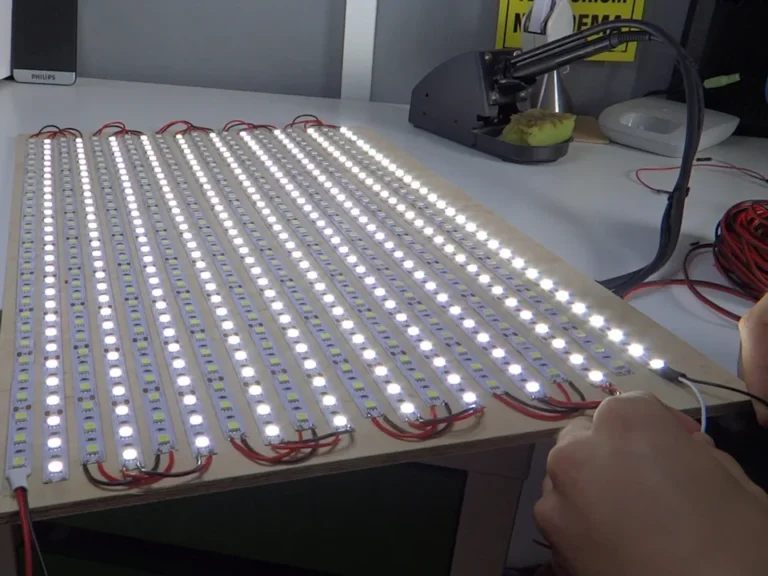
Trong ngành sản xuất điện tử, “PCB” và “PCBA” được đề cập gần như hàng ngày. Tuy nhiên, hai khái niệm này thường gây nhầm lẫn, ngay cả trong số các công ty khởi nghiệp phần cứng hoặc nhóm mua sắm không có nền tảng điện tử.
Một số người tin rằng chúng chỉ là từ đồng nghĩa, những người khác lại cho rằng PCBA chỉ đơn giản là một “phiên bản PCB nâng cấp” và một số nhân viên thu mua thậm chí vẫn chưa rõ họ thực sự yêu cầu dịch vụ nào khi yêu cầu báo giá.
Trên thực tế, sự khác biệt giữa PCB và PCBA vượt ra ngoài định nghĩa, tác động trực tiếp đến chi phí sản phẩm, chu kỳ phân phối, rủi ro chất lượng và độ phức tạp của chuỗi cung ứng. Đặc biệt trong bối cảnh năm 2026, nơi mà các thiết bị điện tử có tính thông minh cao và công nghệ AI được tích hợp sâu vào các quy trình sản xuất, hiểu đúng về sự phân biệt giữa PCB và PCBA đã trở nên quan trọng đối với doanh nghiệp để giảm rủi ro và tăng cường hiệu quả.
Bài viết này sẽ phân tích một cách có hệ thống những khác biệt cốt lõi giữa PCB và PCBA từ nhiều khía cạnh - định nghĩa kỹ thuật, quy trình sản xuất, cấu trúc chi phí, xu hướng ngành và quyết định mua sắm - để giúp các kỹ sư và nhân viên mua sắm đưa ra những lựa chọn sáng suốt hơn trong giai đoạn đầu của dự án.
