Trong các dự án chiếu sáng thực tế, xây dựng phòng mô hình hoặc lắp đặt tại chỗ, không có gì lạ khi các dải LED 12V được kết nối với nguồn điện 24V do cấu hình nguồn không nhất quán. Mặc dù điều này có vẻ như là một “sự không phù hợp điện áp” đơn giản, nhưng nó có thể dẫn đến các vấn đề nghiêm trọng như đèn LED bị cháy, quá nóng và hút thuốc, lỗi sản phẩm và thậm chí là chậm trễ dự án.
Đối với các nhà tích hợp dải LED, nhà thầu chiếu sáng kiến trúc và người mua bán buôn, việc tìm kiếm một giải pháp thay thế kỹ thuật mà không thay thế toàn bộ hệ thống đã trở nên quan trọng.
Bài viết này sẽ phân tích một cách có hệ thống:
- Nguyên lý làm việc và rủi ro của sự không phù hợp điện áp
- Hạn chế ứng dụng của dải LED 12V trong hệ thống 24V
- Giải pháp giảm điện áp và cách ly khả thi
- Cách chọn thiết kế nguồn điện an toàn dựa trên các kịch bản dự án
Nếu bạn đang tìm kiếm một giải pháp ổn định và tiết kiệm chi phí, bài viết cũng sẽ cung cấp các sản phẩm dải LED được khuyến nghị và các đề xuất hỗ trợ kỹ thuật ở phần cuối.
Tại sao không thể sử dụng trực tiếp dải đèn LED 12V với nguồn điện 24V?

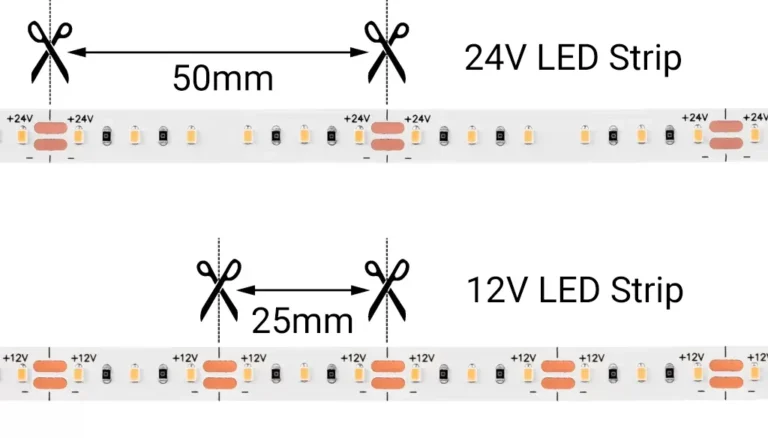
Trong các dự án chiếu sáng LED, 12V và 24V là hai tiêu chuẩn điện áp thấp phổ biến nhất. mặc dầu Dải LED 12V và 24V Xuất hiện tương tự về cấu trúc, thiết kế mạch bên trong của chúng, phân phối điện trở và dung lượng mang dòng điện là hoàn toàn khác nhau. Kết nối dải 12V với nguồn điện 24V sẽ trực tiếp gây ra tình trạng quá tải điện áp, dẫn đến những hậu quả nặng nề sau:
Hậu quả của điện áp quá mức
Một dải 12V hoạt động ở điện áp 12V.Khi được nối với nguồn điện 24V DC, nó chịu điện áp định mức gấp đôi, vượt quá giới hạn của nó. Các vấn đề chung bao gồm:
- cháy ngay lập tức chip LED: Chip LED được thiết kế để hoạt động ở dòng điện 12V. Khi kết nối với 24V, dòng điện tăng gấp đôi, gây ra quá nhiệt nghiêm trọng, có thể dẫn đến tình trạng cháy hoặc đổi màu chip LED.
- Kháng thiệt hại quá nhiệt: Các điện trở giới hạn dòng điện nối tiếp trong dải LED quá nóng nghiêm trọng, có khả năng gây ra sự cố điện trở, biến dạng PCB, thậm chí là nguy cơ khói hoặc cháy.
- Toàn bộ dải ánh sáng không sử dụng được: Khi mạch bị hỏng, chi phí sửa chữa vượt quá chi phí thay thế toàn bộ dải đèn, đặc biệt là trong các tình huống lắp đặt mà điều này đặc biệt khó khăn.
