Устройства защиты от перенапряжения (SPD) классифицируются как тип 1, тип 2 и 3, чтобы отразить, где они работают в электрической системе и как они управляют энергией всплеск в этом месте. Эти типы не взаимозаменяемы. Каждый из них разработан для определенной функции перенапряжения и защиты, и они работают правильно только при применении как часть скоординированной системы.
Эта статья представляет собой сравнительное техническое руководство. Он не повторно вводит основы защиты от перенапряжения. Вместо этого он фокусируется на том, как тип 1, 2 и 3 SPD типа 3 различаются по роли, возможностям и взаимодействию системы, а также на том, как инженеры определяют правильное размещение в реальных электроустановках.
Сравнительная структура: как дифференцируют типы SPD

Классификация SPD не основывается на размере, цене или предполагаемой надежности. Он основан на месте установки и ожидаемом воздействии всплеска.
По мере того, как всплеск энергии проходит по электрической системе, ее характеристики меняются:
- Величина тока уменьшается
- Форма волны развивается
- Остаточное напряжение остается опасным для чувствительного оборудования
Из-за такого поведения защита от перенапряжений делится на зоны. Каждый тип SPD предназначен для работы в определенной зоне, где он может управлять стрессом при перенапряжениях, не подвергаясь перенапряжению или неэффективности.
Сравнение между типом 1, тип 2 и SPD 3 типа всегда следует учитывать:
- Место установки
- Ожидаемый уровень энергии всплеска
- Первичная функция защиты
- Зависимость от других типов SPD
Тип 1 против Тип 2 против Тип 3: Сравнение параллельно
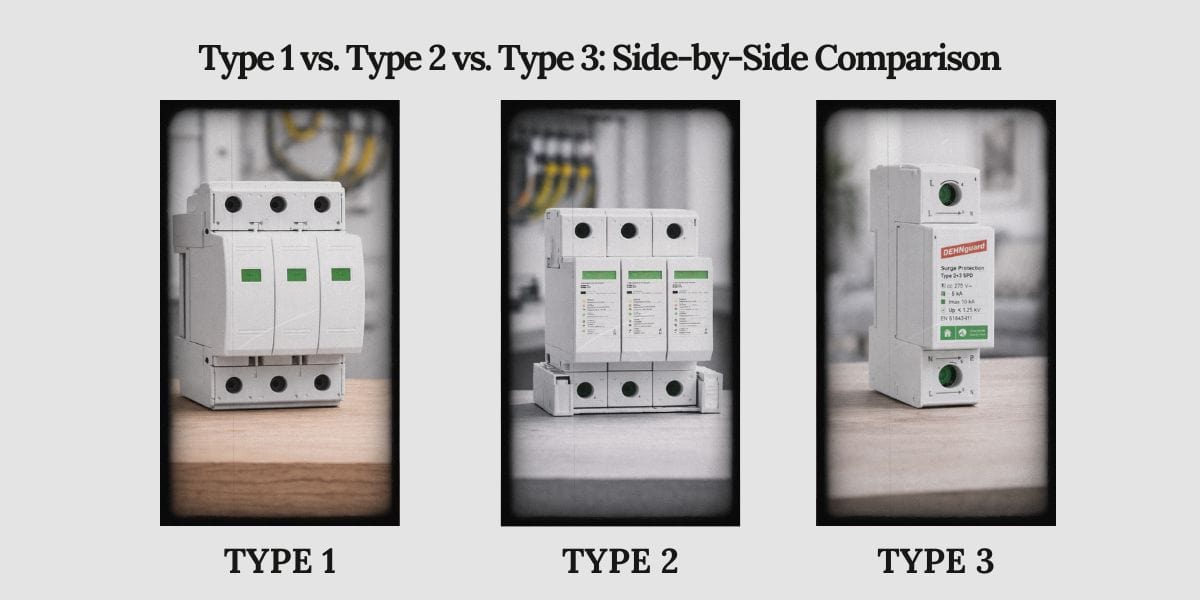
| Параметр | Тип 1 СДПГ | Тип 2 СПД | Тип 3 СПД |
| Типичное место установки | Вход служебный, линия главного отключения | Распределительные панели, нагрузка на сторону отключения | Рядом с чувствительным оборудованием |
| Уровень воздействия всплеска | очень высокий | от среднего до высокого | Низкий |
| основная функция | Отклонить входящий ток всплеска | Зажимные остатки и переключение | Ограничение по напряжению |
| Обработка тока всплеск | очень высокий | От умеренного до высокого | Низкий |
| Точность зажима напряжения | Низкий | Средний | Высокий |
| Отдельная пригодность | Нет | ограниченный | Нет |
| Зависимость от других SPD | Требуется 2 типа ниже по течению | Часто в паре с типом 1 и 3 типом | Требуется восходящий тип 1 или 2 типа |
| Типичный риск при неправильном применении | Недостаточная защита оборудования | Перенапряжение и сокращение срока службы | катастрофический сбой |
Это сравнение подчеркивает ключевой принцип: Типы СПД определяются по функции и размещению, а не по ранжированию производительности.