PCB là gì? (bảng mạch in)
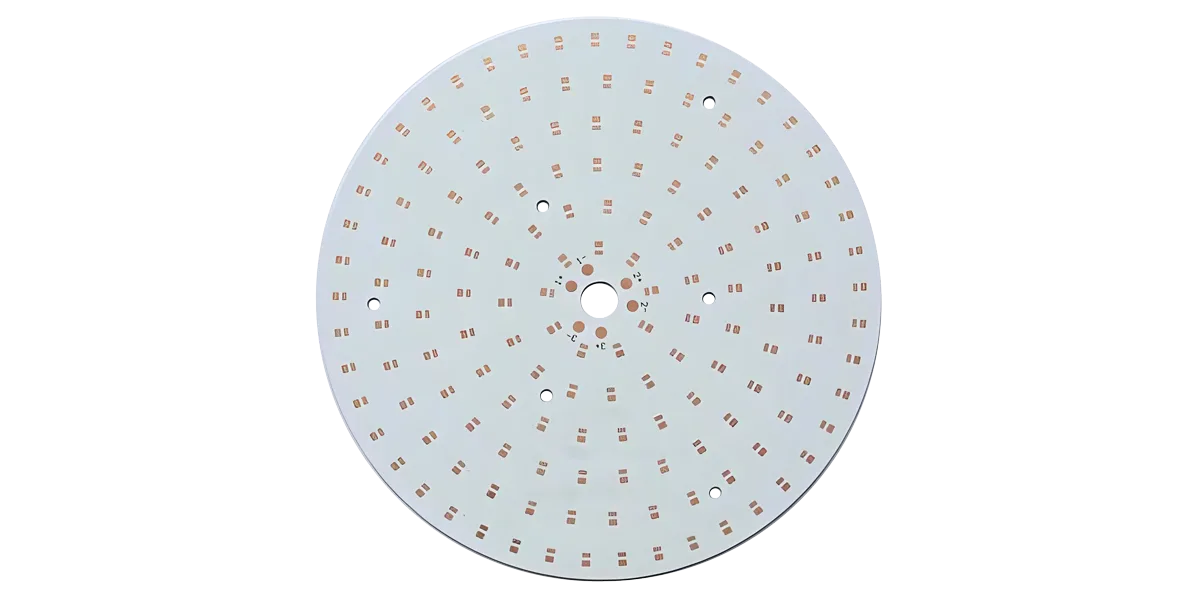

PCB (bảng mạch in) đóng vai trò là nhà cung cấp cơ bản cho các linh kiện điện tử, cho phép kết nối điện thông qua dấu vết lá đồng, miếng đệm và vias. PCB chỉ đề cập đến “bảng trần” mà không có bất kỳ thành phần điện tử nào được gắn trên đó. Tuy nhiên, nó tạo thành nền tảng vật lý của các sản phẩm điện tử, cung cấp chất nền cho mạch điện và tạo điều kiện cho các kết nối điện.
PCB đóng vai trò là điểm khởi đầu cho tất cả các hệ thống chiếu sáng LED, cho dù là dải đèn LED linh hoạt hay các mô-đun LED công suất cao.
Các thành phần cấu trúc của PCB LED
Một PCB LED điển hình thường bao gồm:
1. vật liệu cơ sở
- FR-4: Thích hợp cho đèn LED công suất thấp đến trung bình
- PCB lõi kim loại (MCCB): nhôm hoặc đồng, được sử dụng rộng rãi trong các dải và mô-đun LED công suất cao cho hiệu suất nhiệt vượt trội
- Vật liệu cao tần: Được sử dụng trong hệ thống chiếu sáng thông minh và hệ thống đèn LED IoT
2 . lớp đồng
Độ dày đồng (1 oz-6 oz) Tác động trực tiếp:
- Khả năng mang theo hiện tại
- điều khiển điện áp rơi
- Hiệu suất quản lý nhiệt của dải LED
3. hàn nạ ngoại
Ngăn ngừa ngắn mạch và quá trình oxy hóa. Trong ngành công nghiệp LED, mặt nạ hàn trắng được sử dụng rộng rãi vì tính chất phản chiếu vượt trội của nó.
4. Màn lụa
Các dấu hiệu cho biết cực tính LED, định hướng và số bộ phận, tạo điều kiện thuận lợi cho việc sản xuất và bảo trì hàng loạt.