Phân tích nguyên tắc đằng sau sự cố LED
Đèn LED là thiết bị điều khiển dòng điện cơ bản và sự thay đổi điện áp có thể khiến dòng điện tăng nhanh. Thông thường, một dải đèn 12V bao gồm một chuỗi ba đèn LED được nối tiếp và sau đó song song, với các điện trở giới hạn dòng điện để duy trì độ sáng không đổi. Khi kết nối với 24V, dòng điện không kiểm soát dẫn đến các hiện tượng sau:
- Đèn LED kết nối hàng loạt mất bảo vệ chia sẻ hiện tại: Nếu một đèn LED bị cháy, toàn bộ nhóm sẽ ngừng hoạt động, ảnh hưởng đến toàn bộ dải ánh sáng.
- Điện trở quá nóng, làm cho bề mặt bảng bị cacbon hóa.
- Sự cố quá áp đầu cuối dương gây ra hiện tượng ngắn mạch trong mạch.
Rủi ro sử dụng tại chỗ cao hơn đáng kể so với các phòng thí nghiệm
Trong môi trường phòng thí nghiệm, ngay cả khi kết nối với 24 V trong một thời gian ngắn không làm cháy dải ánh sáng ngay lập tức, rủi ro sẽ tăng lên đáng kể trong các tình huống kỹ thuật sau:
- Cài đặt song song số lượng lớn: Tăng tải điện, và một khi một phần bị lỗi, nó có thể dễ dàng kích hoạt phản ứng dây chuyền của các trường hợp kiệt sức.
- ngoài trời hoặc kèm theo kênh nhôm ngoại cảnh: tản nhiệt kém, dẫn đến nhiệt chạy.
- Cài đặt ẩn các dải ánh sáng: Burnout được phát hiện muộn, dẫn đến chi phí bảo trì cao.
Sự không phù hợp điện áp không phải là “vấn đề nhỏ” mà là một mối nguy hiểm nghiêm trọng ảnh hưởng nghiêm trọng đến tuổi thọ, an toàn và tiến trình giao dự án của dải đèn. Đối với bất kỳ dự án chiếu sáng thương mại nào ưu tiên độ tin cậy, việc ngăn chặn các dải ánh sáng 12V được kết nối với nguồn điện 24V là một trong những tiêu chuẩn thiết kế điện cơ bản nhất.
Tôi có thể chạy đèn dải LED 12V an toàn trên nguồn điện 24V không?
Về mặt kỹ thuật, có, bạn có thể — nhưng chỉ khi bạn kết nối chúng thành chuỗi một cách chính xác.
Mặc dù chúng tôi thực sự khuyên bạn nên sử dụng các sản phẩm và phụ kiện được chỉ định cho điện áp chính xác, chúng tôi sẽ chỉ cho bạn cách kết nối đèn dải LED 12V với Nguồn điện 24V Không làm hỏng đèn dải LED!
Tuyên bố miễn trừ trách nhiệm: Các kết nối không chính xác hoặc ngẫu nhiên gây ra quá áp có thể dẫn đến hư hỏng vĩnh viễn cho đèn LED. Thông tin được cung cấp ở đây chỉ dành cho mục đích giáo dục. Signeled không chịu trách nhiệm đối với bất kỳ thiệt hại nào.
Vì lý do an toàn, chúng tôi khuyên bạn nên thử nghiệm với hai đoạn ngắn của cùng một dải LED 12V để đảm bảo mọi thứ được thiết lập chính xác trước khi kết nối các phần dài hơn.
Phương pháp đấu dây chính xác: kết nối loạt
Về mặt lý thuyết, việc kết nối hai dải đèn LED 12V giống hệt nhau dẫn đến điện áp tổng là 24V, làm cho chúng tương thích với hệ thống 24V. Bằng cách kết nối các dải đèn LED theo cách này, nguồn điện 24V được “tách” hiệu quả giữa hai phân đoạn dải đèn LED, với mỗi phân đoạn nhận 12V. Vì hai dải đèn LED được kết nối nối tiếp, mỗi dải đèn LED tiêu thụ cùng một dòng điện. Đối với phương thức kết nối cụ thể, vui lòng tham khảo sơ đồ dưới đây.