Тип 1 и Тип 2: Разница в защите от восходящего потока
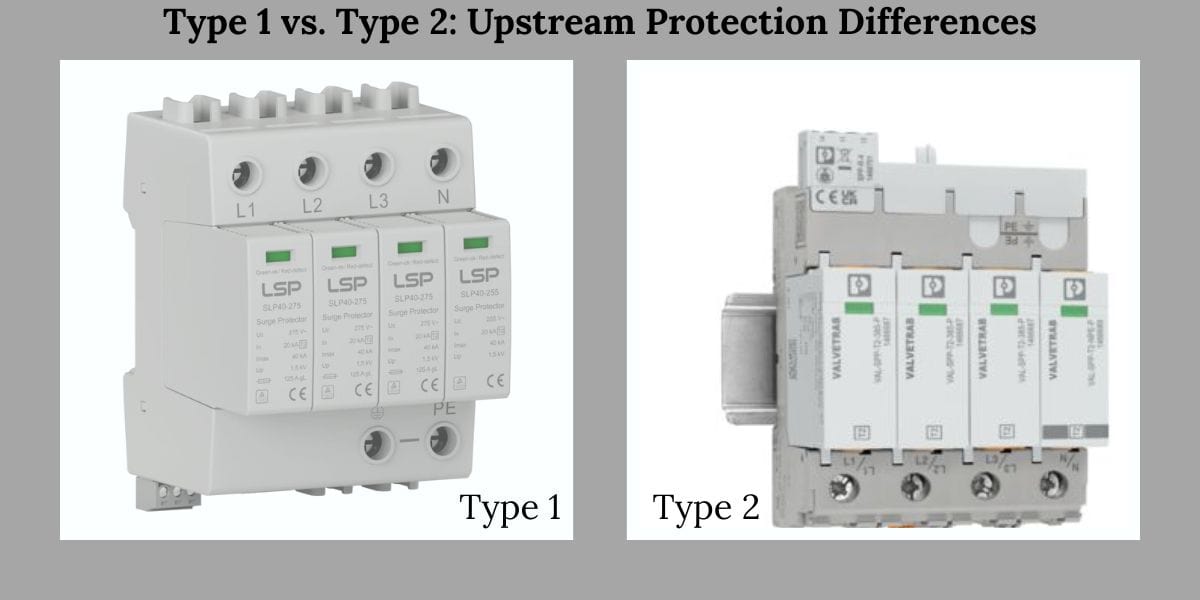
Контекст установки
У СПД типа 1 установлены на служебном входе, где экспозиция по внешнему всплеске самая высокая. SPD типа 2 устанавливаются ниже по течению, во внутренней системе распределения.
Эта позиционная разница коренным образом меняет то, что ожидается от каждого устройства.
Профиль энергии всплеска
- Тип 1 SPDS Сталкиваются с высокоэнергетическими импульсами, связанными с событиями, связанными с молниеносными явлениями, поступающими из коммунальной сети.
- Тип 2 СПД столкнуться с остаточной энергией молнии и частыми внутренними коммутирующими переходными процессами.
Поскольку устройства Type 2 не предназначены для самых высоких энергетических импульсов, они не могут заменить защиту типа 1 на входе в сервисный центр.