Các loại PCB phổ biến trong ngành công nghiệp LED
Các loại PCB và ứng dụng trong ngành công nghiệp LED chủ yếu như sau:
| mẫu | thuộc về vật chất | Ứng dụng |
| PCB dải linh hoạt | Mạch in linh hoạt (FPC) | Khe cắm ánh sáng, tủ, môi trường lắp đặt không đều |
| Đen LED PCB | Bảng sợi thủy tinh FR-4 / Bảng cơ sở nhôm | Đèn tuyến tính, đèn trần (FR-4 cho công suất thấp, nhôm cho công suất cao) |
| PCB dải cứng | Bảng cơ sở nhôm PCB / Bảng đồng FR-4 dày | chiếu sáng tuyến tính, chiếu sáng công nghiệp |
| Bảng PCB tùy chỉnh LED | Bảng PCB tùy chỉnh LED | Chiếu sáng cao cấp / chuyên nghiệp |
PCBA là gì? (lắp ráp bảng mạch in)
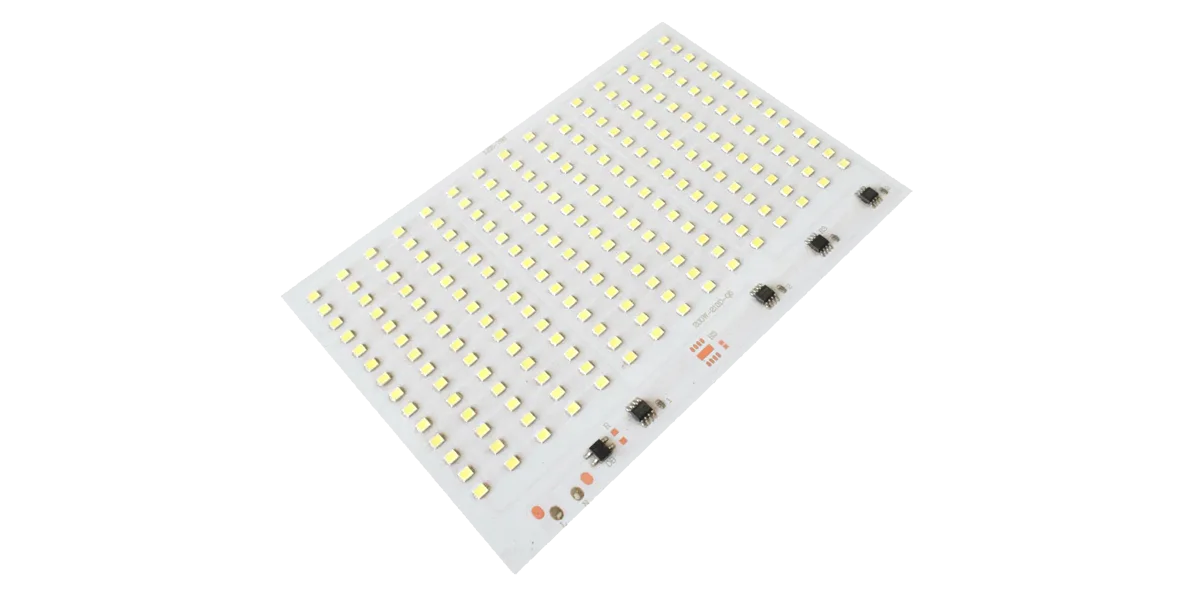

PCBA (hội bảng mạch in) Đề cập đến bảng mạch hoàn chỉnh được sản xuất bằng cách hàn các linh kiện điện tử như điện trở, tụ điện, IC, đèn LED và đầu nối vào PCB bằng các quy trình SMT hoặc THT. Nó sở hữu các đặc tính điện và chức năng hoàn chỉnh. Đó là hệ thống mạch hoàn thiện sau khi các linh kiện điện tử được hàn, lắp ráp và thử nghiệm trên PCB.
PCBA là bước quan trọng giúp PCB “thực sự hoạt động”.
1. Tại sao các sản phẩm LED phải trải qua PCBA?
Không có PCBA:
- Đèn LED không thể chiếu sáng.
- Trình điều khiển dòng điện không đổi không thể hoạt động ổn định.
- Không thể thực hiện các chức năng điều khiển thông minh và làm mờ.
