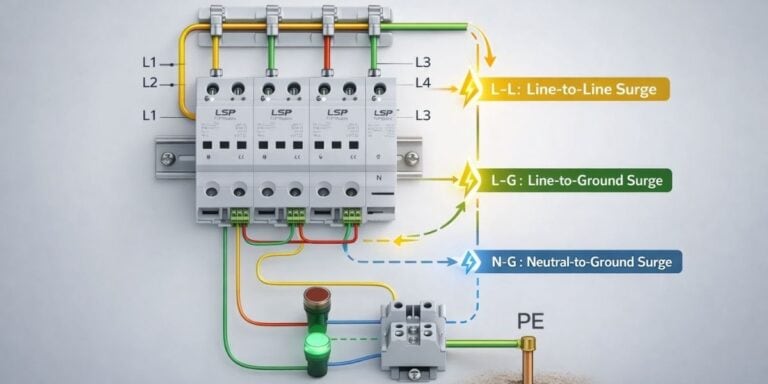
Các thiết bị bảo vệ chống sét lan truyền (SPD) được phân loại là loại 1, loại 2 và loại 3 để phản ánh nơi chúng hoạt động trong hệ thống điện và cách chúng quản lý năng lượng tăng áp tại vị trí đó. Những loại này không thể thay thế cho nhau. Mỗi cái được thiết kế cho một môi trường tăng đột biến và chức năng bảo vệ, và chúng chỉ hoạt động chính xác khi được áp dụng như một phần của hệ thống phối hợp.
Bài viết này là một hướng dẫn kỹ thuật so sánh. Nó không giới thiệu lại các nguyên tắc cơ bản về bảo vệ đột biến. Thay vào đó, nó tập trung vào cách các SPD loại 1, loại 2 và loại 3 khác nhau về vai trò, khả năng và tương tác hệ thống cũng như cách các kỹ sư xác định vị trí chính xác trong các cài đặt điện thực.
Khung so sánh: Cách phân biệt các loại SPD

Phân loại SPD không dựa trên kích thước sản phẩm, giá cả hoặc độ chắc chắn được cảm nhận. Nó dựa trên vị trí lắp đặt và mức độ tiếp xúc đột biến dự kiến.
Khi năng lượng tăng đột biến qua hệ thống điện, các đặc tính của nó thay đổi:
- cường độ dòng điện tăng giảm
- Hình dạng sóng phát triển
- Điện áp dư vẫn nguy hiểm cho các thiết bị nhạy cảm
Vì hành vi này, bảo vệ tăng áp được chia thành các khu vực. Mỗi loại SPD được thiết kế để hoạt động trong một khu vực cụ thể, nơi nó có thể quản lý căng thẳng tăng áp mà không bị căng thẳng quá mức hoặc hoạt động kém hiệu quả.
