Heb je ooit vissers zien gebruiken die vissen aantrokken die licht op hun boten aantrokken? Deze magische bollen zijn niet voor verlichting - ze zijn voor het aantrekken van vissen! Vissen die lichten aantrekken, profiteren van de fototaxis van vissen, waardoor het voor vissers gemakkelijker wordt om ze te vangen. Vissen die lichten aantrekken, maken het vissen niet alleen efficiënter, maar beschermen ook het milieu en de gezondheid van de vissers, echt een perfecte mix van technologie en traditie.
LED-vissen die licht aantrekken, als een uniek verlichtingsapparaat, zijn op grote schaal in de visserij-industrie toegepast. Als een cruciaal onderdeel van LED-vissen die lichten aantrekken, hebben de kwaliteit en prestaties van de lichten een directe invloed op de algehele effectiviteit en levensduur van het verlichtingssysteem. Dit artikel gaat in op de werkingsprincipes van LED-vis die lichte voedingen aantrekt, belangrijke overwegingen voor selectie en onderhouds- en verzorgingsaspecten.
Wat zijn de soorten visaantrekkende lichten?
Door de bioluminescentie-eigenschappen van plankton te simuleren met behulp van specifieke spectra (zoals blauw- en roodlichtcombinaties), trekken deze lichten fototactische vissen aan om te verzamelen. Moderne visaantrekkende lampen gebruiken op grote schaal LED-technologie, met een IP68-waterdichtheid, intelligente temperatuurregeling en multi-spectrumaanpassingsfuncties, met een vermogen variërend van 15W draagbare modellen tot 3000W offshore-modellen.
I. Classificatie door spectrale kenmerken
Blauw licht (450-495 nm): Biedt de sterkste penetratie, is geschikt voor diepwaterbediening (50 meter of dieper) en is zeer effectief voor mid-to-upper laagvissen zoals sardines en makreel. Lichtgevende werkzaamheid kan 100-110 lm/w bereiken, waardoor het de reguliere optie in de markt is.
Geel licht (570-590 nm): Een toegewijde golflengte van de attractie voor inktvis, die uitzonderlijk goed presteert in troebele wateren. Gecombineerd met een 360° licht emissiehoek, kan het een groter gebied beslaan.
Groen licht (495-570 nm): Past bij de fluorescerende kenmerken van plankton en trekt vissen aan door het voedselketeneffect.
Rood licht (620-750 nm): Gebruikt voor aantrekkingskracht in ondiep water, maar heeft een hoge wateropname en een beperkte penetratiediepte.
RGB-combinatielicht: Integreert rode, blauwe en groene chips om maanlicht of bioluminescentie (bijv. krill), te verbeteren, waardoor de aantrekkingskracht op vissen van hogere orde wordt verbeterd. Het blauwgroene combinatiespectrum verbetert bijvoorbeeld de aggregatie-efficiëntie van een zacht lichaam met 40%.
Pulse Strobe-modus : Ondersteunt 200 Hz hoogfrequent knipperen om de visuele stimulatie-intensiteit te verbeteren.