PCBA chip LED, điện trở, tụ điện, IC điều khiển, đầu nối và các thành phần khác trên PCB, biến nó thành hệ thống chiếu sáng chức năng.
2 .Led PCBA lắp ráp quy trình
- SMT (Công nghệ gắn trên bề mặt)
- Quy trình chính cho dải LED và mô-đun
- Tự động hóa cao, hiệu quả và tính nhất quán
- Thích hợp cho việc sắp xếp đèn LED mật độ cao
- THT (thông qua công nghệ lỗ)
- Dùng cho các giao diện nguồn và các thiết bị đầu cuối dòng điện cao
- Độ bền cơ học cao và ổn định
- Lắp ráp lai (SMT + THT)
- Thường gặp trong các thiết bị LED thương mại và công nghiệp, cân bằng hiệu suất và độ tin cậy.
So sánh các quy trình sản xuất PCB và PCBA (từng bước)
Hiểu được các quy trình sản xuất là chìa khóa để nắm bắt sự khác biệt của chúng.
Quy trình sản xuất PCB chủ yếu bao gồm phơi nhiễm, khắc, khoan, mạ, v.v. Tham khảo sơ đồ sau cho quy trình làm việc cụ thể:
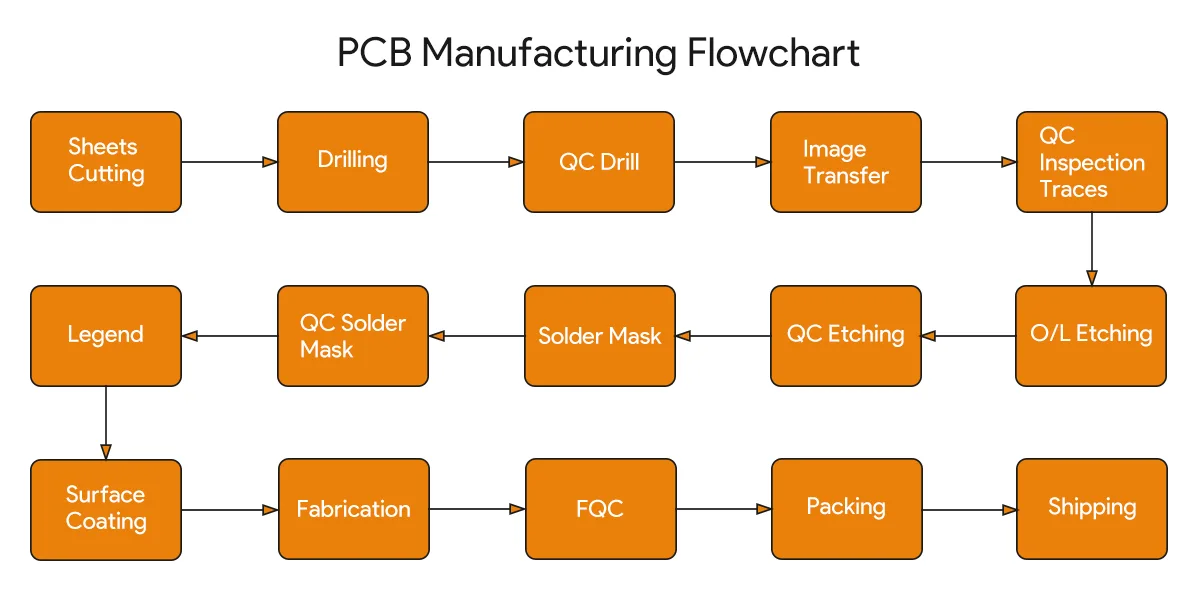
Ở giai đoạn này, PCB hoàn thành vẫn là một bảng trần mà không có bất kỳ chức năng chiếu sáng hoặc điều khiển nào.
