LED lighting has become the backbone of modern illumination — from smart streetlights to high-bay fixtures in factories. Yet, behind their efficiency and long lifespan lies a hidden vulnerability: electrical surges. These unpredictable spikes, often caused by lightning strikes or power grid fluctuations, can silently damage sensitive LED drivers and control circuits. For engineers and lighting designers, surge protection is no longer optional but essential. Choosing the right Surge Protective Device (SPD) is the key to ensuring long-term reliability and safety. Let’s explore why LED systems need SPD protection and how to select the best one for your application.
Why LED Lights Need SPD Protection
LED lighting systems are far more sensitive to voltage fluctuations than traditional fixtures. Because LED drivers and electronic control circuits operate on low-voltage DC power, they can be easily damaged by transient overvoltages caused by lightning strikes, switching operations, or power grid instability. Even a short surge can exceed the tolerance of these delicate components, leading to failure or performance degradation. That’s why surge protection for LED lights has become a critical part of any professional lighting design.
When a surge occurs, it can cause LED drivers to burn out, make the lights flicker, or shorten the overall lifespan of the fixture. In large-scale projects—such as outdoor street lighting or industrial installations—these failures not only increase maintenance costs but also interrupt operations and reduce system reliability. Effective LED surge protection is therefore essential to safeguard the investment and ensure continuous performance.
A Surge Protective Device (SPD) for LED lights acts as a shield that blocks or diverts harmful voltage spikes away from the circuit. By instantly detecting and grounding excess energy, an SPD prevents electrical stress on LED drivers, stabilizes current flow, and helps maintain long-term efficiency. In short, using the right SPD significantly improves LED lighting reliability and reduces the risk of surge-related damage.

Understanding SPD and Its Working Principle
A Surge Protective Device (SPD) is an electrical safety component designed to protect equipment from transient overvoltages. For more details, refer to our article on “Surge Protective Devices: A Complete Technical Guide”
An SPD works by instantly detecting a surge in voltage and diverting the excess current to the ground, preventing it from reaching sensitive components. Once the voltage returns to a normal level, the SPD resets and continues to monitor the circuit, ensuring continuous surge protection for lighting systems.
When selecting an SPD for LED lighting applications, several key parameters must be considered. Response time is crucial — the faster an SPD reacts, the less impact a surge will have on the LED driver. Let-through voltage (or residual voltage) indicates how much surge voltage passes through the device; the lower it is, the better the protection. Additionally, the rated discharge current (In/Imax) defines the surge energy the SPD can safely handle. Choosing an SPD with the right capacity ensures effective LED driver protection, especially in outdoor, high-risk environments such as street lighting or industrial facilities. A well-matched SPD helps maintain system stability, extends LED lifespan, and prevents costly replacements caused by electrical surges.
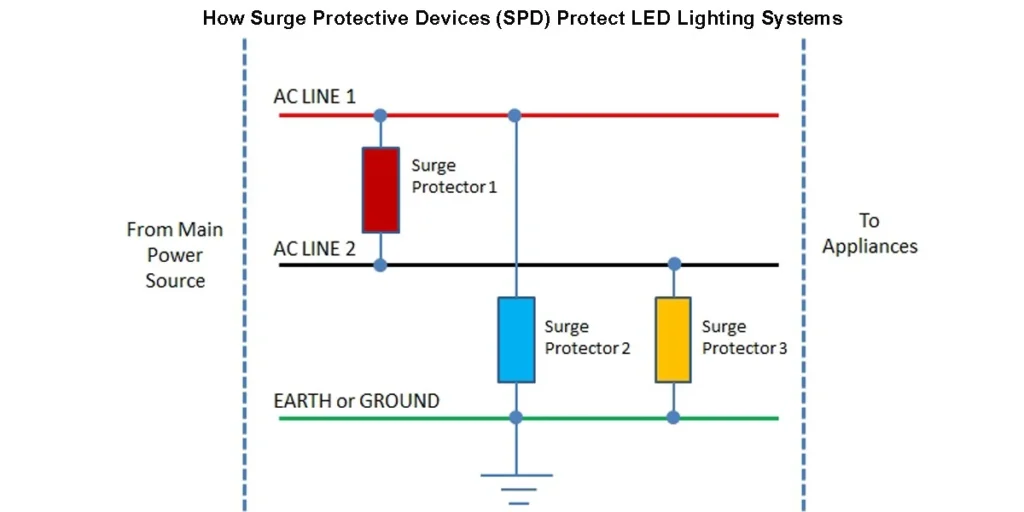
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing SPD for LED Lighting
When selecting the right SPD for LED lighting, it’s essential to evaluate multiple technical and environmental factors to ensure long-term system reliability and compliance with safety standards. Each application—whether indoor, outdoor, or industrial—requires a tailored surge protection approach.