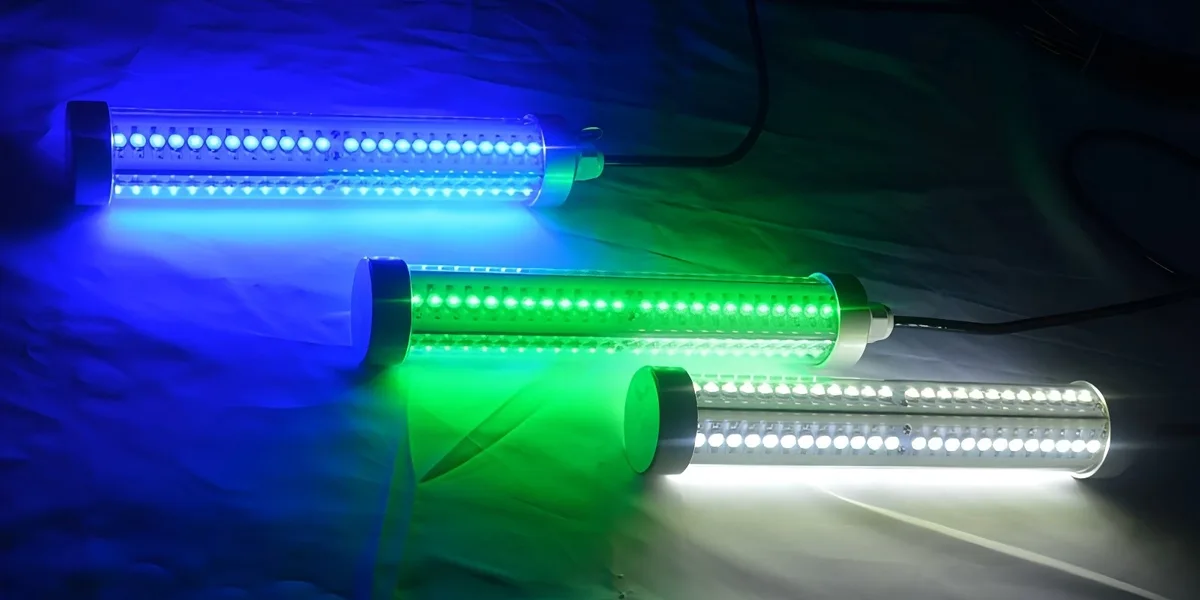

II. Classificatie door installatiescenario
Oppervlaktevissen aggregatie lichten: geïnstalleerd aan de zijkanten van het schip of masten om het wateroppervlak te verlichten en een lichtzone te creëren. Groothoeklenzen, met een stralingshoek van 120°, zijn nodig om de dekking te verbeteren en ze stralen licht uit dat 5.000 lumen overschrijdt. Het nadeel is dat het licht wordt beïnvloed door reflectie van het zeeoppervlak, wat resulteert in een zwakkere penetratie in diep water in vergelijking met onderwaterlichten.
Onderwater visaggregatie lichten: IP68 Beschermingsgraad, bestand tegen druk op 50 meter waterdiepte (ongeveer 5 ATM). De aluminium behuizing in combinatie met een nylon warmteafvoerstructuur is bestand tegen zoutcorrosie. Gebruikt typisch een dual-mode warmteafvoersysteem met kopervinnen en een zeewatercirculatiekanaal om een bedrijfstemperatuur 85°C te behouden, met jaarlijks lichtverval <3%.
Visaggregatielampen worden meestal rond vissersvaartuigen opgehangen voor grootschalige inzet, kunnen aan dek- of dockoppervlakken worden bevestigd voor hoge stabiliteit, of snel worden geïnstalleerd met behulp van klemmen voor verbeterde flexibiliteit.

iii. Classificatie door technisch sballing
| Type | Representatief product | Kerntechnologie | Toepassingsscenario |
| COB geïntegreerd | Multi-chip lensmodule | Driekleuren LED-geïntegreerd substraat, asferische lensfocusing | Offshore portemonnee zegen vissersboten |