Quy trình sản xuất PCBA chủ yếu bao gồm vị trí, lắp ráp và thử nghiệm SMT. Quy trình làm việc cụ thể được minh họa trong biểu đồ dưới đây:
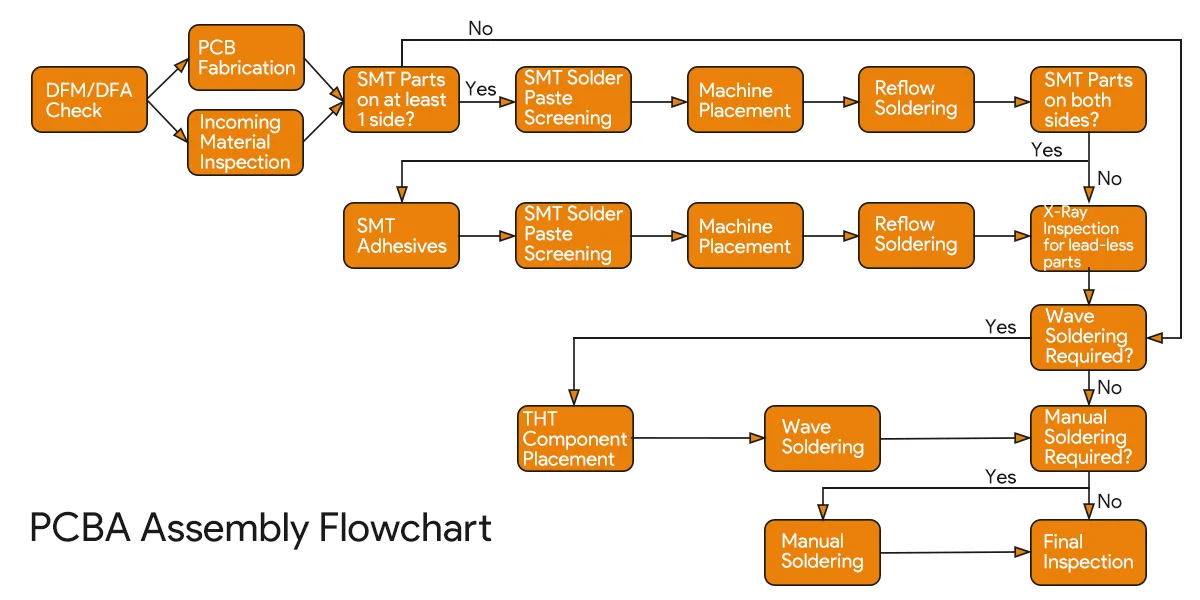
Như đã trình bày, quy trình PCBA dài hơn đáng kể so với sản xuất PCB và phụ thuộc nhiều hơn vào chuyên môn, thiết bị và khả năng quản lý.
PCB so với PCBA: Sự khác biệt chính trong nháy mắt
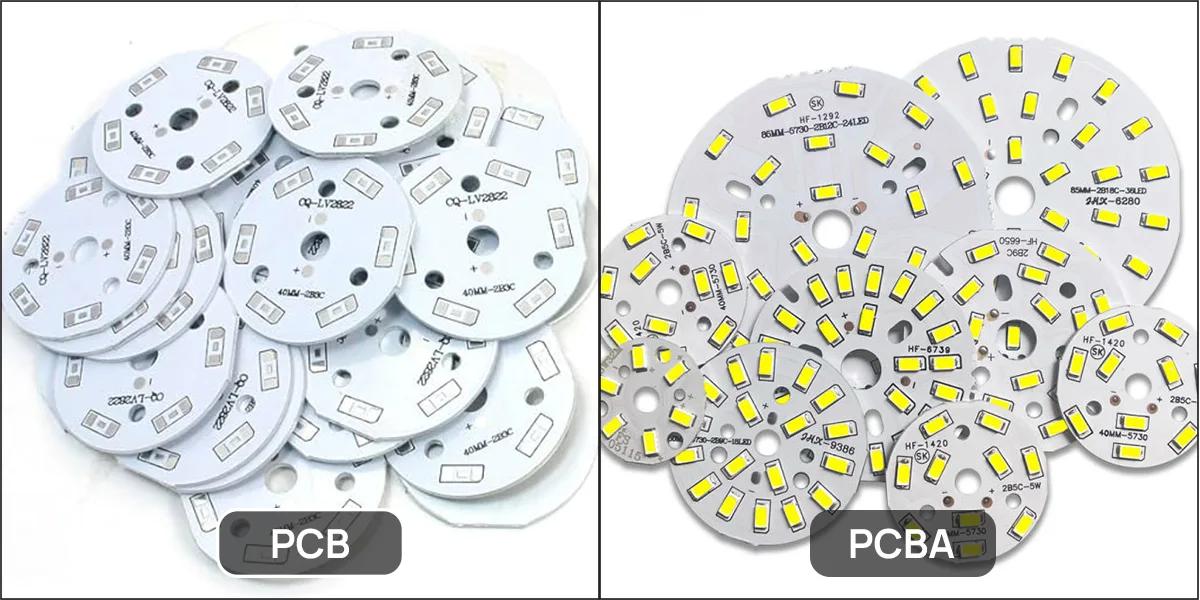
Sự khác biệt giữa PCB và PCBA là gì? Một phép tương tự đơn giản: PCB = cấu trúc nền tảng, tương tự như khuôn khổ và đường ống của tòa nhà; PCBA = thành phẩm chức năng, một tòa nhà được cung cấp năng lượng và vận hành hoàn toàn.
Trong các sản phẩm chiếu sáng LED, một mình PCB trần không thể phát ra ánh sáng. Chỉ sau khi hoàn thành PCBA, dải đèn LED hoặc mô-đun mới hoạt động bình thường.
| nốt đôvăn kiện | PCB (bảng mạch in) | pcba (lắp ráp bảng mạch in) |
| sự định nghĩa | Một tấm ván trần làm bằng chất nền cách điện và các vết đồng dẫn điện, không có linh kiện điện tử | Một mô-đun chức năng được tạo ra bằng cách lắp ráp các linh kiện điện tử (điện trở, tụ điện, IC, v.v.) vào PCB |
| chức năng chính | Cung cấp đường dẫn kết nối điện và hỗ trợ cơ khí cho các thành phần | Thực hiện các chức năng điện tử thực tế như xử lý tín hiệu, quản lý công suất và logic điều khiển |
| trạng thái thể chất | "Bàn trần" không được dân cư | Lắp ráp và hàn đầy đủ "Mô-đun hoàn thành" |
| bề ngoài | Mặt nạ hàn màu xanh lá cây (hoặc màu khác) với dấu vết và miếng đệm đồng có thể nhìn thấy | Được bao phủ bởi các thành phần, mối hàn và dây dẫn; bố trí chức năng có thể nhìn thấy rõ ràng |
| Phạm vi sản xuất | Chỉ chế tạo bảng | Tìm nguồn cung cấp linh kiện + lắp ráp + kiểm tra |
