In today’s world, electrical systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated and sensitive. Even a small power surge can cause serious damage, resulting in costly downtime and equipment failure. That’s why surge protection is essential for any modern installation. However, many engineers and buyers often confuse SPDs (Surge Protective Devices) with surge arresters, leading to incorrect product selection or insufficient protection. Understanding the difference between SPD and surge arrester is crucial to ensure system safety and reliability. In this article, we’ll clearly explain what each device does, their key differences, and how to choose the right surge protection solution for your application.
What is an SPD (Surge Protective Device)?
Definition
A Surge Protective Device (SPD) is an electrical protection component designed to safeguard equipment from transient overvoltages—commonly known as surges. These surges are short, high-energy spikes in voltage that can be caused by lightning strikes, switching operations, or grid disturbances. SPDs are widely used in low- and medium-voltage systems to prevent damage to sensitive electronic components.
Working Principle
The SPD functions by diverting excess surge energy away from the protected circuit. When the voltage exceeds a specific threshold, the SPD instantly activates and channels the surge current to the grounding system. Once the surge passes, it automatically returns to its normal high-impedance state, allowing regular current flow. This fast response minimizes the voltage spike seen by the protected equipment.
Key Features
SPDs are compact, modular, and easy to install. They offer quick response time, high discharge capacity, and replaceable modules in many models. Most modern SPDs are classified into Type 1, Type 2, and Type 3, depending on their installation location and surge exposure level.
Common Applications
SPDs are essential in LED lighting systems, control cabinets, communication devices, power distribution panels, and industrial automation systems. In these applications, they help ensure equipment stability, extend lifespan, and reduce maintenance costs caused by transient voltage damage.
If you want to learn more about SPD, read our article “Surge Protective Devices (SPD) for LED Lighting: Complete Guide for Indoor & Outdoor Applications”
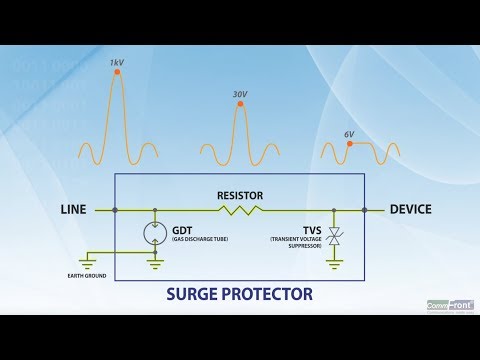
What is a Surge Arrester?
Definition
A Surge Arrester is a protective device primarily used in medium- and high-voltage power systems to protect electrical equipment from lightning strikes or switching surges. Unlike SPDs, which are used in low-voltage installations, surge arresters are installed at key points of power transmission and distribution networks, such as transformers, switchgear, and substations, to prevent insulation breakdown and system failure.
Working Principle
When an overvoltage caused by lightning or switching occurs, the surge arrester provides a low-resistance path for the excessive current to flow safely into the ground. Once the surge has passed, it immediately returns to a high-resistance state, isolating the circuit from the ground again. This action limits the voltage that reaches the protected equipment, ensuring it remains within safe operating levels.
Key Features
Surge arresters are designed to handle extremely high surge currents and are built from metal-oxide varistors (MOVs) or silicon carbide elements enclosed in robust porcelain or polymer housings. They offer long service life, high energy absorption capability, and excellent thermal stability.
Common Applications
Surge arresters are commonly used in power plants, substations, transmission lines, and industrial facilities. They play a crucial role in protecting transformers, circuit breakers, and other high-voltage equipment from direct lightning impacts and high-energy transient surges.