| torpedo-TYPE | Diepwaterdrukbestendige lichten (bijv. 1000W model) | Aluminium fase-verandering koellichaam, 360 ° omnidirectionele verlichting | Diepzeevissen, het oogsten van zachte body |
| Slim Dnarigheid TYPE | PWM-besturingssysteem | Constant Current Drive + traploos dimmen, ondersteunt het maanlichtgradiëntprogramma | Ecologische simulatie voor de aantrekking van vissen |
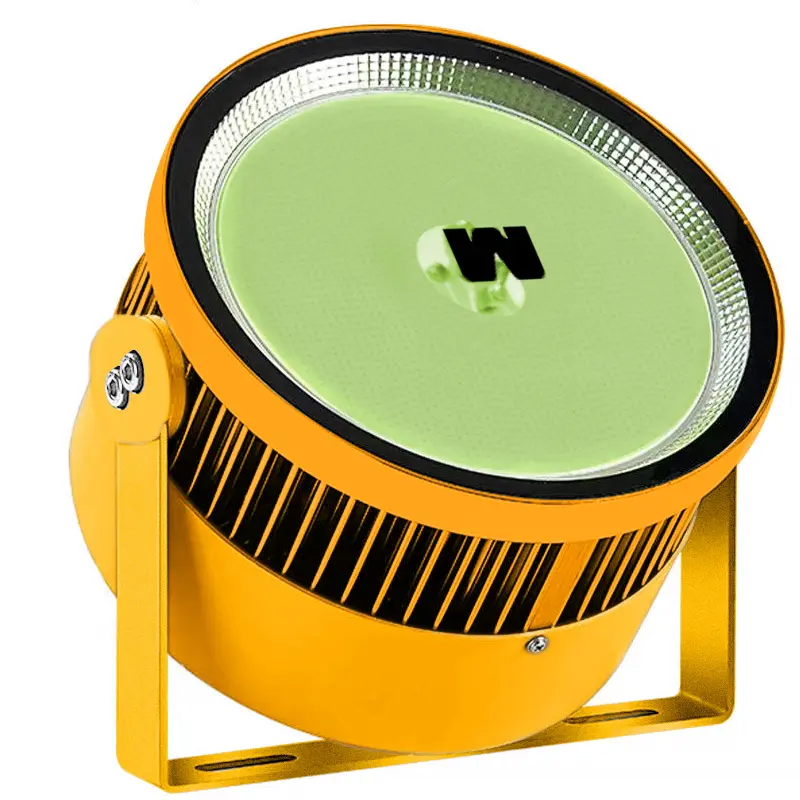

High Power Cob Fish trekt licht aan
Modelnr: Rond Type
Ingangsspanning: AC100-320V
Strompel: 10000V
Watt: 800W/1000W/1200W
Type LED: MAÏSKOLF
Grootte: Φ230 × 140mm/ Φ210 × 140mm
Kleur: 3000K/4000K/5000K/6000K/rood/groen/blauw/paars
CRI: >80@3000K/4000K/5000K/6000K
Lumen: >120lm/w@3000k/4000k/5000k/6000k
Lichaamsmateriaal/kleur: Aluminium / Gouden kleur
Lamp Chlmney Materia/Kleur: Gehard glas / ultrahelder glas (lichtdoorlaatbaarheid 95%)
IP-klasse: IP67
Lichtopbrengst verhouding (Lor): 97%
Vermogensfactor: 0.99
Elektromagnetische compatibiliteit: EMS + EMI
Hoe vissen die lichten aantrekken werken
De kerntechnologie van het aantrekken van vissen is om de fysieke eigenschappen van licht te gebruiken om vissen aan te trekken. 'S Nachts straalt het licht uit dat rijk is aan het blauwe spectrum door middel van hoge intensiteit LED-lampen. Dit type licht kan zeewater in de grootste mate doordringen, direct verhelderende vissen in de diepe zee. In donker water dient licht als een belangrijk referentiepunt voor vissen. Vissen in het water worden gestimuleerd door het licht en verzamelen zich bij de lichtbron, waardoor vissers ze gemakkelijker kunnen vangen.
