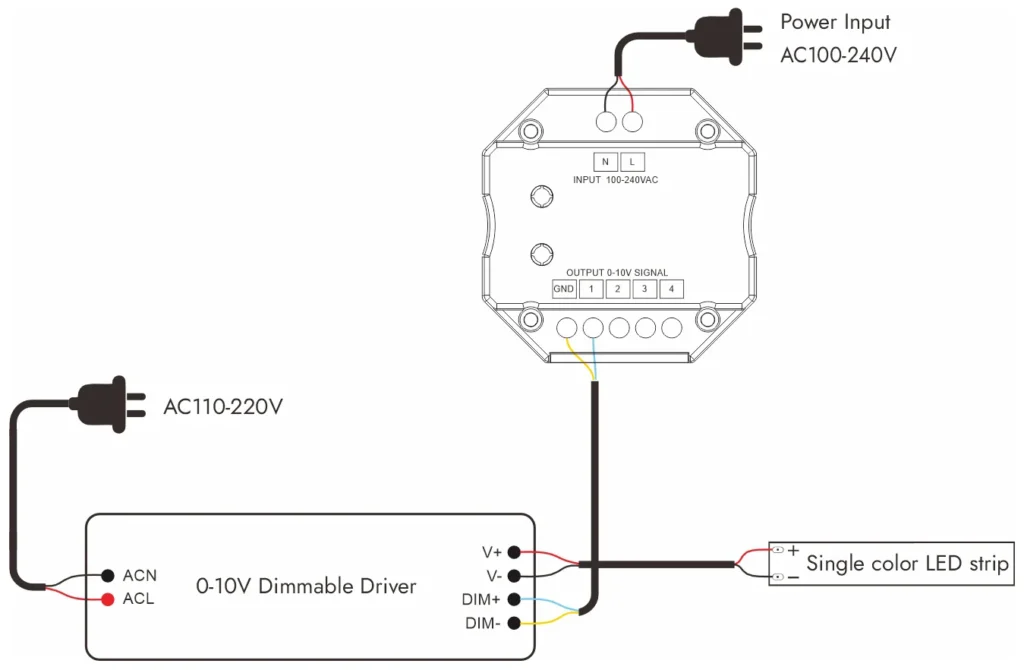
Caraterísticas
Uma das principais características do escurecimento de 0 a 10 V é a confiabilidade. Por ser um sistema analógico, o sinal de controle é simples e não está sujeito a erros de comunicação digital. Isso o torna uma solução confiável para um desempenho de longo prazo em ambientes exigentes.
Outro recurso é a escalabilidade. 0 Os sistemas de 10 V são relativamente fáceis de expandir, permitindo que vários drivers de LED sejam controlados pelo mesmo sinal. Isso é especialmente útil em salas grandes ou em espaços abertos, onde níveis de iluminação consistentes são necessários em muitos acessórios.
No entanto, o sistema exige um par extra de fios para o sinal de controle, além da fiação de alimentação principal. Embora essa seja uma pequena consideração em novas construções, ele pode adicionar complexidade em cenários de retrofit.
Prós e contras
As principais vantagens do escurecimento de 0 a 10 V são estabilidade, simplicidade e ampla aceitação da indústria. É uma tecnologia comprovada que funciona bem com tiras de LED e pode se integrar a sensores de ocupação e sistemas de coleta de luz do dia em edifícios comerciais.
Por desvantagem, 0-10V é limitado em seus recursos de controle em comparação com protocolos digitais como o DALI. Cada grupo de acessórios conectados aos mesmos fios de controle escurecerá juntos, tornando impossível o controle individual ou endereçável. A necessidade de fiação adicional também o torna menos atraente para pequenos projetos residenciais.
Aplicações
O escurecimento de 0 a 10 V é altamente popular em escritórios, escolas, hospitais e prédios industriais, onde a iluminação consistente e confiável é uma prioridade. É frequentemente usado em iluminação de teto combinada com tiras de LED para iluminação ambiente ou tarefa. Nesses cenários, ele oferece o equilíbrio certo entre acessibilidade e controle de nível profissional.