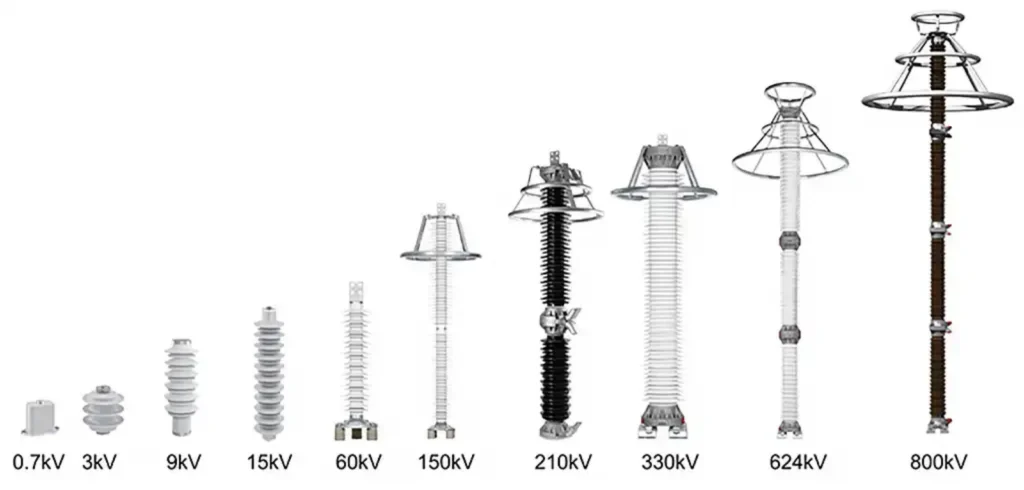
Key Differences Between SPD and Surge Arrester
While both devices are designed to protect electrical systems from overvoltage, their applications, voltage ranges, and protective mechanisms differ significantly. SPDs are mainly used in low-voltage systems to protect electronic devices from internal switching surges or indirect lightning, while Surge Arresters are designed for medium- and high-voltage systems to discharge large lightning currents directly to the ground.
| Aspect | SPD (Surge Protective Device) | Surge Arrester |
| Voltage Range | Low to medium voltage systems (≤1000V) | Medium to high voltage systems (≥1kV) |
| Protection Type | Protects against transient surges and indirect lightning | Protects against direct lightning and high-energy overvoltages |
| Main Function | Limits surge voltage reaching sensitive equipment | Diverts high lightning current safely to the ground |
| Installation Point | Inside distribution panels, control boxes, or near end devices | On transformers, substations, or transmission lines |
| Response Time | Extremely fast (nanoseconds) | Slightly slower (microseconds) |
| Structure | Compact, modular, easy to replace | Large, robust housing, long service life |
| Typical Application | LED lighting, communication, industrial control | Power grid, substations, transmission networks |
| Maintenance | Often includes replaceable modules | Requires periodic inspection but not frequent replacement |

Common Misconceptions and Mistakes
1. Thinking SPD and Surge Arrester Are the Same
One of the most common mistakes is assuming SPDs and Surge Arresters are interchangeable. In reality, they serve different voltage levels and protection purposes. Using an SPD in a high-voltage system may leave equipment unprotected, while installing a Surge Arrester in a low-voltage panel is unnecessary and costly.
2. Ignoring Multi-Level Protection
Some users install only one SPD at the main distribution board, neglecting downstream circuits or signal lines. Effective surge protection requires a coordinated, multi-stage approach—Type 1 at the main panel, Type 2 for sub-panels, and Type 3 for end devices.
3. Overlooking Maintenance and Testing
Another issue is poor maintenance. SPDs, especially modular ones, should be regularly inspected and replaced after severe surges to ensure continued protection performance.
4. SPD and Surge Arrester Should Work Together
Instead of replacing each other, SPDs and Surge Arresters should operate in coordination to form a complete surge protection system. The Surge Arrester handles large lightning currents at the power entry point, while the SPD absorbs residual surges that penetrate into low-voltage networks. When properly combined, they provide layered protection, ensuring both high-voltage and sensitive low-voltage equipment are safeguarded against different surge threats.