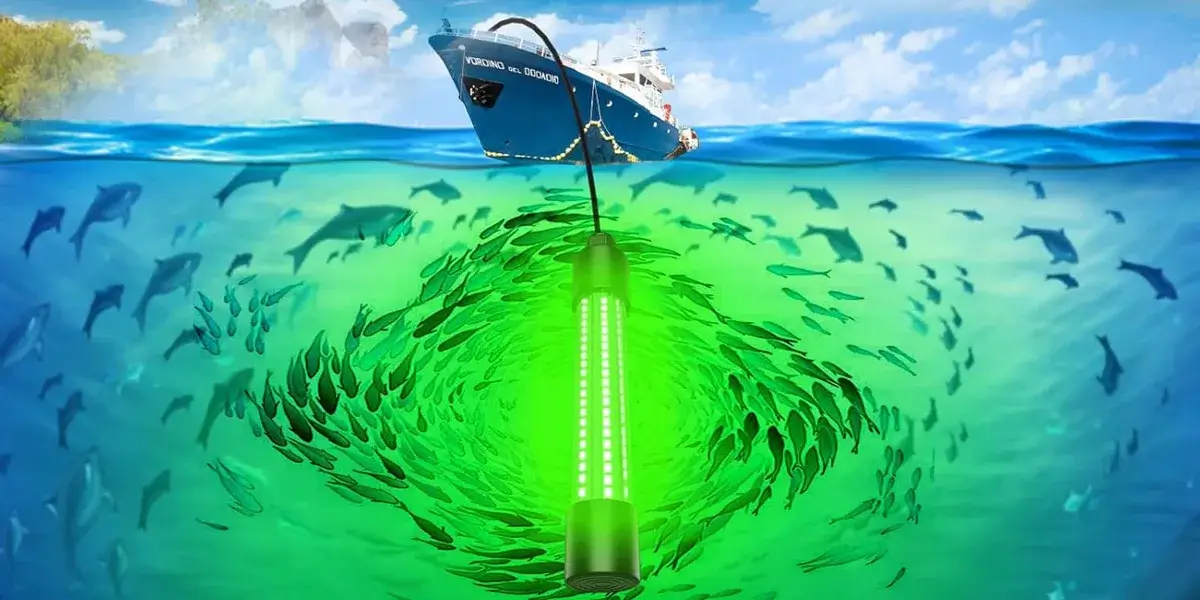

Door gebruik te maken van het fototaxiseffect zijn de netvliezen van mid-to-upper laagvissen (zoals sardines en makreel) gevoelig voor specifieke golflengtebanden. Blauwgroen licht stimuleert hun kegelcellen, waardoor fototaxis-gedreven clustergedrag wordt geactiveerd; bovendien, door het cascade-effect van de voedselketen te benutten, stralen LED-lampen ultraviolet licht uit (365-420 nm) en blauw licht om plankton aan te trekken, dat op zijn beurt kleine vissen aantrekt om het plankton in het verlichte gebied te volgen, waardoor grotere roofvissen worden getrokken om de kleine visscholen te volgen.
Daarom worden blauwe of groene lichtbronnen vaak gebruikt in licht aantrekkende lichten omdat deze kleuren verder in het water reizen en een sterkere aantrekkingskracht op vissen hebben. Het gebruik van blauwe of groene lichtbronnen kan dus effectiever vissen aantrekken en de visefficiëntie verbeteren.
Doelvissoorten zoals inktvis en makreel zijn gevoelig voor specifieke golflengtebereiken van licht (bijv. inktvis worden het gemakkelijkst aangetrokken door blauw licht in het bereik van 450-490 nm). Ze identificeren ten onrechte gebieden van intens licht als veilige omgevingen of voedselbronnen en benaderen de lichtbron actief.
Bovendien stralen sommige vis-aantrekkende lichten bepaalde geluidsgolven uit die zich door water kunnen voortplanten, waardoor vissen worden gewaarschuwd en ze gemakkelijker door het licht worden aangetrokken.
Hoe kies je het juiste visaantrekkelijk licht?
Visaantrekkende lichten zijn er in verschillende kleuren, waaronder blauw, groen en geel licht, onder andere. Het selecteren van het juiste visaantreklicht vereist rekening houden met de fototaxis-kenmerken van doelvissoorten, operationele waterdiepte en omgevingsfactoren. Het volgende is een wetenschappelijke selectiegids:
Diepzeeoperaties >40 meter: Blauw/groen licht met een golflengte van 450-560 nm, met een sterke penetratiecapaciteit, geschikt voor diepzee-operaties van meer dan 40 meter diep, waardoor vissoorten in de midden- tot onderlaag aangetrokken worden; 300 W groene LED-onderwaterbelichting kan een maximale diepte van 85 meter bereiken. Doelvissoorten zoals inktvis en makreel zijn gevoelig voor specifieke golflengtebereiken van licht (bijv. inktvis worden het gemakkelijkst aangetrokken door blauw licht in het bereik van 450-490 nm), waarbij ze ten onrechte gebieden met intens licht identificeren als veilige omgevingen of voedselbronnen en actief de lichtbron naderen.