Dali escurecimento (interface de iluminação endereçável digital)
Definição
Dali, abreviação de interface de iluminação digital endereçável, é um protocolo digital padronizado desenvolvido especificamente para o controle de iluminação. Ao contrário dos métodos analógicos, o DALI permite a comunicação bidirecional entre os acessórios e o sistema de controle. Cada driver ou controlador conectado a uma rede DALI pode ser endereçado individualmente, permitindo um controle preciso e flexível sobre grandes grupos de tiras de LED e outros acessórios.
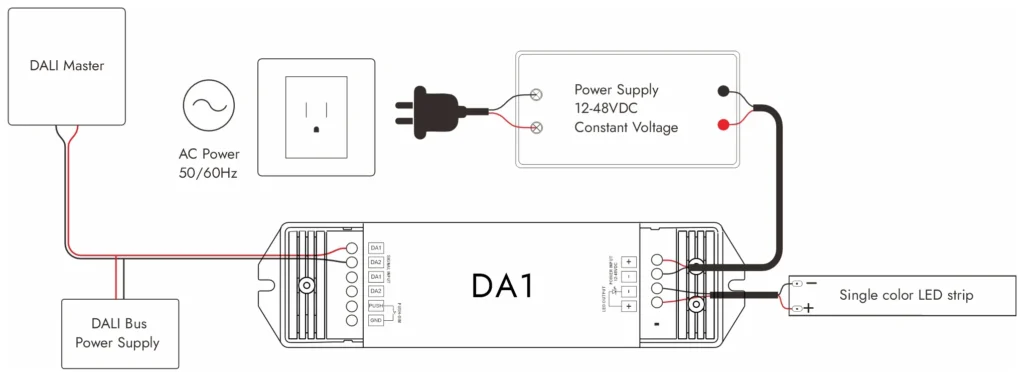
Caraterísticas
A característica mais importante do DALI é a capacidade de endereçamento. Cada dispositivo no barramento DALI pode ser programado para operar de forma independente ou como parte de um grupo. Isso dá aos designers de iluminação uma liberdade muito maior na forma como os espaços são iluminados e ajustados ao longo do tempo.
Outro recurso é a integração. Dali é frequentemente usado em edifícios inteligentes, onde a iluminação precisa funcionar perfeitamente com os sistemas de gerenciamento de edifícios (BMS). Ele suporta agendamento, colheita de luz do dia e controle baseado em ocupação, tornando-o uma escolha pronta para o futuro.
Dali também oferece comunicação bidirecional. Os acessórios podem enviar feedback para o sistema de controle, como status, consumo de energia ou informações de falhas. Isso agrega valor para os gerentes de instalações que precisam de monitoramento contínuo de grandes instalações.
Prós e contras
As principais vantagens do DALI são a flexibilidade, a precisão e a escalabilidade. Ele permite a configuração avançada da cena e pode ser reprogramado facilmente sem uma religação principal. Para projetos de alto padrão, esse nível de controle pode justificar o investimento.
As desvantagens estão relacionadas principalmente ao custo e à complexidade. Os motoristas da Dali e os equipamentos de controle são mais caros do que as soluções mais simples, e a instalação requer comissionamento adequado por pessoal treinado. Para projetos pequenos, a despesa adicional pode superar os benefícios.
Aplicações
O escurecimento Dali é amplamente utilizado em projetos comerciais premium, como hotéis, torres de escritórios, museus e campi inteligentes. Nesses ambientes, a iluminação não é apenas funcional, mas também faz parte da experiência geral do usuário e da estratégia de eficiência de construção. As luzes de tiras de LED controladas pela DALI podem ser integradas perfeitamente em tetos, paredes ou móveis, proporcionando estética e controle inteligente.

Dimming DMX (multiplex digital)
Definição
DMX, abreviação de Digital Multiplex, é um protocolo de controle desenvolvido originalmente para iluminação de palco e teatral. Desde então, tornou-se um padrão em entretenimento e iluminação arquitetônica, onde efeitos dinâmicos e precisão são essenciais. Na iluminação LED, o DMX é particularmente valorizado para aplicações RGB e RGBW, onde os canais individuais precisam ser controlados para uma mistura de cores suaves e sequências complexas.
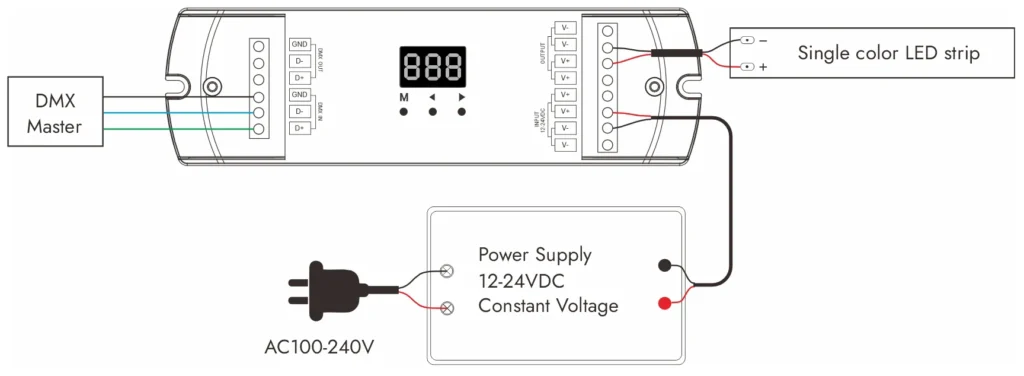
Caraterísticas
Uma das características que definem o DMX é a precisão. O protocolo fornece 256 níveis de controle por canal, o que se traduz em um escurecimento suave e mudanças de cor precisas. Para projetos que dependem de efeitos dramáticos de iluminação, esse nível de detalhe é crucial.
Outra característica é a versatilidade. Um único controlador DMX pode gerenciar centenas de canais, permitindo que os designers criem iluminação sincronizada em grandes fachadas, palcos ou espaços de eventos. Cada faixa de LED ou driver pode ser atribuído a endereços específicos, tornando possível criar designs altamente personalizados.
O DMX também oferece suporte a programação dinâmica. Com softwares especializados ou consoles de controle, as cenas de iluminação podem ser pré-definidas e acionadas em tempo real, geralmente sincronizadas com músicas, vídeos ou apresentações ao vivo.
Prós e contras
A maior vantagem do DMX é o seu potencial criativo. Ele abre a porta para efeitos infinitos, desde desbotamentos suaves até estroboscópios, perseguições ou shows coloridos de espectro total. Para locais de entretenimento ou projetos de arquitetura que desejam se destacar, o DMX oferece possibilidades incomparáveis.
A desvantagem é a complexidade. O DMX requer planejamento cuidadoso, cabeamento dedicado e configuração profissional. Embora poderoso, é um exagero para aplicações simples de tiras de LED brancas ou projetos de pequena escala. O sistema também exige conhecimentos contínuos, pois os controladores e softwares precisam ser programados adequadamente.
Aplicações
O escurecimento do DMX é a escolha certa para teatros, clubes, parques temáticos e eventos ao vivo, onde o controle dinâmico é essencial. Também é cada vez mais usado em iluminação arquitetônica, como fachadas de construção, pontes e pontos de referência públicos, onde os efeitos coloridos melhoram a identidade visual. Para iluminação LED, o DMX é mais frequentemente escolhido para projetos RGB/RGBW que exigem efeitos vibrantes e programáveis.