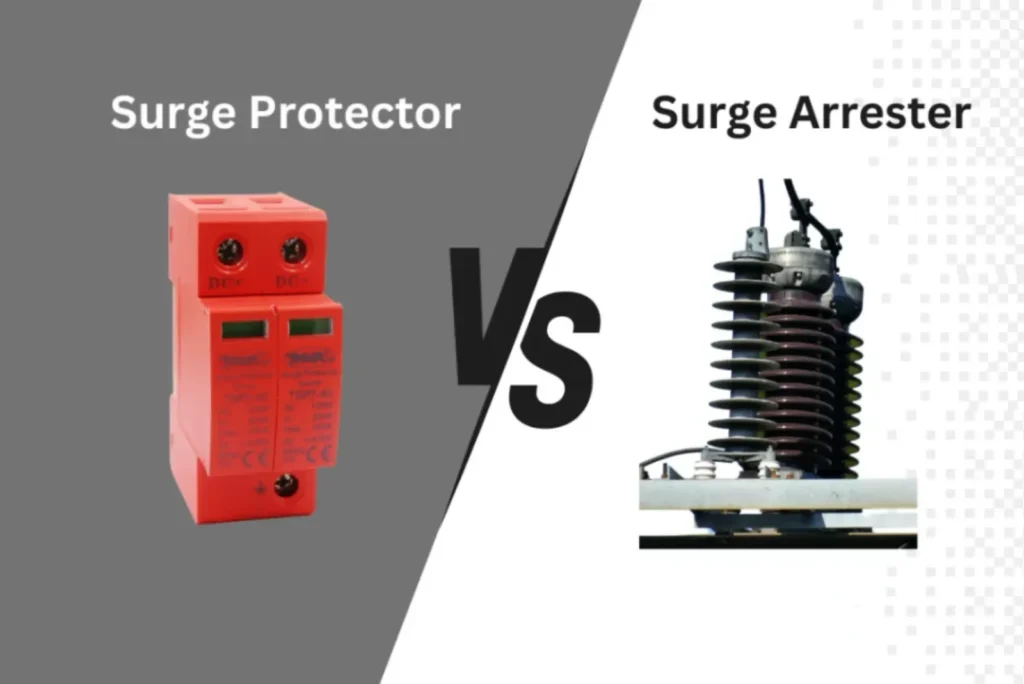
How to Choose the Right Protection for Your Project
1. Identify System Voltage and Application
Start by determining your system’s voltage level and installation type. Low-voltage systems, such as LED lighting, control panels, and communication devices, require SPDs. Medium- or high-voltage systems, like substations or transformers, need Surge Arresters.
2. Evaluate Environmental and Surge Conditions
Consider the installation environment—outdoor systems or lightning-prone areas demand higher protection levels. Choose products that comply with standards such as IEC 61643 or UL 1449 for reliable performance.
3. Design a Multi-Level Protection Scheme
Combine Surge Arresters and SPDs to achieve layered protection. Use a Type 1 SPD at the main panel, Type 2 at sub-distribution, and Type 3 close to sensitive loads for maximum safety.
4. Choose Certified, Quality Products
Always select certified devices from reputable manufacturers to ensure long-term durability and consistent surge suppression.
SPD

Surge Arrester
Conclusion
Proper surge protection is not just about installing a single device—it’s about understanding your system’s needs and applying the right solution in the right place. While Surge Arresters protect high-voltage infrastructure, SPDs are essential for safeguarding low-voltage equipment such as lighting systems, control panels, and electronic devices.
At SignliteLED, we provide high-quality Surge Protective Devices (SPDs) designed for LED lighting and industrial power systems. Our SPDs feature fast response, stable performance, and international certifications to ensure reliable protection in demanding environments.
If you’re looking for a trusted SPD supplier for your commercial or industrial project, contact SignliteLED today. We’ll help you choose the best surge protection solution to keep your system safe and running smoothly.