Ondiepe wateroperaties (<40 meter): Rood licht met een golflengte van 620-750 nm heeft een langere bestralingsafstand in ondiepe gebieden (<40 meter) en wordt vaak gebruikt voor makreelvisserij en de laatste fasen van netto behuizingsoperaties; geel licht (2700K-3000K): met een lange bestralingsafstand, is het geschikt voor ondiepe zeegebieden zoals de Zuid-Chinese Zee en Zuidoost-Azië en wordt vaak gebruikt in combinatie met groen licht (bij een verhouding van 20%1P31000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000-30000000-3000000-300000-300000-m/m-side-scms, zoals de Zuid-Chinese Zee en Zuidoost-Azië en wordt vaak gebruikt in combinatie met groen licht (bij een verhouding van 2201Tp3

Wit licht (4200K en hoger): Zeer veelzijdig, het wordt vaak gebruikt in diepzee-operaties in combinatie met hoge kleurtemperatuur (5000K-6500K) en groen licht om de effectiviteit te verbeteren.

Vissoorten en optimale lichtkleurselectielijst
| vissoorten | Optimale kleur | Kernmechanisme van werking |
| inktvis | Diepblauw licht (450-490nm) | Piek fototaxis golflengte band, ten onrechte gezien als een veilige omgeving |
| sardine | roodevoldoening | Stimuleert schoolgedrag, verbetert de netto-efficiëntie |
| Fototactische oppervlaktevissen | geel licht | Warme tonen trekken scholen van whitebait, enz. |
| Bodembewonende vis | Vermijd wit licht | Sterk doordringend licht kan ervoor zorgen dat visscholen zich verspreiden |
Opmerkingen: Karper en crucian karpers hebben een sterke tolerantie voor blauw licht. Hoewel ultraviolet licht de vlottersignalen verbetert, is het schadelijk voor de ogen en is de technologie nog niet volwassen, dus het wordt op dit moment niet aanbevolen. Wit licht is alleen geschikt voor hulpverlichting; directe verlichting kan de bodem van de vis uitdrijven. Ultraviolet licht heeft aanzienlijke stralingsgevaren en de controle van lichtverval is een uitdaging, dus het is nog niet gecommercialiseerd.
Diepzeevissersvaartuigen worden aanbevolen om een combinatie van blauw licht en wit licht met hoge kleurentemperatuur te gebruiken voor verlichting om de dekking van de fototactische zone uit te breiden. Ondiep water operaties moeten een geel-groene lichtcombinatie gebruiken om de penetratiekracht en de efficiëntie van visaggregatie in evenwicht te brengen. LED-lichtbronnen moeten prioriteit krijgen: ze verbruiken slechts een derde van de kracht van metaalhalogenidelampen en vormen geen risico op UV-straling.
Vis-aantrekkende lichtintensiteit Parameter Referentietabel
| lichtkleur | Toepassingsscenario | Onderwater verlichting dorpel | Technische volwassenheid |
| Blauw licht | Diepzee-inktvisvissen | ≥0.1lx | weloverwogen |
| groenlicht | Offshore uitgebreide visattractie | 0,01lx·85m | weloverwogen |
| Rood licht | herfstmakreel netvissen | — | weloverwogen |
| geel licht | Ondiepe zee <40m | Optimale penetratieafstand | schraal |
Samenvatting: Diepblauw, ondiep geel en rood voor de aantrekkingskracht van vissen, met wit licht als hulp om ultraviolet licht te voorkomen. Op basis van de bovenstaande parameters kan een enkel schip uitgerust met 200 krachtige blauwe LED-lampen een efficiënte operationele zone van 0,5 zeemijl afleggen.