Como escolher a opção certa para o escurecimento do seu projeto
Quando se trata de selecionar um método de escurecimento para iluminação LED, não existe uma solução “tamanho único”. A escolha certa depende da escala, do orçamento, da compatibilidade do sistema e dos objetivos de design do seu projeto. Abaixo está um guia prático para ajudá-lo a decidir:
1. Para iluminação comercial ou de escritório básico – 0-10V
Se o seu projeto é relativamente simples, sem necessidade de programação avançada, o escurecimento de 0 a 10 V oferece uma escolha econômica e confiável. É especialmente adequado para escritórios, armazéns e áreas comerciais de uso geral, onde o escurecimento suave é suficiente.
2 . Para projetos de construção inteligente – Dali
Quando seu projeto exige controle centralizado, configuração de cena e escalabilidade futura, Dali é a solução profissional. Ele se integra perfeitamente com os sistemas de gerenciamento de edifícios (BMS) e atende a grandes escritórios, hospitais, escolas e espaços comerciais de última geração.
3. Para iluminação residencial e decorativa – Triac
Se você deseja compatibilidade com os dimmers de parede existentes, especialmente em casas, restaurantes ou varejo, o escurecimento Triac é a escolha mais conveniente. Ele evita a fiação extra e funciona bem com ambientes de iluminação aconchegantes e aconchegantes.
4. Para projetos que exigem um controle suave no nível de fixação – PWM
O escurecimento PWM é ideal para tiras de LED, onde o brilho preciso e a consistência da cor são importantes. É amplamente utilizado em iluminação decorativa, iluminação de destaque e projetos em que é necessária uma performance sem cintilação.
5. Para projetos de entretenimento e arquitetura – DMX
Quando você precisa de efeitos dinâmicos, mudanças de cores vibrantes ou de iluminação sincronizada com música ou vídeo, o DMX é o vencedor claro. É mais adequado para teatros, clubes, pontos de referência ou grandes fachadas onde o impacto visual é fundamental.
Considerações finais
Escolher o protocolo de escurecimento correto significa equilibrar a simplicidade e a flexibilidade. Projetos de pequena escala se beneficiam de soluções fáceis como 0 a 10 V ou Triac, enquanto sistemas grandes e complexos geralmente exigem DALI ou DMX. Para aplicações em que a qualidade da luz é crítica, o PWM continua sendo uma escolha confiável.

Na Signliteld, fornecemos uma gama completa de tiras de LED reguláveis e drivers compatíveis, trabalhando com marcas confiáveis como Tridonic, Euchips, Sunricher e LiFUD. Se você precisa de uma configuração básica ou de um sistema de iluminação inteligente profissional, nossa equipe pode ajudá-lo a encontrar a melhor solução.







meu irmão sugeriu que eu gostasse deste site, ele estava totalmente certo, este post realmente fez meu dia, você não pode imaginar quanto tempo eu passei para esta informação, obrigado
Site maravilhoso, muitas informações úteis aqui, estou enviando para alguns amigos e, além disso, compartilhando deliciosos e obviamente graças ao seu esforço