функциональное различие
- Тип 1 фокусируется на отвлечении тока
- Тип 2 фокусируется на ограничении напряжения и повторном контроле скачков
Установка только защиты типа 2 в условиях высокой экспозиции смещает чрезмерную нагрузку на устройства, которые не предназначены для нее, что приводит к преждевременному ухудшению.
Тип 2 против Тип 3: распределение и защита на уровне оборудования
Близость установки
SPD 2 типа защищают распределительные сети, а SPD 3 типа 3 защищают отдельное оборудование или цепи. Расстояние между SPD и защищенной нагрузкой является критическим дифференциатором.
Контроль остаточного напряжения
После защиты от восходящего потока остаточное напряжение переходного процесса может превысить импульсную выдерживаемость чувствительной электроники. SPD типа 3 обеспечивают тонкое уточнение напряжения в точке использования.
Ограничение по обработке энергии
SPD типа 3 не предназначены для поглощения энергии всплеска. Если они подвергаются непосредственному воздействию энергий, они могут быстро потерпеть неудачу. Вот почему их никогда не следует использовать без защиты от восходящего потока.
Сравнение между типом 2 и 3 — не о том, что «лучше», а в том, где точность заменяет управление энергией.
Почему не хватает одного типа SPD
Защита от перенапряжений не является аддитивной. Установка нескольких устройств одного типа не обеспечивает многоуровневой защиты.
Каждый тип SPD работает оптимально только в пределах предполагаемого диапазона напряжений:
- Тип 1 снижает поступающую энергию всплеска
- Тип 2 управляет оставшимся перенапряжением
- Тип 3 ограничивает конечное остаточное напряжение
Попытка выполнить все эти функции с помощью одного устройства приводит к снижению защиты, сокращению срока службы или тому и другому.
Координированное использование 1-го типа 1, 2 и 3 SPDS
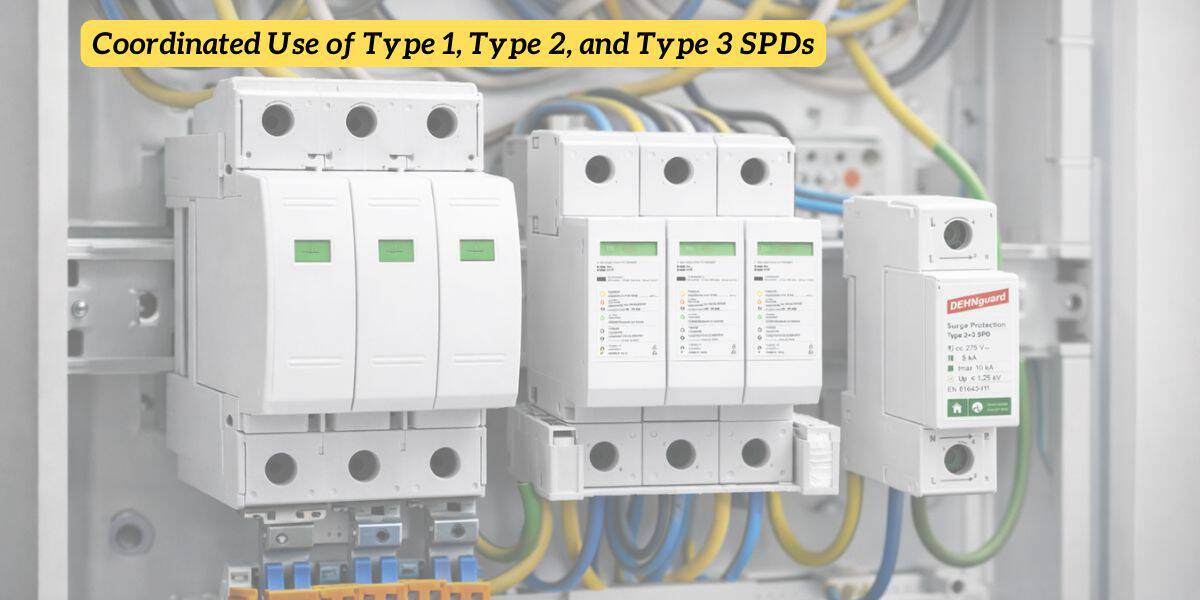
Как работает координация
Система скоординированной системы защиты от перенапряжений отражает то, как распространяется энергия накачивания:
- Тип 1 Отклоняет высокоэнергетические импульсы при входе в систему
- Тип 2 Оставшиеся скачки в системе распределения
- Тип 3 Защищает чувствительные нагрузки от остаточного напряжения
Каждая стадия снижает нагрузку на следующую.