Wil je meer weten over het kiezen van LED-visaantrekkers? Lees de blog Vissersboot vissen Trekken schijnwerpers koopgids 2025.
Prijsklasse van LED-vis die lichten aantrekt
Volgens de laatste marktgegevens is er een aanzienlijk prijsverschil tussen LED-aantrekkende lichten, voornamelijk beïnvloed door factoren zoals stroom, spectraal type, waterdichte classificatie en functioneel ontwerp. De specifieke prijsklassen zijn als volgt:
● Basis mini-vislichten met laag vermogen (≤100W)
Vermogen: 1–10W (bijv. 12V geel/blauw onderwaterlichten); prijs: $0.4–$4.3 per eenheid, bijvoorbeeld zeevissende vislicht ($0.37), waterdicht netto markeringslicht ($1), 12V eenkleurige onderwaterlicht ($3.1–4); kenmerken: IP68 waterdicht, geschikt voor RAFT-visserij, aquariumverlichting, 12V onderwaterlicht ($3.1–4);
Multifunctioneel dimbaar type
Vermogen: 50–100 W (ondersteunt schakelen tussen wit licht/geel licht/groen licht/blauw licht); prijs: $4.3–$12.1 per eenheid, bijv. 12V vierkleuren instelbaar visaantreklicht ($4.3), 120W high-power nachtlicht ($12.1).
● Mid-to-high power professioneel type (300-1200 W), werklampen voor vissersboot (wit licht/blauw licht)
Vermogen: 300–500 W; Prijs: $62–$121 per eenheid, bijvoorbeeld 500 W blauw licht visaantrekkende lamp ($62), vierkante 300W waterdichte maritieme lamp ($121); kenmerken: luchtverlichting, lichtintensiteit ≥5000 lumen, gebruikt voor aantrekkingskracht op het oppervlak.
● Hoogrendementslichten voor diepwater (groen licht/blauw licht)
Vermogen: 600–1200 W; Prijs: $93–$1086 per eenheid, bijvoorbeeld 600 W dimbaar diepwaterlicht ($685), 1200W groen onderwaterlicht ($1086); kenmerken: waterbestendig tot 50 meter (IP68), koperen vinnen + zeewatercirculatie, per jaar licht decay <3%.
Hoogwaardig intelligent spectrum programmeerbaar licht
Vermogen: 500–1000 W; Prijs: $538–$1580 per set, bijvoorbeeld 220V programmeerbare blauwlicht FISH-aantrekkende lamp ($538), RGB combinatie smart lamp ($1,580); Ondersteunt Moonlight Gradient en Pulse Strobe (200 Hz), met een 40%-toename in SquidGregeGregation.
● Aangepaste industriële kwaliteit
Vermogen: meer dan 1000 W; Prijs: $871–$1085 Per eenheid, bijvoorbeeld 1200 W wit licht visaantrekkende lamp voor offshore-schepen ($871), 1000 W diepwatergroen lichtlamp ($1085).
Belangrijke factoren die van invloed zijn op prijsverschillen
| Parameters | Lage prijsklasse | Hoge prijsklasse | Typische voorbeelden |
| Power | 10-100W | 500-1200W | $22 versus $1085 |
| Spectrale technologie | monochroom vast | RGB programmeerbaar | $28 versus $226 |
| Waterdichte beoordeling | IP65 | IP68 (50 meter diep) | $30 versus $1085 |
| Ontwerp van warmteafvoer | Basis aluminium behuizing | Kopervinnen + waterkoeling | $84.55 versus $871 |
Industrietrend: tegen 2025 zal de gemiddelde prijs van LED-vislampen dalen tot $399 per eenheid (een daling van 12,71 TP3T ten opzichte van 2013), maar krachtige intelligente modellen zullen nog steeds premium prijzen hebben.
Wat is de typische levensduur van een LED-aantrekkend licht?