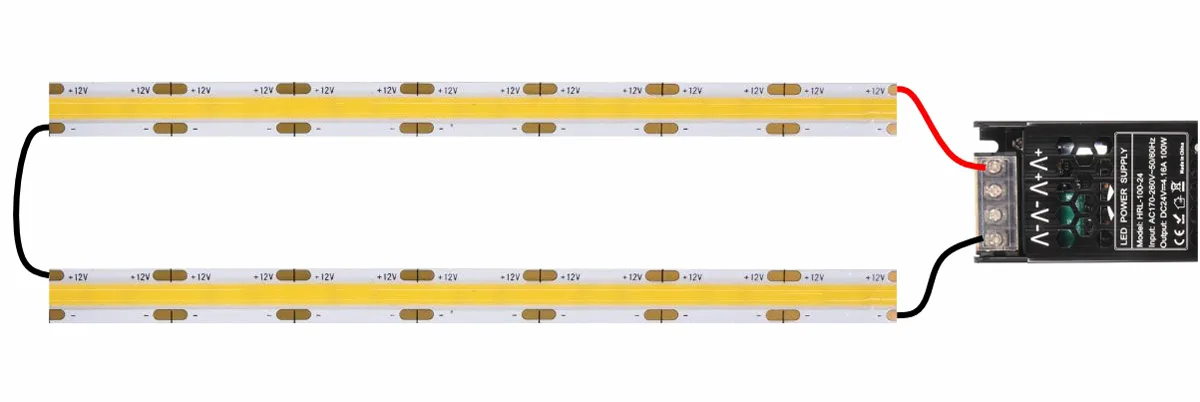
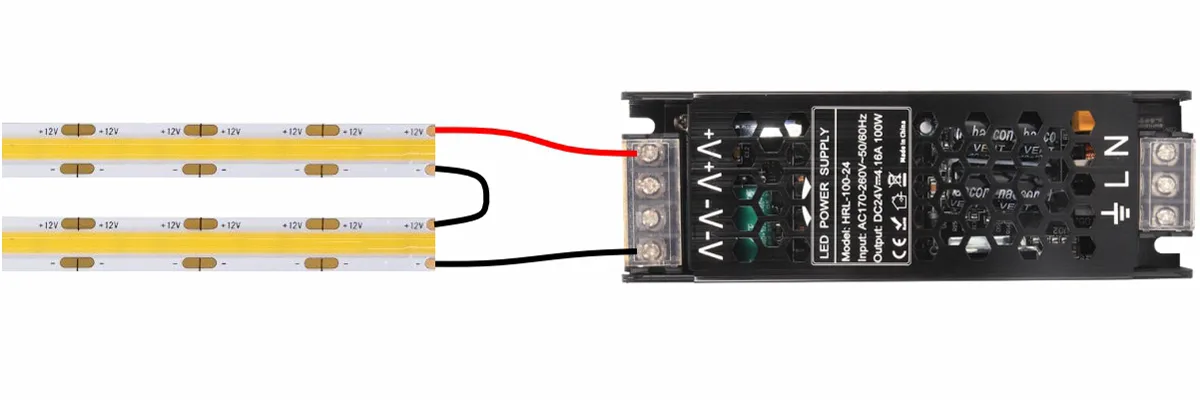

CẢNH BÁO: Hai dải đèn LED nối tiếp nối tiếp phải hoàn toàn giống nhau!
Tại sao điều này lại quan trọng như vậy?
Giả sử hai dải đèn LED 12V có độ dài khác nhau được nối tiếp. Ở điện áp 12V, chúng tiêu thụ lần lượt là 0,5A và 1,0A. Vì chúng được kết nối nối tiếp, chúng sẽ buộc phải chia sẻ cùng một giá trị hiện tại tương tự. Giả sử giá trị hiện tại chính xác là 0,75A (điểm giữa).
Đối với dải đèn LED dài hơn, để phù hợp với dòng điện thấp hơn 0,75A (thay vì 1.0A định mức), điện áp có thể cần giảm xuống 11V hoặc thậm chí 10V. Tuy nhiên, điện áp không đổi 24V, như tên cho thấy, vẫn không đổi ở 24V. Do đó, dải đèn LED ngắn hơn bây giờ buộc phải “tạo ra” điện áp 13V hoặc 14V còn lại. Điều này sẽ khiến dải đèn LED ngắn hơn gặp phải tình trạng quá dòng và có thể làm hỏng đèn LED.
Chỉ trong cấu hình loạt, dải đèn LED 12V mới có thể hoạt động trên nguồn điện 24V. Mặc dù công nghệ này là thông minh, có thể mở rộng và rất hữu ích cho mục đích giảng dạy và lắp đặt, nhưng nó có thể gây ra những rủi ro đáng kể trong việc lắp đặt dự án kỹ thuật thực tế:
- cùng chiều dài và loại dải phải được sử dụng.