So sánh giữa SPD loại 1, loại 2 và loại 3 luôn luôn nên xem xét:
- Vị trí lắp đặt
- Mức năng lượng tăng đột biến dự kiến
- Chức năng bảo vệ chính
- Phụ thuộc vào các loại SPD khác
Loại 1 so với Loại 2 so với Loại 3: So sánh song song
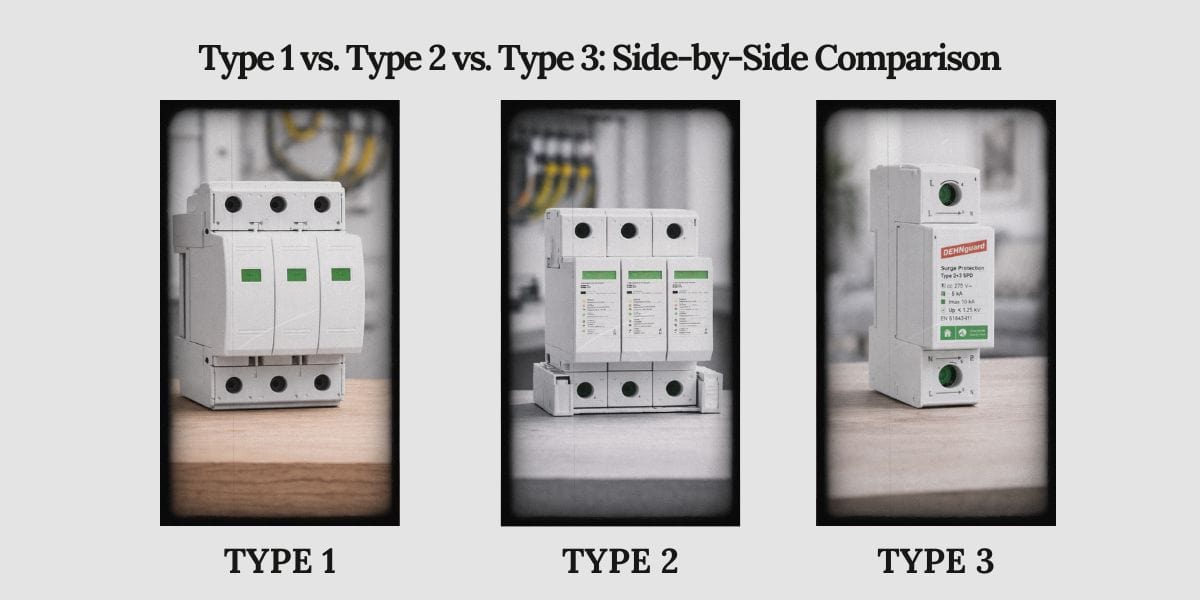
| thông số | Loại 1 SPD | Loại 2 SPD | Loại 3 SPD |
| Vị trí lắp đặt điển hình | Lối vào dịch vụ, phía đường dây của ngắt kết nối chính | bảng phân phối, phía tải của ngắt kết nối | Thiết bị gần nhạy cảm |
| Mức độ tiếp xúc đột biến | rất cao | Trung bình đến Cao | thấp kém |
| chức năng chính | chuyển hướng dòng điện đột nhập | Kẹp dư và tăng chuyển mạch | giới hạn điện áp tốt |
| Xử lý hiện tại tăng đột biến | rất cao | Trung bình đến cao | thấp kém |
| Độ chính xác kẹp điện áp | thấp kém | trung bình | địa vị cao |
| Tính phù hợp độc lập | không chút nào | có giới hạn | không chút nào |
| Phụ thuộc vào các SPD khác | yêu cầu loại 2 hạ lưu | Thường được ghép nối với loại 1 và loại 3 | Yêu cầu ngược dòng loại 1 hoặc loại 2 |
| Rủi ro điển hình nếu áp dụng sai | Bảo vệ thiết bị không đầy đủ | Quá căng thẳng và giảm tuổi thọ | thất bại thảm hại |
So sánh này nêu bật một nguyên tắc chính: Các loại SPD được xác định bởi chức năng và vị trí, không phải bởi xếp hạng hiệu suất.