De levensduur van een LED-aantrekkend licht wordt aanzienlijk beïnvloed door technische specificaties, gebruiksomgeving en onderhoudsomstandigheden. De theoretische levensduur van reguliere producten en hun werkelijke prestaties worden als volgt vergeleken: de meeste professionele LED-visaantreklichten van professionele kwaliteit worden beoordeeld voor een levensduur van 50.000 uur (bijvoorbeeld een groen licht onderwaterlicht van 1200 W). De hier genoemde 50.000 uur verwijst naar het punt waarop de lichtopbrengst is afgenomen tot 701 TP3T van zijn initiële waarde (L70-standaard), op welk punt het licht nog steeds kan functioneren, maar de efficiëntie van het aantrekken van vissen afneemt.
Factoren die de levensduur van vis aantrekkende lichten beïnvloeden:
- Onvoldoende ontwerp van warmteafvoer: Slecht ontworpen lichten met onvoldoende warmteafvoer kunnen een verdubbelde lichtvervalsingsgraad ervaren, wat leidt tot sneller LED-verval en een kortere levensduur; diepwaterlichten (IP68) met behulp van koperen vinnen en zeewatercirculatiekoeling zorgen voor voldoende warmteafvoer, waardoor het jaarlijkse lichtverval onder de 31 TP3T blijft, met een levensduur die dichter bij de theoretische 50.000 uur is.
- Slechte spanning/stroomstabiliteit: Overspanningsbedrijf of onstabiele stroom kan de LED-chips ernstig beschadigen, waardoor de levensduur tot 1.000 uur daalt.
- Milieucorrosie: Producten die gedurende langere tijd zijn blootgesteld aan zoutrijke, hoge temperaturen onder water door het 30%-50% in levensduur.
- bestuurdersuitval: Verklaart 80% van storingen in verlichtingsarmaturen, voedingen van lage kwaliteit hebben een levensduur van slechts 20.000 uur;
- Mechanische schade: Golfinslag of installatiebotsingen kunnen de afgedichte structuur beschadigen;
- Spectrale overbelasting: Werken met overmatig vermogen om de aantrekking van de vis te verbeteren, versnelt het verouderen van chips.
Belangrijkste maatregelen om de levensduur te verlengen:
- Geef prioriteit aan diepwatermodellen met IP68-bescherming en ontwerp van koperen substraatwarmteafvoer;
- Vermijd frequente aan/uit cycli (5 keer per dag) om slijtage van het bestuurderscircuit te verminderen;
- Reinig drie keer per kwartaal zoutafzettingen van het lampoppervlak om de efficiëntie van de warmteafvoer te behouden;
- Installeer Waterdichte aansluitdozen in vochtige omgevingen om zoutmistcorrosie te isoleren.
Onder de juiste gebruiksomstandigheden is de werkelijke levensduur van professionele LED-visaantrekkende lichten 4-10 jaar, ver boven de traditionele metalen halogenidelampen (ongeveer 1 jaar). Wees echter op uw hoede voor misleidende specificaties in goedkope producten - sommige handelaren claimen een "levensduur van 100.000 uur", wat verwijst naar de theoretische levensduur van de LED-chip, niet de hele lamp.
Samenvatting
De toepassingsscenario's voor visaggregatielampen zijn voornamelijk geconcentreerd in de visserij-industrie. Ze kunnen worden gebruikt in verschillende soorten visserijapparatuur, zoals visnetten, trawls en hengels. Bovendien kunnen visaggregatielampen ook worden gebruikt in de aquacultuur om de groei van de vis en de efficiëntie van de landbouw te helpen verbeteren.
Signlitetled heeft de normen voor moderne visaantrekkende lichten opnieuw gedefinieerd door continue technologische innovatie, waarbij 450-490 nm zeer nauwkeurige blauwe LED-modules zijn ontwikkeld. Deze modules zijn 651 TP3T energiezuiniger dan traditionele metalen halogenidelampen en verbeteren de efficiëntie van de aantrekkingskracht van de inktvis met 22%. De door SigliteLed ontwikkelde vislampen hebben meerdere patenten gekregen. Als u gerelateerde behoeften heeft, alstublieft contact met ons opnemen.