- có thể xảy ra sự phân bố điện áp không đều.
- Lỗi ở một dải có thể ảnh hưởng đến dải khác.
Bất kỳ thay đổi nào về điện trở, hàn không nhất quán hoặc sự lão hóa không đồng đều của các dải có thể gây ra sự phân bố điện áp không đồng đều, do đó làm tăng nguy cơ hư hỏng. Do đó, chúng tôi khuyên bạn chỉ nên sử dụng phương pháp này trong các tình huống khẩn cấp!
Để biết thêm thông tin về cách kết nối đèn LED dải với nguồn điện, hãy đọc bài đăng trên blog Hướng dẫn cơ bản để đấu dây đèn LED dải đèn LED đến nguồn điện Và Cách kết nối đèn dải LED với nguồn điện.
Giải pháp kỹ thuật tốt hơn: Cách sử dụng đèn dải LED 12V trong hệ thống 24V
Ở một số địa điểm dự án, hệ thống cung cấp điện 24V đã được triển khai thống nhất. Tuy nhiên, do vấn đề tồn kho, gia công hoặc thay đổi yêu cầu giai đoạn sau, có thể cần tạm thời sử dụng đèn dải LED 12V. Nếu bản thân đèn LED dải không thể được thay thế, có cách nào để kết nối chúng một cách an toàn với hệ thống cấp điện 24V không? Câu trả lời là có, nhưng phải thực hiện bằng phương pháp giảm điện áp chuyên nghiệp để đảm bảo hệ thống ổn định và vận hành an toàn.
Giải pháp 1: Sử dụng bộ chuyển đổi bước xuống DC-DC
Đây là phương pháp phổ biến và an toàn nhất. Bằng cách chèn bộ chuyển đổi bước xuống DC-DC giữa đầu ra nguồn điện và dải LED, điện áp 24V được chuyển đổi đáng tin cậy thành đầu ra 12V, đảm bảo dải LED hoạt động bình thường.
Ưu điểm:
- Đầu ra chính xác 12V, tương thích với tất cả các mẫu dải LED 12V;
- Nhiều mô-đun có thể được kết nối song song để cung cấp điện phân đoạn, tạo điều kiện cho hệ thống dây điện;
- Các mô-đun cấp công nghiệp có bảo vệ quá áp và bảo vệ quá tải có sẵn để tăng cường sự ổn định của hệ thống.
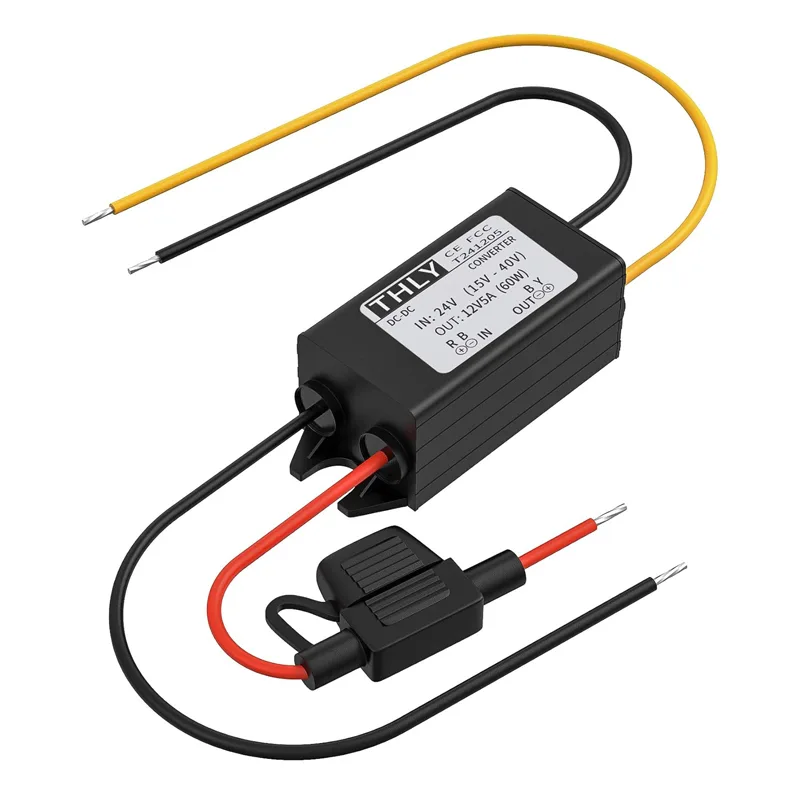

Bộ chuyển đổi bước xuống DC24V-12V
Điện áp đầu ra: DC12V
Dòng điện tối đa: 5A 60W
Hiệu quả: 96%
Chống nước: IP67
Kích thước sản phẩm: L114 x W79 x H20 mm
Trọng lượng tịnh: 264g
Các kịch bản ứng dụng:
- Trung tâm mua sắm trưng bày tủ trưng bày và ánh sáng cửa sổ;
- điều chỉnh ánh sáng cho triển lãm và trưng bày;
- Hệ thống chiếu sáng trong nhà với điều khiển phân khúc.