Почему координация важнее количества
Неправильная координация может вызвать:
- Неравномерное совместное использование энергии
- Локальный перегрев
- Непредсказуемое поведение неудачи
Правильное расположение и разделение импеданса имеют значение больше, чем установка дополнительных устройств.
Сценарии сравнения на основе приложений
Вход в сервис с внешним воздействием
Установки с воздушными линиями или электрической инфраструктурой на открытом воздухе требуют защиты типа 1 на служебном входе, а затем следуют защиту типа 2.
Коммерческие и промышленные системы распределения
Переключающиеся операции доминируют в скачковой активности. SPD типа 2 обеспечивают основную роль защиты, часто координируемую с устройствами типа 1 выше.
Чувствительные электронные системы
Контроллеры автоматизации, интерфейсы и интерфейсы связи требуют защиты типа 3, но только тогда, когда энергия перенапряжения выше по течению была снижена.
Однофазные и трехфазные системы
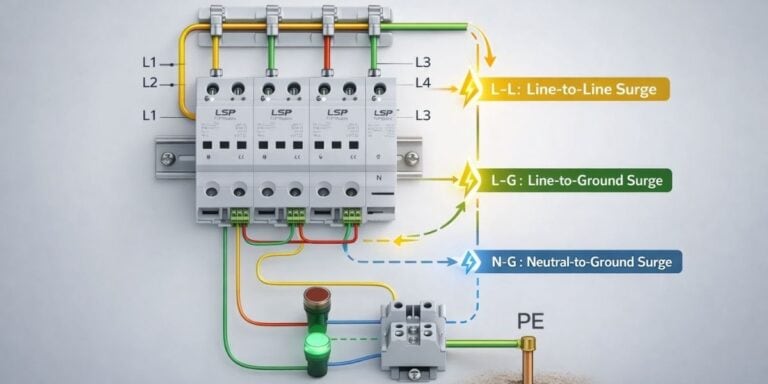
3 фазы Устройство защиты от перенапряжения Должен последовательно управлять переходными процессами фазы-фазы и фазы-земля. Выбор типа SPD должен соответствовать конфигурации системы, а не только номинала напряжения.
Распространенные ошибки сравнения, которые делают инженеры
- Предполагая, что устройства типа 3 могут работать автономно
- Увеличение размера одного SPD вместо координации нескольких типов
- Установка нескольких устройств Type 2 без учета импеданса
- Обработка типов SPD как уровней производительности, а не функциональных ролей
Эти ошибки снижают эффективность защиты и увеличивают риск технического обслуживания.
Стандартный контекст
Стандарты, такие как UL 1449 и IEC 61643, определяют условия испытаний и критерии классификации для типов SPD. Они поддерживают последовательное сравнение, но не заменяют инженерное суждение на системном уровне в отношении размещения и координации.
Заключение
Устройства защиты от перенапряжений типа 1, типа 2 и 3 выполняют различные дополняющие друг друга роли в электрической системе. Их различия определяются местом установки, экспозицией при всплескании и функцией защиты, а не классом продукта или позиции по маркетингу.
Эффективная защита от перенапряжений зависит от координации, а не от чрезмерного размера или избыточности. Когда каждый тип SPD применяется там, где он работает лучше всего, энергия накачивания постепенно контролируется, напряжение оборудования снижается, а долгосрочная надежность системы повышается.
Вопросы и ответы
нет , йо- Устройства типа 2 не предназначены для самых высоких уровней воздействия при всплеске, присутствующих при входе в систему.
Только косвенно и только тогда, когда защита восходящего потока уже уменьшила энергию всплеска.
В условиях с низким уровнем воздействия это может быть приемлемо, но риск значительно возрастает без защиты от восходящего потока.
Потому что неправильное размещение может перенапрягать устройства независимо от рейтинга.
Не всегда, но большинство современных установок выигрывают от координации по крайней мере типа 1 и 2.