| Quy trình sản xuất | Cắt vật liệu → cán đồng → khắc mạch → khoan → hoàn thiện bề mặt | Kiểm tra đến → Vị trí SMT → Hàn sóng / hàn → Kiểm tra & kiểm tra chức năng |
| Trọng tâm kỹ thuật chính | Độ chính xác theo dõi, kiểm soát trở kháng, độ chính xác khắc độ micron | Chất lượng hàn, độ chính xác của vị trí, kiểm soát năng suất (thường là ≥99,9%) |
| Cơ cấu chi phí | Nguyên liệu + Quy trình chế tạo PCB | Linh kiện điện tử (BOM) + lắp ráp + kiểm tra |
| Mức chi phí điển hình | Tương đối thấp (PCB tùy chỉnh: xấp xỉ. $0.1–$5 mỗi bảng) | Cao hơn (các nguyên mẫu PCBA thường bắt đầu từ $30, tùy thuộc vào BOM) |
| Đầu ra phân phối | Máy mang điện không có chức năng | Mạch điện tử sẵn sàng sử dụng với các chức năng xác định |
1. Sự khác biệt về chức năng
- PCB: Chỉ cung cấp các đường dẫn mạch
- PCBA: Hệ thống LED hoạt động đầy đủ sẵn sàng để khởi động
2. Phạm vi sản xuất
- PCB: chế tạo bảng mạch
- PCBA: Mua sắm linh kiện + lắp ráp + kiểm tra
3. Tài liệu bắt buộc (Câu hỏi mua sắm thường gặp)
Sản xuất PCB yêu cầu:
- Tệp Gerber
- NC Drill Files
PCBA yêu cầu:
- BOM (Bill of VẬT LIỆU)
- Chọn và đặt (tệp tọa độ)
- Tệp Stencil
4. Kiểm tra và kiểm tra chất lượng
PCB:
- Kiểm tra tính liên tục điện
- kiểm tra trực quan
- Đo độ dày đồng
- kiểm tra trở kháng
PCBA:
- Kiểm tra dán hàn SPI
- Kiểm tra quang học tự động AOI
- X-quang (BGA, kiểm tra khớp hàn IC)
- ICT / Kiểm tra chức năng (độ sáng, hiện tại, ổn định)
- Kiểm tra độ tuổi và độ tin cậy
- Kiểm tra thông lượng và điện năng sáng
5. Bao bì và hậu cần
- PCB: Bao bì chống ẩm chân không
- PCBA: Bao bì chống tĩnh điện (ESD), khay tùy chỉnh
Tại sao PCBA đắt hơn PCB đáng kể?