Cân nhắc khuyến nghị:
- Công suất mô-đun phải đáp ứng tổng mức tiêu thụ điện của các dải ánh sáng; nên để lại biên độ 20%-30%.
- Ưu tiên sản phẩm có chức năng bảo vệ ngắn mạch và ổn áp;
- Chú ý tản nhiệt và chống thấm trong quá trình lắp đặt (nếu dùng cho các công trình ngoài trời).
Giải pháp 2: Cấu hình hệ thống điện kép (cung cấp điện cách ly)
Trong các dự án quy mô vừa đến lớn, hệ thống cung cấp điện kép cũng có thể được áp dụng, trong đó nguồn điện chính 24V dẫn động thiết bị 24V và thêm nguồn điện 12V được thêm vào các dải đèn 12V.
Ưu điểm:
- Kiểm soát độc lập từng hệ thống để bảo trì dễ dàng hơn;
- phù hợp hơn cho các dự án cao cấp nhạy cảm với nhiễu cung cấp điện;
- Có thể triển khai kết hợp với các hệ thống điều khiển thông minh như DMX và DALI.
Các kịch bản áp dụng:
- các dự án chiếu sáng đa hệ thống trong khách sạn, khu phức hợp thương mại, bảo tàng, v.v.;
- Tích hợp dễ dàng hơn khi thêm các mô-đun 12V trong quá trình thực hiện dự án.
LƯU Ý:
- Hai nhóm cấp điện không được chung một mặt bằng và phải hoàn toàn cách ly;
- Cần ghi nhãn rõ ràng các mạch để ngăn chặn lỗi dây trong quá trình thực hiện;
- Hệ thống điều khiển phải được nhóm theo phân đoạn điện áp.
Giải pháp 3: Cung cấp điện tập trung + Thiết kế đầu ra mô-đun (phù hợp với hệ thống tích hợp)
Đối với hệ thống điều khiển ánh sáng phân tán (như hệ thống chiếu sáng thông minh quy mô lớn), tủ cấp điện tập trung có thể được sử dụng để nhập đồng đều nguồn điện 24V, sau đó được chuyển đổi thành tín hiệu 12V thông qua bảng đầu ra mô-đun.
Ưu điểm:
- quản lý tập trung và cài đặt mô-đun;
- Thích hợp cho hệ thống chiếu sáng công nghiệp và hệ thống điều khiển tòa nhà thông minh;
- Giảm chi phí bảo trì và tạo điều kiện cho chẩn đoán lỗi.
Nhược điểm:
- chi phí triển khai ban đầu cao hơn;
- một số yêu cầu nhất định đối với hệ thống dây điện xây dựng.
Không được khuyến nghị giải pháp: dải ánh sáng nối tiếp, giảm điện trở, vv
Mặc dù, từ góc độ lý thuyết mạch, có thể đạt được việc giảm điện áp bằng cách thêm điện trở nối tiếp hoặc nhiều kết nối nối tiếp, và chúng tôi cũng đã trình bày chi tiết về kết nối và nguyên tắc của giải pháp này trong chương trước, các phương pháp này gây ra tỷ lệ hỏng hóc cao và nguy cơ an toàn trong các dự án chiếu sáng thực tế:
- Dải đèn LED nối tiếp bị ảnh hưởng đáng kể bởi tính đồng nhất của thành phần;
- Phương pháp giảm điện trở điện trở không hiệu quả và sinh nhiệt quá mức;
- Giải pháp thiếu các cơ chế bảo vệ và dao động điện áp có thể dễ dàng làm hỏng thiết bị.