1. Nominal Voltage & System Compatibility
The SPD’s nominal voltage should match the operating voltage of the LED driver or power supply (commonly 120V, 230V, 277V, or 347V). Installing an SPD with incorrect voltage ratings can reduce efficiency or fail to trigger protection during a surge. For most LED street lights and commercial fixtures, a 277V SPD is commonly used.
2. Discharge Current (In/Imax)
The rated discharge current determines how much surge energy the SPD can safely dissipate. Outdoor applications exposed to lightning typically require higher In/Imax ratings (10kA–20kA), while indoor or office lighting can use lower ratings (3kA–5kA). Selecting the right surge current capacity ensures reliable LED surge protection in any environment.
3. Protection Modes (L-N, L-G, N-G)
Different electrical systems require different protection modes. For example, L-N protection is suitable for basic single-phase LED lighting, while L-G/N-G provides additional safety in grounded systems. Multi-mode SPDs offer the most comprehensive protection.
4. Let-Through Voltage (Residual Voltage)
A lower residual voltage means less stress on the LED driver. For sensitive LED fixtures, choose SPDs with let-through voltage under 1.2kV to prevent partial damage over time.
5. Environmental Durability
For outdoor or industrial installations, select SPDs with IP65 or higher enclosures and UV-resistant materials. These prevent water ingress and corrosion, ensuring continuous protection in harsh conditions.
6. Standards & Certification
Choose SPDs that meet IEC 61643 or UL 1449 standards to guarantee tested safety performance and reliability for global markets.
| Selection Factor | Recommended Value / Range | Application Example |
| Nominal Voltage | 120V / 230V / 277V / 347V | Indoor, street, or industrial LEDs |
| Discharge Current (In/Imax) | 3kA–20kA | From indoor to outdoor lighting |
| Protection Modes | L-N, L-G, N-G | Based on electrical system type |
| Let-Through Voltage | ≤ 1.2kV | Sensitive LED drivers |
| Enclosure Rating | IP65 or above | Outdoor and humid environments |
| Certification Standard | IEC 61643 / UL 1449 | International compliance |
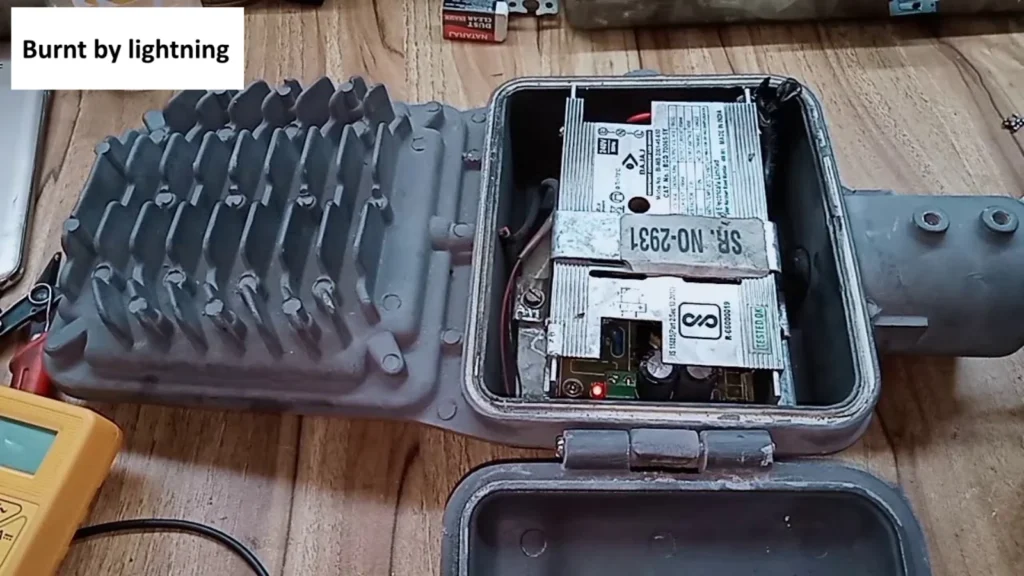

Practical Tips & Recommendations for LED Projects
Different LED applications require tailored SPD configurations. Street lights installed in open outdoor environments face frequent lightning surges, so SPDs with higher discharge capacity (≥10kA) and IP65-rated waterproof housing are essential. Industrial lighting systems in factories or warehouses should use SPDs with robust L-N and L-G protection modes to handle switching surges from heavy machinery. For architectural or commercial lighting, compact SPDs with low let-through voltage help maintain visual consistency and protect delicate LED drivers in control systems.