Loại 1 so với Loại 2: Sự khác biệt về bảo vệ thượng nguồn
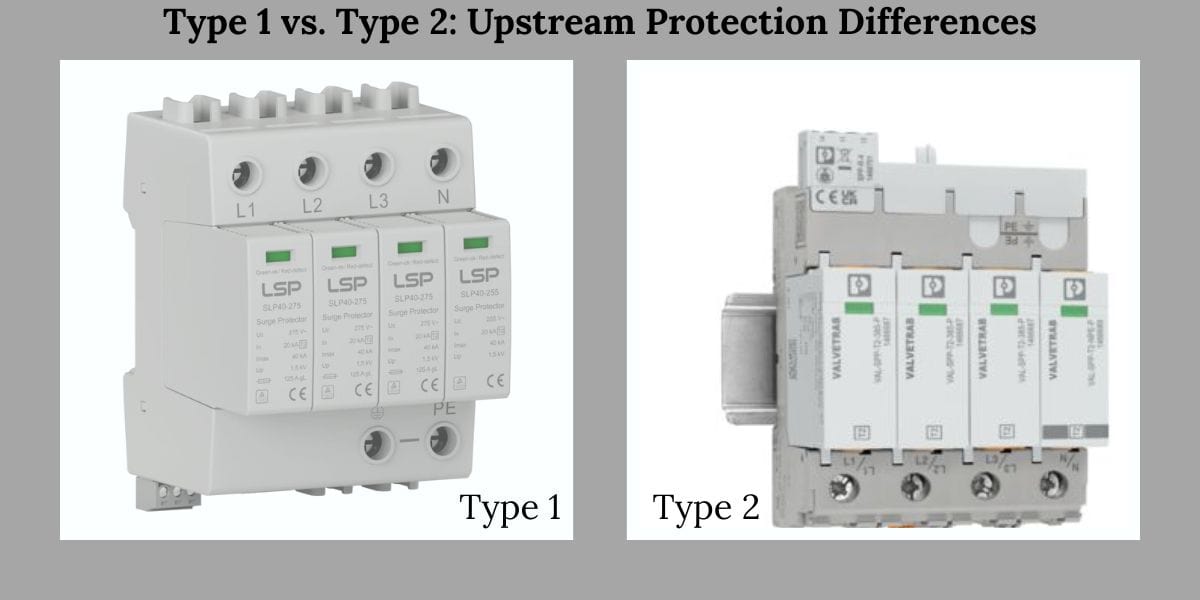
bối cảnh cài đặt
SPD loại 1 được lắp đặt ở lối vào dịch vụ, nơi tiếp xúc với nước ngoài cao nhất. SPD loại 2 được cài đặt ở hạ lưu, trong hệ thống phân phối nội bộ.
Sự khác biệt về vị trí này thay đổi cơ bản những gì mỗi thiết bị dự kiến sẽ xử lý.
Hồ sơ năng lượng tăng đột biến
- Loại 1 SPD gặp các xung năng lượng cao liên quan đến các sự kiện liên quan đến sét xâm nhập từ mạng tiện ích.
- Loại 2 SPD gặp phải năng lượng sét dư và quá độ chuyển mạch thường xuyên được tạo ra bên trong.
Vì các thiết bị loại 2 không được thiết kế cho các xung năng lượng cao nhất, chúng không thể thay thế bảo vệ loại 1 ở lối vào dịch vụ.
Sự khác biệt về chức năng
- Loại 1 tập trung vào dòng điện tăng đột biến
- Loại 2 tập trung vào giới hạn điện áp và kiểm soát tăng áp lặp lại
Chỉ lắp đặt bảo vệ loại 2 trong môi trường tiếp xúc cao sẽ làm thay đổi căng thẳng quá mức lên các thiết bị không được thiết kế cho nó, dẫn đến suy thoái sớm.
Loại 2 so với Loại 3: Phân phối so với Bảo vệ cấp thiết bị
Khoảng cách lắp đặt
SPD loại 2 bảo vệ mạng phân phối, trong khi SPD loại 3 bảo vệ các thiết bị hoặc mạch riêng lẻ. Khoảng cách giữa SPD và tải được bảo vệ là một yếu tố khác biệt quan trọng.
điều khiển điện áp dư
Sau khi bảo vệ ngược dòng, điện áp quá độ dư vẫn có thể vượt quá khả năng chịu xung của các thiết bị điện tử nhạy cảm. SPD loại 3 cung cấp tinh chỉnh điện áp tốt tại điểm sử dụng.
Hạn chế xử lý năng lượng
SPD loại 3 không được thiết kế để hấp thụ năng lượng đột biến. Nếu tiếp xúc trực tiếp với các sự kiện năng lượng cao, chúng có thể thất bại nhanh chóng. Đây là lý do tại sao chúng không bao giờ được sử dụng nếu không có bảo vệ ngược dòng.