Do đó, đối với các dự án chuyên nghiệp, việc lựa chọn các mô-đun giảm điện áp được tiêu chuẩn hóa hoặc hệ thống cung cấp điện theo nhóm có đầu ra ổn định và chức năng bảo vệ.
Mặc dù tồn tại các giải pháp cho vấn đề dải ánh sáng 12V không tương thích với hệ thống 24V, chúng yêu cầu lập kế hoạch phù hợp và lựa chọn tiêu chuẩn. Tùy thuộc vào quy mô dự án, môi trường lắp đặt và hệ thống điều khiển, việc lựa chọn phương pháp giảm điện áp thích hợp có thể vừa giảm chi phí cải tạo vừa đảm bảo hệ thống hoạt động ổn định lâu dài.
Khuyến nghị thay thế: Chọn sản phẩm dải LED với điện áp tương thích
Mặc dù giải pháp bước xuống có thể cho phép các dải LED 12V tương thích với hệ thống 24V, từ quan điểm an toàn, ổn định và chi phí bảo trì của dự án, chúng tôi khuyên bạn nên lựa chọn Sản phẩm dải LED với điện áp tương thích cho hệ thống ngay từ đầu dự án. Chiến lược này có thể làm giảm hiệu quả tỷ lệ lỗi kỹ thuật, cải thiện hiệu quả hệ thống tổng thể và kéo dài tuổi thọ.
Do đó, bạn cần chọn giải pháp chính xác dựa trên dự án của bạn. Khi quyết định có nên sử dụng dải đèn LED 12V trong hệ thống 24V hay không, hãy tự hỏi:
- Đây là thiết lập tạm thời hay vĩnh viễn?
- Tôi có thể sử dụng bộ chuyển đổi bước xuống hoặc nguồn điện bổ sung không?
- Tôi có thể kết nối một cách an toàn trong chuỗi không?
- Việc nâng cấp lên dải nguồn 24V có hiệu quả hơn về lâu dài không?
Giải pháp thiết thực nhất là nâng cấp lên dải đèn LED 24V. Nếu hệ thống của bạn đã được chuẩn hóa cho 24 V, việc nâng cấp có thể đơn giản hóa việc cài đặt và quản lý nguồn điện. Tại sao 24V được ưu tiên hơn 12V? So với hệ thống 12V, dải đèn LED 24V mang lại lợi thế đáng kể trong việc lắp đặt đường dài từ trung bình đến dài:
- tổn thất điện áp thấp hơn: Trong cùng điều kiện hiện tại, tổn thất đường dây của hệ thống 24V bằng một nửa so với hệ thống 12V, làm cho nó phù hợp hơn với hệ thống dây điện đường dài;
- dòng điện thấp hơn trên mỗi đơn vị, làm cho hệ thống an toàn hơn: Giảm nguy cơ cáp quá nhiệt và ngắn mạch;
- có thể được tạo thành các phân đoạn dài hơn: tránh các điểm nối quá mức, nâng cao tính nhất quán hiệu quả ánh sáng;
- Khả năng tương thích tốt hơn với các hệ thống chiếu sáng thông minh như DALI và DMX: Dễ dàng hơn để đạt được nguồn điện tập trung và làm mờ kỹ thuật số.
Do đó, nếu dự án của bạn đã là hệ thống điện 24V thì việc lựa chọn dải đèn 24V là lựa chọn đáng tin cậy nhất.