Engineers and procurement teams should also consider the SPD replacement cycle, especially after major surge events, as protection performance may degrade over time. Proper grounding is critical to ensure surge energy is safely dissipated. Always confirm voltage compatibility between the SPD and LED driver to avoid mismatch or false triggering.
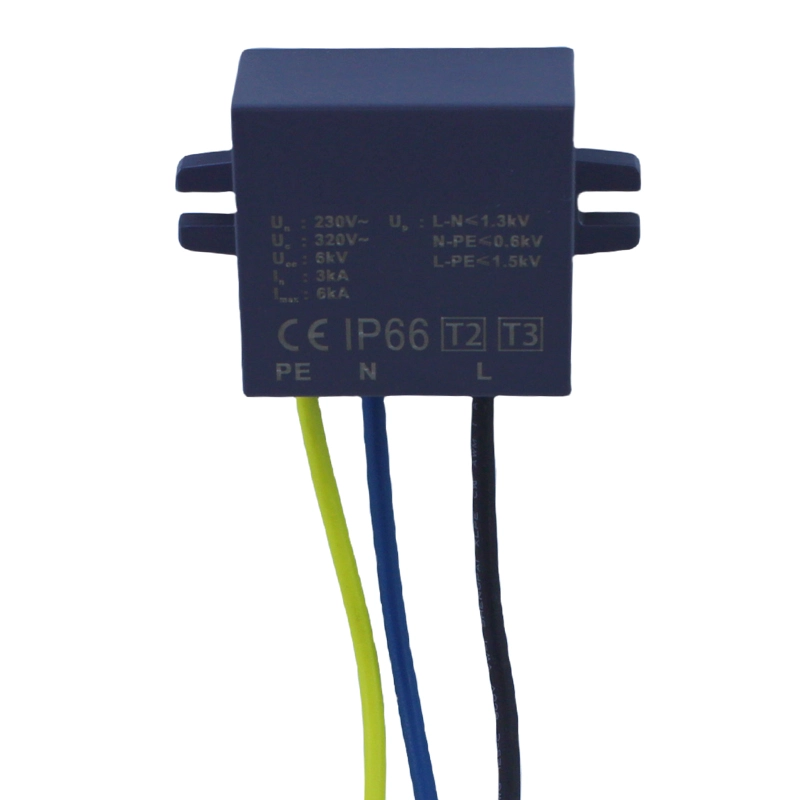
SPD03-DC320-P/G Type2+3
Designation: Type2+3
Classification: Class III
Protection mode: L-N , N-PE ,L-PE
Rated input voltage Un(L-N): 230VAC, 50/60Hz
Max. continuous operating voltage Uc (L-N): 320VAC, 50/60Hz
Max discharge current (8/20μs) Imax:6 kA
Nominal discharge current (8/20μs) In:3 kA
Voltage protective level Up: L-N ≤1.5 kV, N-PE ≤0.6 kV, L-PE ≤1.5 kV
Open circuit voltage Uoc: 6 kV
Backup fuse: 16A
Housing material: UL94V-0
Degree of protection: IP66
At SignliteLED, we not only manufacture high-quality LED strip lights, floodlights, and industrial high-bay fixtures, but also supply reliable SPDs specifically designed for LED applications. Our SPDs are tested to international standards, ensuring superior protection and longer service life for your lighting projects.