So sánh giữa loại 2 và loại 3 không phải là “tốt hơn”, mà là về nơi độ chính xác thay thế việc xử lý năng lượng.
Tại sao không có loại SPD duy nhất là đủ
Bảo vệ chống sét lan truyền không phải là phụ gia. Cài đặt nhiều thiết bị cùng loại không cung cấp bảo vệ theo lớp.
Mỗi loại SPD chỉ hoạt động tối ưu trong phạm vi ứng suất dự kiến của nó:
- Loại 1 làm giảm năng lượng tăng đột biến
- Loại 2 quản lý quá điện áp còn lại
- Loại 3 Giới hạn điện áp cuối cùng
Cố gắng thực hiện tất cả các chức năng này với một thiết bị duy nhất dẫn đến bảo vệ bị xâm phạm, tuổi thọ dịch vụ bị rút ngắn hoặc cả hai.
Phối hợp sử dụng loại 1, loại 2 và loại 3 SPDs
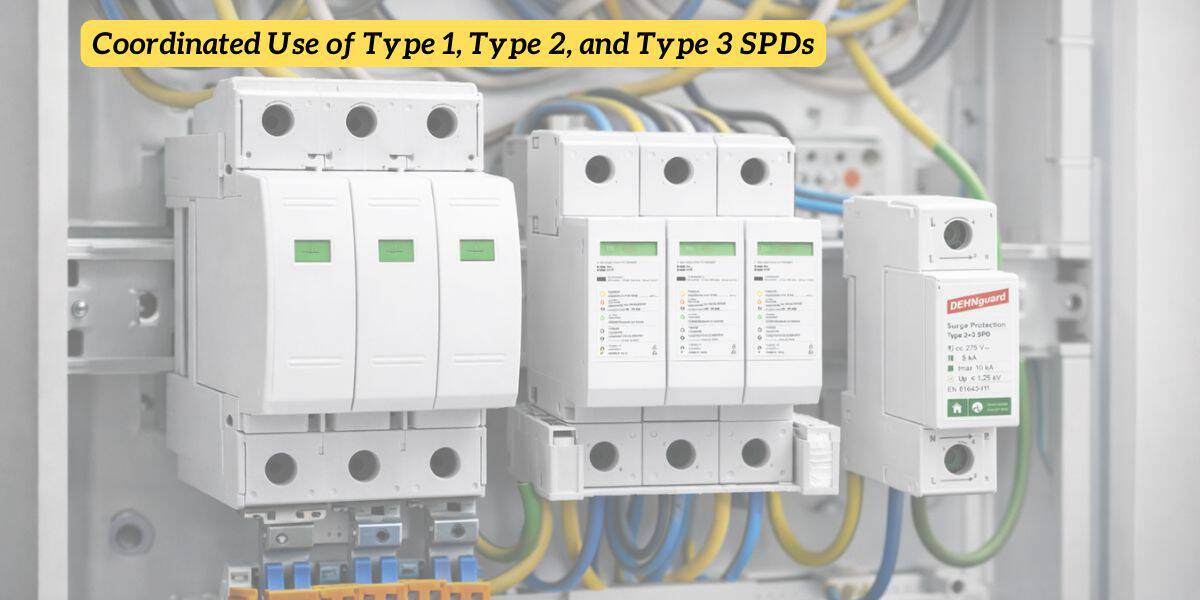
Cách thức hoạt động của phối hợp
Hệ thống bảo vệ tăng cường phối hợp phản ánh cách năng lượng tăng truyền:
- Loại 1 Chuyển hướng các xung năng lượng cao khi nhập hệ thống
- Loại 2 Kẹp tăng còn lại trong hệ thống phân phối
- Loại 3 Bảo vệ các tải nhạy cảm từ điện áp dư
Mỗi giai đoạn làm giảm căng thẳng cho giai đoạn tiếp theo.