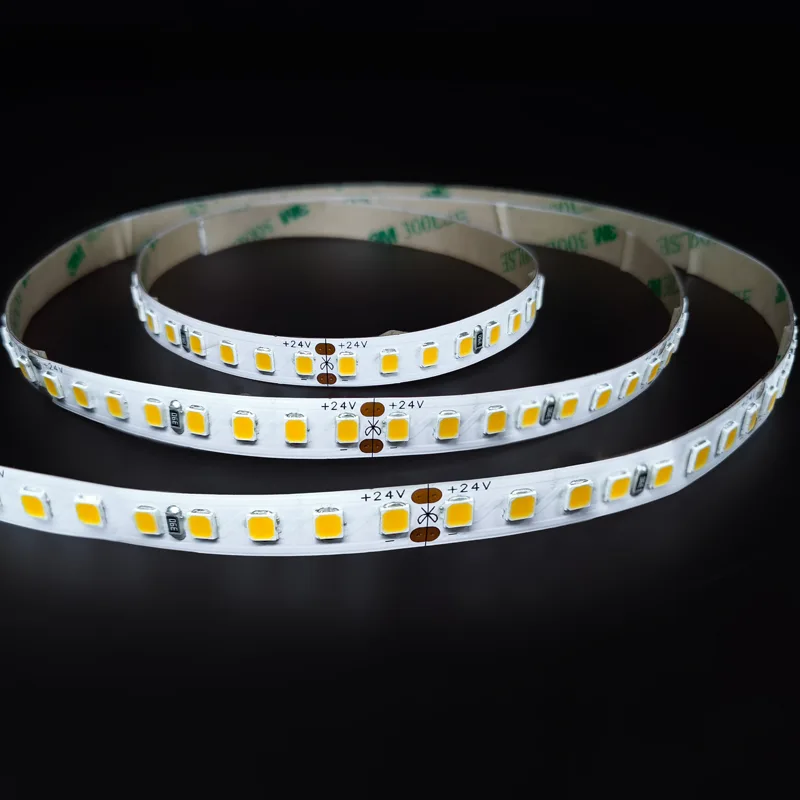

Đèn LED DC24V hiệu quả cao
Số mô hình: FQX10T128C
Điện áp: DC24V
Sức mạnh: 12W / m
Hiệu quả: 190-200lm / W
RA: 80
CCT: 3000K - 6500K
Loại LED: SMD2835
Số lượng LED: 128LED / m
Chiều rộng PCB: 10mm
Đơn vị cắt: 62,5mm / 8LED
IP cấp: IP20/IP54/IP65/IP67/IP68
Bảo hành: 5 năm
Đề xuất lựa chọn: Chọn dải LED điện áp thích hợp cho dự án của bạn
| Loại dự án | Điện áp khuyến nghị | biện hộ |
| Máng đèn trần không gian thương mại | 24v | Khoảng cách lắp đặt dài, nguồn điện tập trung, tổn thất đường dây tối thiểu |
| Tủ trưng bày hoặc ánh sáng cửa sổ | 12V/24V | Phụ thuộc vào chiều dài của dải ánh sáng và vị trí cấp điện |
| Hệ thống làm mờ tòa nhà thông minh | 24v | Tương thích hơn với bộ điều khiển DALI và DMX |
| Chiếu sáng đồ nội thất tùy chỉnh | 12v | Nguồn điện phân tán, độ dài khác nhau của dải ánh sáng và dây dẫn linh hoạt |
| Hệ thống dải ánh sáng chống thấm nước ngoài trời | 24v | Ổn định tốt hơn cho trình điều khiển công suất cao và điện áp mạnh hơn |
Chọn đúng điện áp là bước đầu tiên để xác định sự thành công của dự án của bạn. Thay vì thực hiện các hiệu chỉnh trong giai đoạn sau của quá trình xây dựng, tốt hơn là xem xét khả năng tương thích hệ thống, thiết kế mạch và hiệu suất sản phẩm kỹ lưỡng trong giai đoạn lựa chọn ban đầu để đảm bảo lắp đặt một lần và ổn định lâu dài. Trong thực hiện dự án thực tế, chúng tôi khuyên bạn nên làm việc với các nhà cung cấp có kinh nghiệm kỹ thuật để tùy chỉnh hệ thống dựa trên điện áp, yêu cầu hiện tại, phương pháp điều khiển và môi trường lắp đặt.
Nếu bạn vẫn còn thắc mắc về việc chọn dải LED 24V hoặc 12V, Signitel có thể cung cấp hỗ trợ sau:
- cung cấp điện kỹ thuật và thiết kế phù hợp hệ thống dải LED;
- Mô-đun DC-DC Buck và các giải pháp cung cấp điện tập trung;
- Cung cấp số lượng lớn và dịch vụ tùy biến OEM, phù hợp cho các dự án thương mại khác nhau.
làm theo ý muốn Liên hệ với chúng tôi để đánh giá dự án và tư vấn chuyên nghiệp.
Tóm tắt: Cách giảm thiểu rủi ro liên quan đến hệ thống 12V / 24V không khớp
Trong các dự án chiếu sáng và kỹ thuật thương mại, việc vận hành ổn định hệ thống chiếu sáng dải LED không chỉ phụ thuộc vào chất lượng của bản thân sản phẩm mà còn vào tính hợp lý của hệ thống cấp điện và tuân thủ các tiêu chuẩn lắp đặt. Bài viết này xác định thông qua nhiều giải pháp và phân tích kỹ thuật kết nối trực tiếp dải đèn LED 12V với nguồn điện 24V là một thực hành có nguy cơ cao dễ dẫn đến việc bị hư hỏng và làm lại dự án.