Đây là một trong những câu hỏi thường gặp nhất của nhân viên thu mua. Chi phí PCBA cao hơn không chỉ đơn giản là do phí xử lý tăng lên, mà là kết quả của nhiều yếu tố:
- Chi phí thành phần: Chip, điện trở, tụ điện, đèn LED, IC điều khiển và các thành phần khác thường chiếm phần lớn nhất trong chi phí PCBA.
- Đầu tư lao động và thiết bị: Máy móc và máy móc tốc độ cao, lò nướng, hệ thống AOI và thiết bị kiểm tra đều là những tài sản có giá trị cao.
- Chi phí sản xuất và rủi ro: Các lỗi hàn, lỗi vật liệu và các vấn đề thiết kế đều mang rủi ro khi làm lại hoặc phế liệu.
- Chi phí quản lý chuỗi cung ứng: Sự thiếu hụt vật liệu, thay thế thành phần và sự biến động của lịch trình giao hàng đòi hỏi sự phối hợp bổ sung.
Từ góc độ kinh doanh, PCBA về cơ bản là một “dịch vụ kỹ thuật hệ thống”, không chỉ đơn thuần là xử lý sản xuất.
Xu hướng ngành 2026: AI biến đổi PCB / PCBA như thế nào?
Đến năm 2026, trí tuệ nhân tạo đã vượt ra khỏi các giai đoạn khái niệm để tích hợp sâu vào sản xuất PCB và PCBA, thúc đẩy sự chuyển dịch của ngành sang lĩnh vực sản xuất thông minh và tích hợp cao.
Các xu hướng chính bao gồm:
- Phân tích DFM hỗ trợ AI: Dự đoán các vấn đề sản xuất tiềm ẩn trước khi sản xuất, giảm chạy thử.
- Phát hiện lỗi AOI-Ai-Powered: Xác định các sai sót phức tạp như khớp hàn lạnh và lệch thông qua việc học sâu, giảm tỷ lệ đánh giá sai.
- Lập lịch thông minh và dự báo vật liệu: Tối ưu hóa việc sử dụng công suất đồng thời giảm sự không chắc chắn về phân phối.
- Dữ liệu chất lượng vòng kín: liên tục cải thiện năng suất và tính nhất quán thông qua phân tích dữ liệu.
Trong tương lai, các nhà máy PCBA hỗ trợ AI sẽ đạt được lợi thế đáng kể trong thời gian giao hàng, kiểm soát chất lượng và quản lý chi phí.
Bạn nên chọn PCB trần hay PCBA một cửa?