Tại sao sự phối hợp lại quan trọng hơn số lượng
Sự phối hợp không đúng cách có thể gây ra:
- Chia sẻ năng lượng không đồng đều
- Quá nóng cục bộ
- Hành vi thất bại không thể đoán trước
Vị trí chính xác và sự phân tách trở kháng hơn là lắp đặt các thiết bị bổ sung.
Các kịch bản so sánh dựa trên ứng dụng
Lối vào dịch vụ với phơi sáng bên ngoài
Các cơ sở có đường dây điện trên cao hoặc hạ tầng điện ngoài trời yêu cầu bảo vệ loại 1 tại lối vào dịch vụ, tiếp theo là bảo vệ loại 2 ở hạ lưu.
Hệ thống phân phối thương mại và công nghiệp
Hoạt động chuyển mạch chi phối hoạt động đột biến. SPD loại 2 cung cấp vai trò bảo vệ chính, thường được phối hợp với các thiết bị loại 1 thượng nguồn.
Hệ thống điện tử nhạy cảm
Bộ điều khiển tự động hóa, thiết bị đo đạc và giao diện truyền thông yêu cầu bảo vệ loại 3, nhưng chỉ khi năng lượng tăng áp thượng nguồn đã được giảm bớt.
Hệ thống một pha so với ba pha
một giai đoạn 3 Thiết bị bảo vệ chống sét phải quản lý quá trình chuyển tiếp giai đoạn và pha-đất một cách nhất quán. Lựa chọn loại SPD phải phù hợp với cấu hình hệ thống, không chỉ định mức điện áp.
Những sai lầm so sánh phổ biến mà các kỹ sư mắc phải
- Giả sử thiết bị loại 3 có thể hoạt động độc lập
- Quá khổ một SPD thay vì phối hợp nhiều loại
- Cài đặt nhiều thiết bị loại 2 mà không xem xét trở kháng
- coi các loại SPD là cấp hiệu suất hơn là các vai trò chức năng
Những lỗi này làm giảm hiệu quả bảo vệ và tăng nguy cơ bảo trì.
Bối cảnh tiêu chuẩn
Các tiêu chuẩn như UL 1449 và IEC 61643 xác định điều kiện thử nghiệm và tiêu chuẩn phân loại cho các loại SPD. Chúng hỗ trợ so sánh nhất quán, nhưng chúng không thay thế phán đoán kỹ thuật cấp hệ thống liên quan đến vị trí và phối hợp.
Phần kết luận
Các thiết bị bảo vệ đột biến loại 1, loại 2 và loại 3 đóng vai trò riêng biệt và bổ sung trong hệ thống điện. Sự khác biệt của chúng được xác định bởi vị trí lắp đặt, tiếp xúc với mức tăng đột biến và chức năng bảo vệ, không phải theo loại sản phẩm hoặc vị trí tiếp thị.
Bảo vệ đột biến hiệu quả phụ thuộc vào sự phối hợp, không quá khổ hoặc dư thừa. Khi mỗi loại SPD được áp dụng ở nơi nó hoạt động tốt nhất, năng lượng tăng dần được kiểm soát dần dần, căng thẳng thiết bị được giảm bớt và độ tin cậy của hệ thống lâu dài được cải thiện.
hỏi Ẩn
không chút nào. Các thiết bị loại 2 không được thiết kế cho mức độ tiếp xúc đột biến cao nhất hiện có khi nhập hệ thống.
chỉ gián tiếp, và chỉ khi bảo vệ thượng nguồn đã giảm năng lượng đột biến.
Trong môi trường tiếp xúc thấp, nó có thể được chấp nhận, nhưng rủi ro tăng lên đáng kể mà không có sự bảo vệ thượng nguồn.
Bởi vì vị trí không chính xác có thể quá áp thiết bị bất kể xếp hạng.
Không phải luôn luôn, nhưng hầu hết các cài đặt hiện đại đều được hưởng lợi từ sự phối hợp ít nhất loại 1 và loại 2.