Nếu do yêu cầu của dự án hoặc hạn chế về hàng tồn kho, cần sử dụng dải 12V trong hệ thống 24V, thì các mô-đun giảm điện áp chuyên nghiệp hoặc hệ thống điện cách ly phải được lựa chọn làm biện pháp chuyển tiếp để đảm bảo an toàn và tuổi thọ cho thiết bị.
Từ góc độ dài hạn, việc lựa chọn các sản phẩm dải LED phù hợp với điện áp hệ thống cung cấp điện ngay từ đầu dự án là chiến lược tối ưu để giảm độ phức tạp của kỹ thuật và giảm thiểu bảo trì sau lắp đặt.
Danh sách đề xuất các tiêu chuẩn điện cho các dự án đèn LED
| Giai đoạn dự án | khuyến cáo |
| giai đoạn thiết kế sơ đồ | Chỉ định điện áp cung cấp hệ thống (12V hoặc 24V) để tránh trộn nhiều điện áp |
| Lựa chọn sản phẩm dải ánh sáng | Ưu tiên lựa chọn các phiên bản điện áp tương thích với hệ thống, ví dụ, dải chiếu sáng 24V cho hệ thống 24V |
| Lắp đặt hệ thống dây điện tại chỗ | Nghiêm cấm kết nối các dải chiếu sáng 12V trực tiếp với nguồn điện 24V; phải sử dụng các mô-đun bước xuống DC-DC hoặc nguồn điện cách ly |
| Cung cấp thiết bị cung cấp điện | Chọn nguồn điện và các mô-đun bước xuống với các tính năng bảo vệ ngắn mạch, quá áp và quá nhiệt |
| Thử nghiệm lắp đặt dải ánh sáng | Tiến hành các thử nghiệm chiếu sáng phân đoạn trước khi lắp đặt từng phần để tránh lỗi sau khi bật nguồn toàn mạch |
| Giao và nghiệm thu dự án | Xác minh rằng các mô hình nguồn điện và dải ánh sáng phù hợp, đồng thời tài liệu sơ đồ cấp điện và kế hoạch đấu dây dải ánh sáng |
Nếu dự án của bạn yêu cầu các giải pháp tương thích điện áp chéo, thiết kế nguồn điện tập trung hoặc mô-đun tùy chỉnh, vui lòng liên hệ với nhóm Signelited. Chúng tôi cung cấp toàn diện Đèn LED dải Hỗ trợ thiết kế hệ thống giúp dự án của bạn đạt được hiệu quả và vận hành ổn định.
FAQ
Chúng tôi không khuyên bạn nên làm điều này. Ngay cả khi nó không bị cháy trong thời gian ngắn, nó sẽ làm giảm đáng kể tuổi thọ của dải ánh sáng và có thể gây nguy hiểm an toàn. Một số hạt ánh sáng có thể bị đổi màu nhẹ hoặc giảm độ sáng ở nhiệt độ cao và các rủi ro rất khó kiểm soát.
Điều này không được khuyến khích. Mặc dù về mặt lý thuyết, việc chia sẻ điện áp là có thể, nhưng trở kháng và điện trở không nhất quán có thể dễ dàng khiến một phần bị cháy trước, khiến phần kia không được bảo vệ và gây ra phản ứng dây chuyền.
1. Đảm bảo công suất đầu ra đáp ứng tổng mức tiêu thụ điện năng của các dải LED và cho phép biên.
2. Mô-đun phải có chức năng bảo vệ quá áp, quá áp và quá nhiệt.
3. Trong môi trường ngoài trời hoặc nhiệt độ cao, tăng cường các biện pháp tản nhiệt hoặc chống thấm.
Hệ thống điện kép hoặc nguồn điện tập trung + cấu hình đầu ra mô-đun có thể được sử dụng. Điều quan trọng là đảm bảo cách ly vật lý giữa các hệ thống điện áp khác nhau, hệ thống dây điện rõ ràng, điều khiển độc lập và ghi nhãn rõ ràng trên bản vẽ.
Kiểm tra nhãn dải ánh sáng, nhãn giao diện nguồn hoặc sử dụng đồng hồ vạn năng để đo điện áp hoạt động. Nên quản lý các lô điện áp dải ánh sáng trước khi thi công để tránh kết nối sai do trộn các điện áp khác nhau.