Không có câu trả lời nào phù hợp với tất cả — nó hoàn toàn phụ thuộc vào loại dự án của bạn.
Nếu bạn có một đội ngũ điện tử có kinh nghiệm và các nguồn lực đáng tin cậy của SMT và chỉ cần bảng trần, PCB cung cấp tính linh hoạt cao hơn và có thể tiết kiệm chi phí hơn.
Nếu bạn muốn giảm chi phí điều phối, giảm thiểu rủi ro chất lượng và đẩy nhanh thời gian đưa ra thị trường, PCBA một cửa thường là sự lựa chọn ưu việt.
Đối với các sản phẩm như bảng đèn LED, Mô-đun LED, và ánh sáng thông minh, PCBA tăng cường đáng kể tính nhất quán và độ tin cậy của phân phối.
Cạm bẫy mua sắm PCB / PCBA phổ biến
Các lỗi sau thường gặp trong các dự án thực tế:
- Cung cấp các tệp thiết kế chưa hoàn chỉnh hoặc chưa được xác minh
- BOM khác biệt với thiết kế thực tế
- Bỏ qua các yêu cầu kiểm tra trong khi chỉ tập trung vào đơn giá
- Giao các dự án PCBA phức tạp cho các nhà cung cấp PCB
Những vấn đề này thường không được chú ý trong quá trình trích dẫn nhưng tăng cường rủi ro trong quá trình sản xuất hàng loạt.
Hướng dẫn quyết định mua sắm: Bạn nên chọn như thế nào?
Trước khi hoàn thành việc lựa chọn, hãy ưu tiên đánh giá các yếu tố sau:
- Độ phức tạp của dự án và kích thước lô
- Kỹ thuật nội bộ và khả năng chuỗi cung ứng
- Yêu cầu về thời gian và tính nhất quán
- Cần một đối tác lâu dài, ổn định
Sự lựa chọn tối ưu không nhất thiết phải là báo giá thấp nhất mà là giải pháp có rủi ro tổng thể thấp nhất.
Phần kết luận
Tóm lại, PCB và PCBA đóng vai trò riêng biệt nhưng bổ sung trong sản xuất điện tử. PCB cung cấp cấu trúc cơ bản và kết nối điện, trong khi PCBA cung cấp chức năng hoàn toàn và giá trị thương mại cho sản phẩm.
Đối với các nhà sản xuất đèn LED, hiểu được sự khác biệt giữa PCB và PCBA vượt qua các cân nhắc kỹ thuật — đó là một quyết định chiến lược. Lựa chọn giải pháp sản xuất và lắp ráp phù hợp giúp giảm chi phí, nâng cao chất lượng, đẩy nhanh việc ra mắt sản phẩm trên thị trường toàn cầu. Khi tích hợp sản phẩm tiếp tục phát triển, các giải pháp PCBA với khả năng kỹ thuật và lợi thế kiểm soát chất lượng sẽ ngày càng đóng vai trò quan trọng trong thị trường điện tử và đèn LED toàn cầu.
hỏi Ẩn
không chút nào. PCB chỉ là một nhà cung cấp dịch vụ; không có các thành phần, nó không thể thực hiện bất kỳ chức năng nào.
Thông thường 7–15 ngày, tùy thuộc vào thời gian dẫn đầu của thành phần và yêu cầu thử nghiệm.
PCB phải tuân thủ ROHS / Reach. PCBA cũng yêu cầu kiểm tra chức năng và chứng nhận môi trường (ví dụ: hàn không chì). Thông thường 7–15 ngày, tùy thuộc vào thời gian dẫn của thành phần và yêu cầu thử nghiệm.
Thuật toán AI phân tích dữ liệu thử nghiệm trong thời gian thực, dự đoán các lỗi tiềm ẩn và giảm chi phí làm lại thủ công.
Vị trí và hàn lại SMT vẫn chiếm ưu thế, nhưng công nghệ hàn laser và in 3D sẽ dần dần đạt được sức hút.






